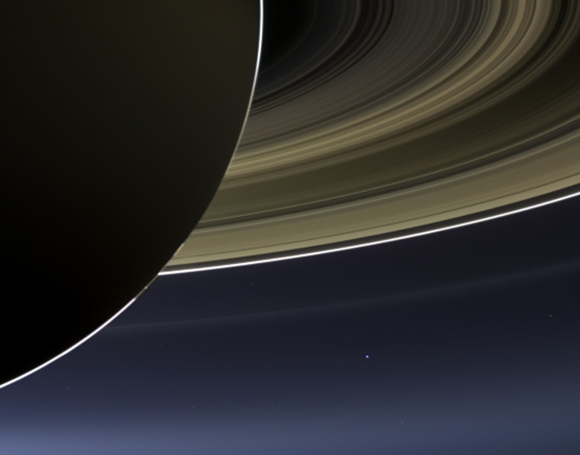
This summer, for the first time ever, the world was informed that its picture was going to be taken from nearly a billion miles away as the Cassini spacecraft captured images of Saturn in eclipse on July 19. On that day we were asked to take a moment and smile and wave at Saturn, from wherever we were, because the faint light from our planet would be captured by Cassini’s camera, shielded by Saturn from the harsh glare of the Sun.
A few preliminary images were released just a few days later showing the “pale blue dot” of Earth nestled within the glowing bands of Saturn’s rings. It was an amazing perspective of our planet, and we were promised that the full mosaic of Cassini images was being worked on and would be revealed in the fall.
Well, it’s fall, and here it is:

Simply beautiful!
Cassini Imaging Team leader Carolyn Porco wrote on her Facebook page:
“After much work, the mosaic that marks that moment the inhabitants of Earth looked up and smiled at the sheer joy of being alive is finally here. In its combination of beauty and meaning, it is perhaps the most unusual image ever taken in the history of the space program.”
Download a full-size version here.

In this panorama of the Saturnian system, a view spanning 404,880 miles (651,591 km), we see the planet silhouetted against the light from the Sun. It’s a unique perspective that highlights the icy, reflective particles that make up its majestic rings and also allows our own planet to be seen, over 900 million miles distant. And it’s not just Earth that was captured, but the Moon, Venus, and Mars were caught in the shot too.
Read more: Could Cassini See You on the Day the Earth Smiled?
According to the description on the CICLOPS page, “Earth’s twin, Venus, appears as a bright white dot in the upper left quadrant of the mosaic… between the G and E rings. Mars also appears as a faint red dot embedded in the outer edge of the E ring, above and to the left of Venus.”
This was no simple point-and-click. Over 320 images were captured by Cassini on July 19 over a period of four hours, and this mosaic was assembled from 141 of those images. Because the spacecraft, Saturn, and its moons were all in constant motion during that time, affecting not only positions but also levels of illumination, imaging specialists had to adjust for that to create the single image you see above. So while all elements may not be precisely where they were at the same moment in time, the final result is no less stunning.
“This version was processed for balance and beauty,” it says in the description. (And I’ve no argument with that.)
See below for an annotated version showing the position of all visible objects, and read the full article on the CICLOPS page for an in-depth description of this gorgeous and historic image.

“I hope long into the future, when people look again at this image, they will recall the moment when, as crazy as it might have seemed, they were there, they were aware, and they smiled.”
–Carolyn Porco, Cassini Imaging Team Leader
Also, check out another version of this image from NASA made up of submitted photos from people waving at Saturn from all over the world. (Full NASA press release here.)
All images credit NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute
UPDATE 11/13: CICLOPS Director Carolyn Porco describes how this image was acquired and assembled in this interview video from the World Science Festival: