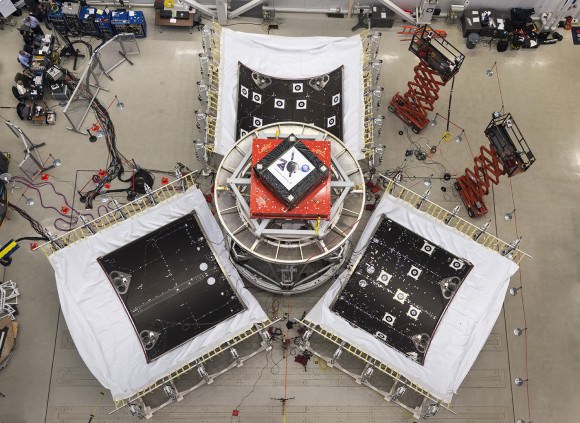
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – All of the key hardware elements being assembled for NASA’s new Orion spacecraft launching just under one year from now are nearing completion at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) – at the same time as a crucial and successful hardware test in California this week helps ensure that the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) vehicle will be ready for an on-time liftoff.
Orion is NASA’s first spaceship designed to carry human crews on long duration flights to deep space destinations beyond low Earth orbit, such as asteroids, the moon, Mars and beyond.
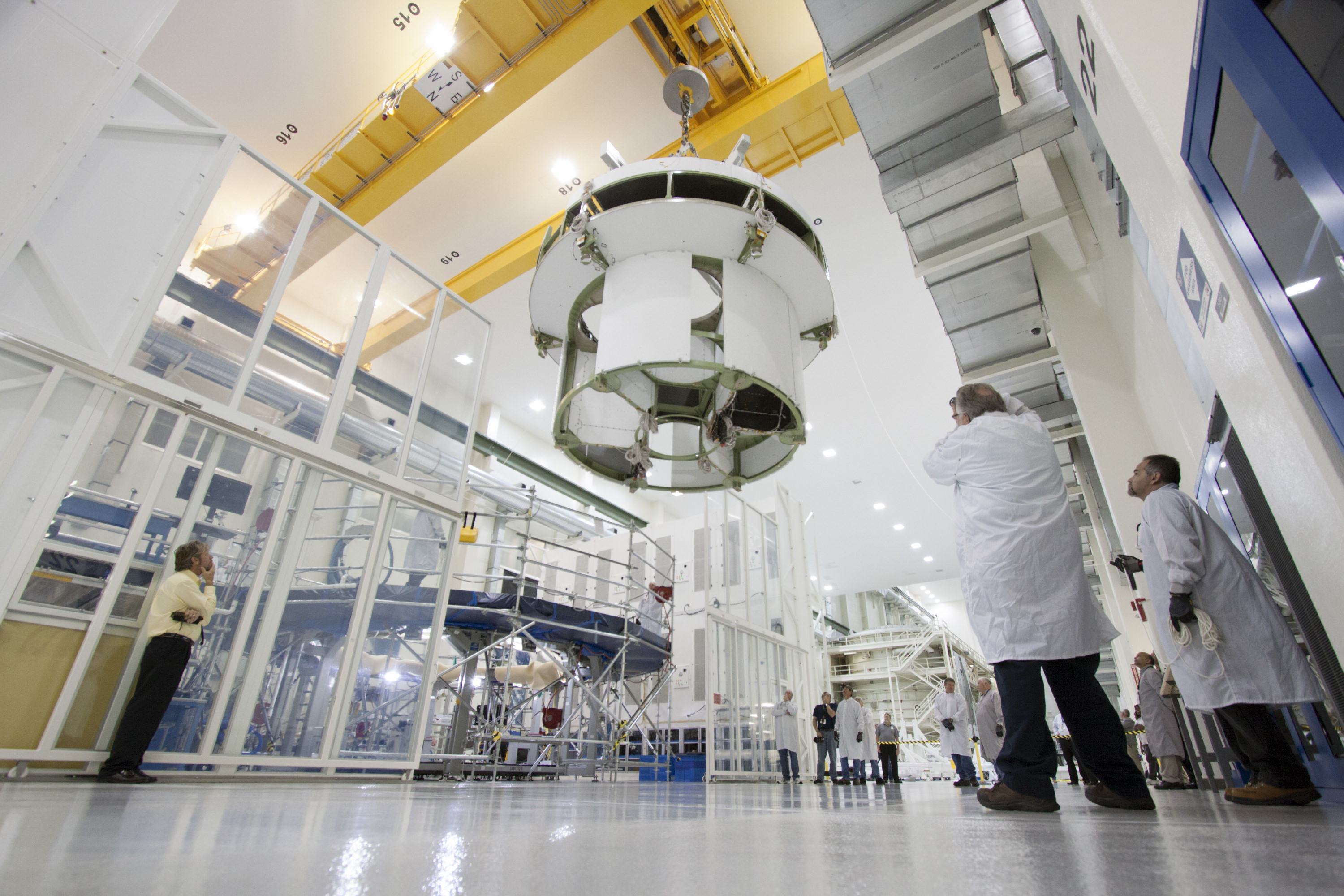
In a major construction milestone, Orion’s massive Service Module (SM) was hoisted out from the tooling stand where it was manufactured at the Operations and Checkout Building (O & C) at KSC and moved to the next assembly station where it will soon be mated to the spacecraft adapter cone.
The SM should be mated to the crew module (CM) by year’s end, Orion managers told Universe Today during my recent inspection tour of significant Orion hardware at KSC.
“We are working 24 hours a day, 7 days a week,” said Jules Schneider, Orion Project manager for Lockheed Martin at KSC, during an exclusive interview with Universe Today inside the Orion clean room at KSC. “We are moving fast!”

