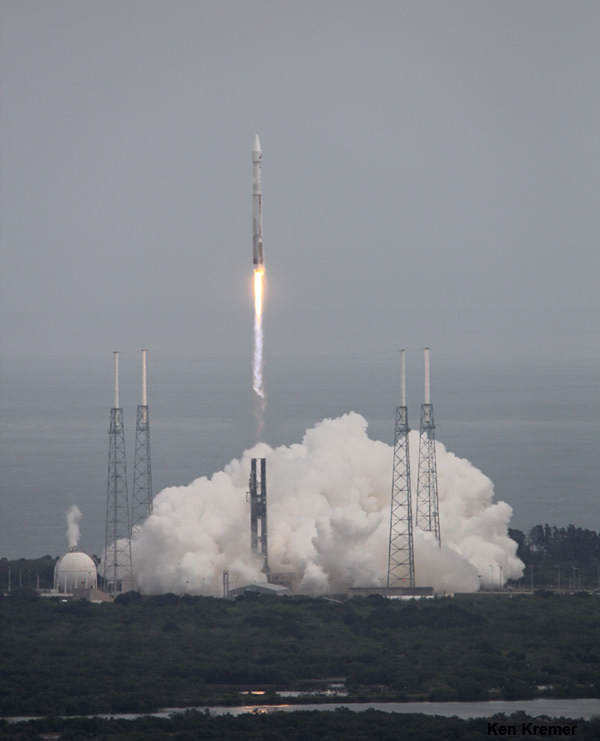
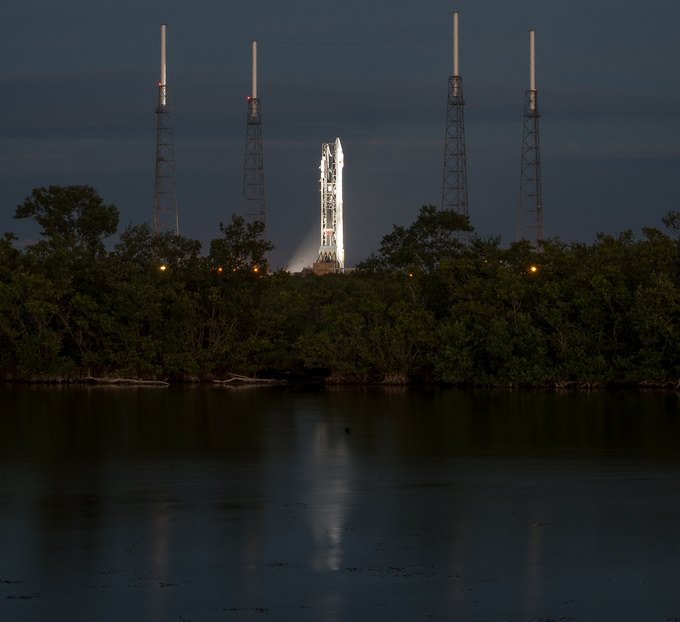
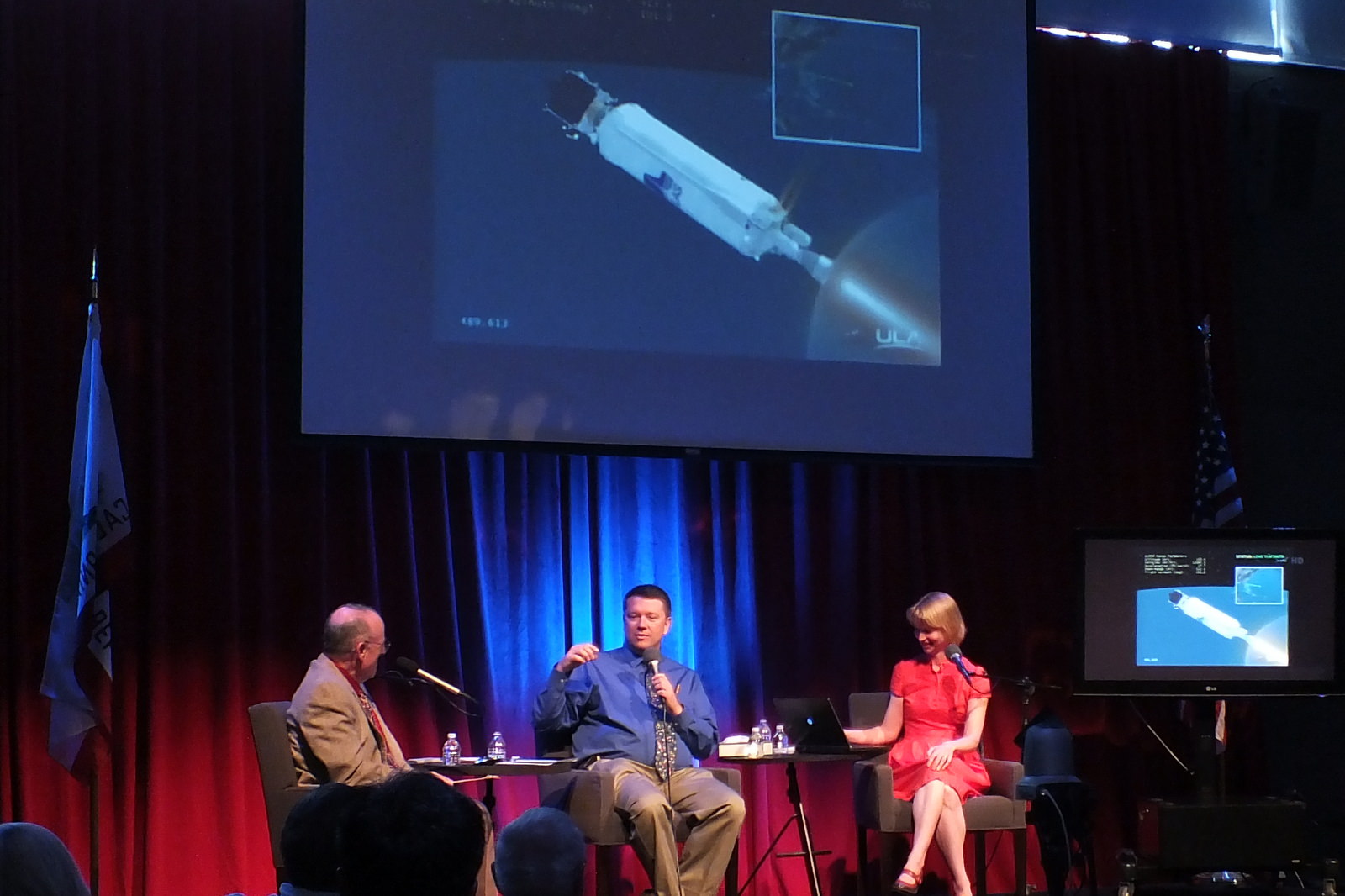
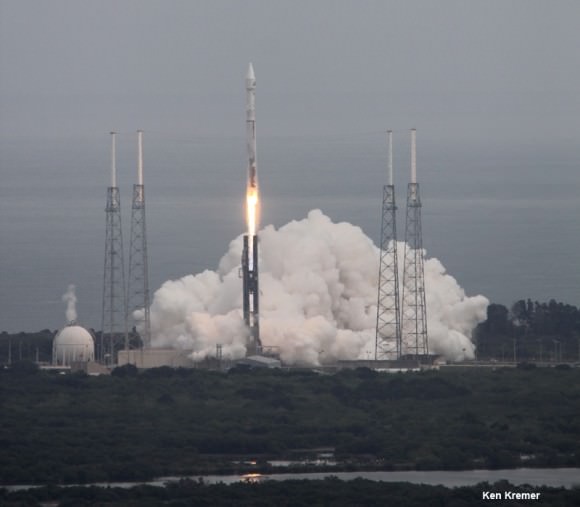
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) space probe thundered to space today (Nov. 18) following a flawless blastoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 at 1:28 p.m. EST atop a powerful Atlas V rocket.
