With the Dawn spacecraft now heading towards the dwarf planet/asteroid Ceres, the mission has suddenly gotten even more intriguing. The Herschel space observatory has discovered water vapor around Ceres, and the vapor could be emanating from water plumes — much like those that are on Saturn’s moon Enceladus – or it could be from cryovolcanism from geysers or icy volcano.
“This is the first time water vapor has been unequivocally detected on Ceres or any other object in the asteroid belt and provides proof that Ceres has an icy surface and an atmosphere,” said Michael Küppers of ESA in Spain, lead author of a paper in the journal Nature.
Ceres might be considered to have a bit of an identity crisis, and this new discovery might complicate things even more. When it was discovered in 1801, astronomers thought it was a planet orbiting between Mars and Jupiter. Later, other bodies with similar orbits were found, marking the discovery of our Solar System’s main belt of asteroids.
Ceres laid claim as the largest asteroid in our Solar System, but in 2006, the International Astronomical Union reclassified Ceres as a dwarf planet because of its large size.
But now, could Ceres also have comet-like attributes? Herschel scientists say the most straightforward explanation of the water vapor production is through sublimation, where ice is warmed and transformed directly into gas, dragging the surface dust with it, and exposing fresh ice underneath to sustain the process. This is how comets work.
Ceres is roughly 950 kilometers (590 miles) in diameter. The best guess on Ceres composition is that it is layered, perhaps with a rocky core and an icy outer mantle. Ice had been theorized to exist on Ceres but had not been detected conclusively, until now.
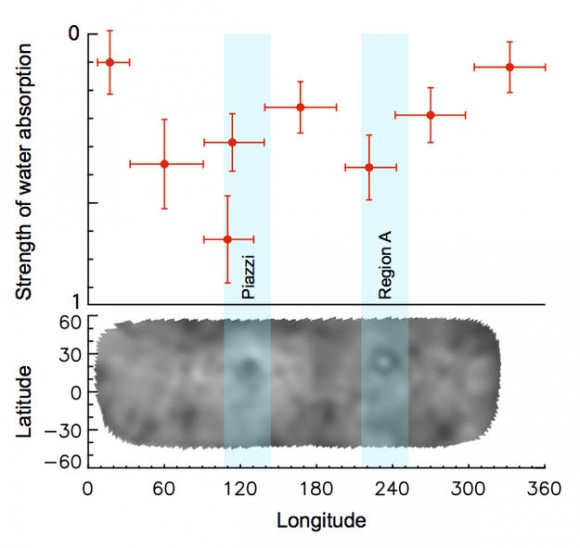
Herschel used its far-infrared vision with the HIFI instrument to see a clear spectral signature of the water vapor. But, interestingly, Herschel did not see water vapor every time it looked. There were variations in the water signal during the dwarf planet’s 9-hour rotation period. The telescope spied water vapor four different times, on one occasion there was no signature. The astronomers deduced that almost all of the water vapor was seen to be coming from just two spots on the surface.
Although Herschel was not able to make a resolved image of Ceres, the team was able to derive the distribution of water sources on the surface.
“We estimate that approximately 6 kg of water vapour is being produced per second, requiring only a tiny fraction of Ceres to be covered by water ice, which links nicely to the two localised surface features we have observed,” says Laurence O’Rourke, Principal Investigator for the Herschel asteroid and comet observation programme called MACH-11, and second author on the paper.
The two emitting regions are about 5% darker than the average on Ceres. Since darker regions are able to absorb more sunlight, they are then likely the warmest regions, resulting in a more efficient sublimation of small reservoirs of water ice, the team said.
They added that this new finding could have significant implications for our understanding of the evolution of the Solar System.
“Herschel’s discovery of water vapour outgassing from Ceres gives us new information on how water is distributed in the Solar System,” said Göran Pilbratt, ESA’s Herschel Project Scientist. “Since Ceres constitutes about one fifth of the total mass of asteroid belt, this finding is important not only for the study of small Solar System bodies in general, but also for learning more about the origin of water on Earth.”
Dawn is scheduled to arrive at Ceres in the spring of 2015 after spending more than a year orbiting the large asteroid Vesta. Dawn will give us the closest look ever at Ceres surface and provide more insight into this latest finding.
“We’ve got a spacecraft on the way to Ceres, so we don’t have to wait long before getting more context on this intriguing result, right from the source itself,” said Carol Raymond, the deputy principal investigator for Dawn. “Dawn will map the geology and chemistry of the surface in high resolution, revealing the processes that drive the outgassing activity.”