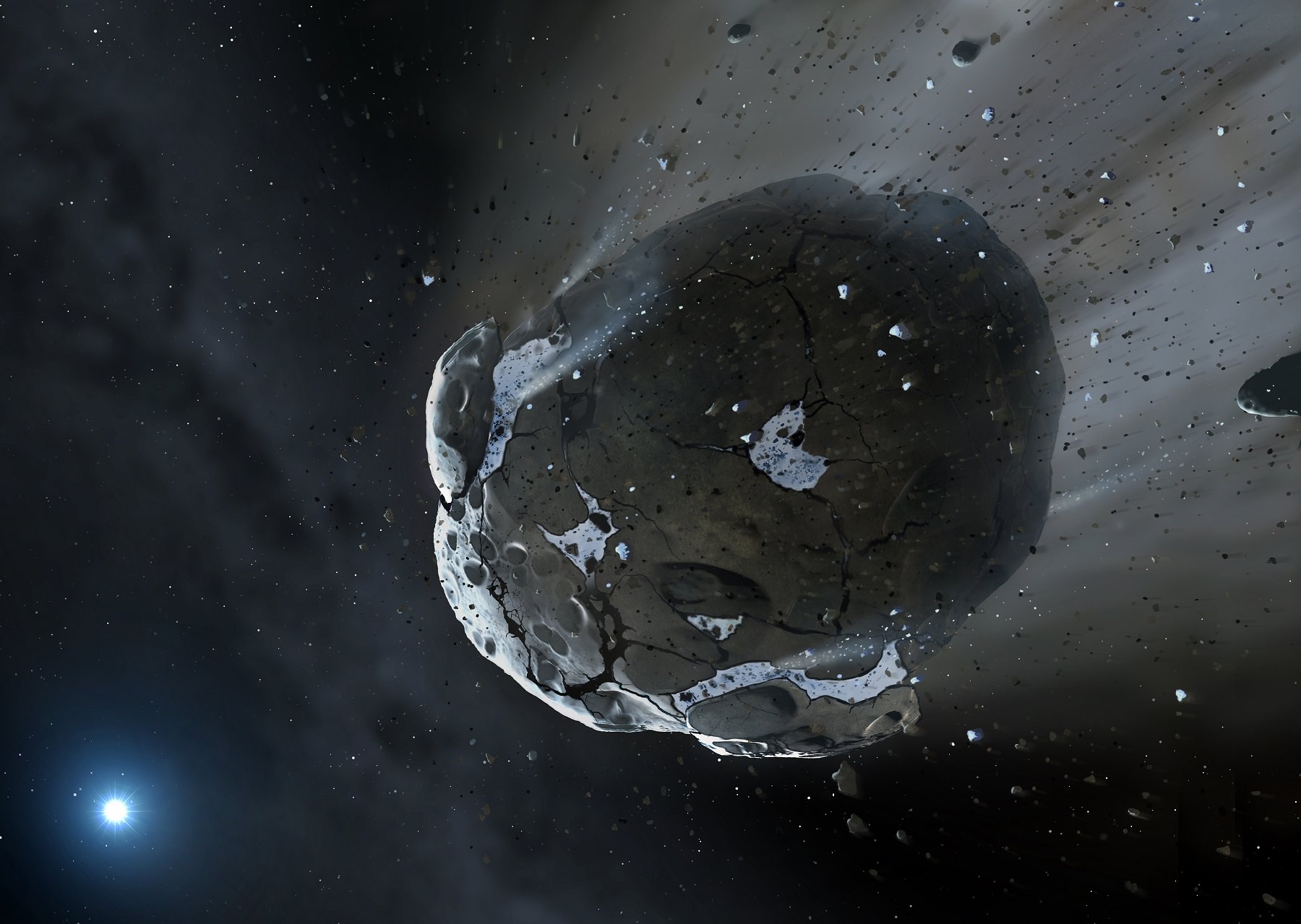
Remains of a water-filled asteroid are circling a dying white dwarf star, right now, about 150 light-years from us. The new find is the first demonstration of water and a rocky surface in a spot beyond the solar system, researchers say.
The discovery is exciting to the astronomical team because, according to them, it’s likely that water on Earth came from asteroids, comets and other small bodies in the solar system. Finding a watery rocky body demonstrates that this theory has legs, they said. (There are, however, multiple explanations for water on Earth.)
“The finding of water in a large asteroid means the building blocks of habitable planets existed – and maybe still exist – in the GD 61 system, and likely also around substantial number of similar parent stars,” stated lead author Jay Farihi, from Cambridge’s Institute of Astronomy.
“These water-rich building blocks, and the terrestrial planets they build, may in fact be common – a system cannot create things as big as asteroids and avoid building planets, and GD 61 had the ingredients to deliver lots of water to their surfaces. Our results demonstrate that there was definitely potential for habitable planets in this exoplanetary system.”
More intriguing, however, is researchers found this evidence in a star system that is near the end of its life. So the team is framing this as a “look into our future”, when the Sun evolves into a white dwarf .
The water likely came from a “minor planet” that was at least 56 miles (90 kilometers) in diameter. Its debris was pulled into the atmosphere of the star, which was then examined by spectroscopy. This study revealed the ingredients of rocks inside the star, including magnesium, silicon and iron. Researchers then compared these elements to how abundant oxygen was, and found that there was in fact more oxygen than expected.

“This oxygen excess can be carried by either water or carbon, and in this star there is virtually no carbon – indicating there must have been substantial water,” stated co-author Boris Gänsicke, from the University of Warwick.
“This also rules out comets, which are rich in both water and carbon compounds, so we knew we were looking at a rocky asteroid with substantial water content – perhaps in the form of subsurface ice – like the asteroids we know in our solar system such as Ceres.”
The measurements were obtained in ultraviolet with the Hubble Space Telescope’s cosmic origins spectrograph. What’s more, the researchers suspect there are giant exoplanets in the area because it would take a huge push to move this object from the asteroid belt — a push that most likely came from big planet.
“This supports the idea that the star originally had a full complement of terrestrial planets, and probably gas giant planets, orbiting it – a complex system similar to our own,” Farihi added.
The discovery was recently published in Science.
Source: University of Cambridge