“Hey Guys we’re going to Mars!” gushed Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN’s Principal Investigator at a post launch briefing for reporters.
“Now I am a Martian,” beamed Jakosky gleefully, as well as is everyone else who has worked on MAVEN since the project was conceived some ten years ago, he noted.
Today’s countdown was absolutely perfect culminating in a spectacular and on time lift off that rumbled across the Florida Space Coast to the delight of cheering crowds assembled for the historic launch aimed at discovering the history of water and habitability stretching back over billions of years on Mars.
“I take great pride in the entire team,” said Jakosky.
“Everyone was absolutely committed to making this work.”

The $671 Million MAVEN spacecraft separated from the Atlas Centaur upper stage some 52 minutes after liftoff, unfurled its wing like solar panels to produce life giving power and thus began a 10 month interplanetary voyage to the Red Planet.
“We’re currently about 14,000 miles away from Earth and heading out to the Red Planet right now,” said MAVEN Project Manager David Mitchell of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center at the briefing, after the 5,400-pound spacecraft had been soaring through space for barely two and a half hours.
“The first trajectory correction maneuver (TCM) is set for Dec. 3,” added Mitchell. There are a minimum of four TCM’s to ensure that the majestic probe remains precisely on course for Mars.
“Safe travels MAVEN!” said Mitchell. “We’re with you all the way.”

It will take the spacecraft 10 months to reach the Red Planet, with arrival scheduled for Sept. 22, 2014.
Jakosky noted that while the launch is a big milestone, it’s just the beginning.
MAVEN’s purpose is to accomplish world class science after arriving at Mars and completing a check-out period before it can finally begin collecting science data.
MAVEN will answer key questions about the evolution of Mars, its geology and the potential for the evolution of life.
“MAVEN is an astrobiology mission,” says Jakosky.
Mars was once wet billions of years ago, but no longer. Now it’s a cold arid world, not exactly hospitable to life.
“We want to determine what were the drivers of that change?” said Jakosky. “What is the history of Martian habitability, climate change and the potential for life?”
MAVEN will study Mars upper atmosphere to explore how the Red Planet may have lost its atmosphere over billions of years. It will measure current rates of atmospheric loss to determine how and when Mars lost its atmosphere and water.
The MAVEN probe carries nine sensors in three instrument suites.
The Particles and Fields Package, provided by the University of California at Berkeley with support from CU/LASP and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., contains six instruments to characterize the solar wind and the ionosphere of Mars. The Remote Sensing Package, built by CU/LASP, will determine global characteristics of the upper atmosphere and ionosphere. The Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer, built by Goddard, will measure the composition of Mars’ upper atmosphere.
“We need to know everything we can before we can send people to Mars,” said Dr. Jim Green, NASA’s Director of Planetary Science at NASA HQ in Washington, DC.
“MAVEN is a key step along the way. And the team did it under budget!” Green elaborated. “It is so exciting!”

Over the course of its one-Earth-year primary mission, MAVEN will observe all of Mars’ latitudes at altitudes ranging from 93 miles to more than 3,800 miles.
MAVEN will execute five deep dip maneuvers during the first year, descending to an altitude of 78 miles. This marks the lower boundary of the planet’s upper atmosphere.
Stay tuned here for continuing MAVEN and MOM news and Ken’s MAVEN launch reports from on site at the Kennedy Space Center press site.
…………….
Learn more about MAVEN, MOM, Mars rovers, Orion and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Nov 18-21: “MAVEN Mars Launch and Curiosity Explores Mars, Orion and NASA’s Future”, Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, 8 PM
Dec 11: “Curiosity, MAVEN and the Search for Life on Mars”, “LADEE & Antares ISS Launches from Virginia”, Rittenhouse Astronomical Society, Franklin Institute, Phila, PA, 8 PM