The Orion CM recently passed a significant milestone when it was “powered on” for the first time at KSC.
“We are bringing Orion to life. Lots of flight hardware has now been installed.”
And on the other side of the country, the Service Module design passed a key hurdle on Wednesday (Nov. 6) when the trio of large spacecraft panels that surround the SM were successfully jettisoned from the spacecraft during a systems test by Lockheed Martin that simulates what would happen during an actual flight several minutes after liftoff.
“Hardware separation events like this are absolutely critical to the mission and some of the more complicated things we do,” said Mark Geyer, Orion program manager at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. “We want to know we’ve got the design exactly right and that it can be counted on in space before we ever launch.”

Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor for Orion and responsible for assembly, testing and delivery of the Orion EFT-1 spacecraft to NASA that’s slated for an unmanned test flight targeted to lift off from Cape Canaveral, Florida in September 2014.
The CM rests atop the SM similar to the Apollo Moon landing program architecture.
However in a significant difference from Apollo, the Orion fairings support half the weight of the crew module and the launch abort system during launch and ascent. The purpose is to improve performance by saving weight thus maximizing the vehicles size and capability.
The SM also provides in-space power, propulsion capability, attitude control, thermal control, water and air for the astronauts.
At Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, California facility a team of engineers used a series of precisely-timed, explosive charges and mechanisms attached to the Orion’s protective fairing panels in a flight-like test to verify that the spacecraft can successfully and confidently jettison them as required during the ascent to orbit.
The trio of fairing panels protect the SM radiators and solar arrays from heat, wind and acoustics during ascent.

“This successful test provides the Orion team with the needed data to certify this new fairing design for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) next year. The test also provides significant risk reduction for the fairing separation on future Orion manned missions,” said Lance Lininger, engineering lead for Lockheed Martin’s Orion mechanism systems in a statement.
This was the 2nd test of the fairing jettison system. During the first test in June, one of the three fairing panels did not completely detach due to an interference “when the top edge of the fairing came into contact with the adapter ring and kept it from rotating away and releasing from the spacecraft,” said NASA.

2013 has been an extremely busy and productive year for the Orion EFT-1 team.
“There are many significant Orion assembly events ongoing this year,” said Larry Price, Orion deputy program manager at Lockheed Martin, in an interview with Universe Today at Lockheed Space Systems in Denver.
“This includes the heat shield construction and attachment, power on, installing the plumbing for the environmental and reaction control system, completely outfitting the crew module, attached the tiles, building the service module and finally mating the crew and service modules (CM & SM),” Price told me.

Credit: Lockheed Martin
The two-orbit, four- hour flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.