As Day 2 of the United States government shutdown continues, some short-term effects are already in evidence when it comes to Earth and space.
Most of the NASA and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) websites are offline. Social media updates are silent. At NASA, 97% of agency employees are off work and media reports indicate that 55% of NOAA’s employees are furloughed.
If the shutdown lasts for very long, however, long-term programs could feel the pain. This includes a couple of Mars missions NASA is developing, as well as Earth-based climate research and satellite observation from NOAA.
Mars 2020
A twin rover to Mars Curiosity, called Mars 2020 for now, is expected to leave for the Red Planet in 2020 and do investigations into past life and habitability. Planning is still in the early stages, but an announcement of opportunity for science investigators was supposed to happen on Oct. 8. Notices of intent were due Oct. 15.
“The preproposal conference, scheduled for 10/8, may be rescheduled and the due date for NOIs (currently 10/15) could be delayed, if the government is still shut down closer to those dates,” NASA officials wrote in an update before the shutdown on Monday.

MAVEN
As widely reported yesterday, the next Mars orbiter from NASA is expected to lift off from Earth on Nov. 18. Now, however, preparatory work has ceased and there is some concern from team members that it will miss the launch window, which extends into December. At worst, this means MAVEN’s launch could be delayed until 2016, when the next opportunity opens.
“The hardware is being safed, meaning that it will be put into a known, stable, and safe state,” Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN’s principal investigator, told Universe Today‘s Ken Kremer yesterday. “We’ll turn back on when told that we can. We have some margin days built into our schedule.”
NOAA
As with NASA, NOAA is keeping up with mission-critical activities — which in their case, includes weather forecasting. Long-term climate research, however, is reportedly being shelved.
“For example, Harold Brooks, a top tornado researcher who works at the National Severe Storms Laboratory in Norman, Okla., reported his furlough notice on Facebook on Tuesday,” Climate Central wrote on Oct. 1. “Much of the staff at NOAA’s Earth Systems Research Lab and the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, except for positions related to maintaining computing resources, have also been furloughed. Those two labs are heavily involved in NOAA’s climate research programs.”

Observers are also worried that a lengthy shutdown could push back the time when new weather satellites become available. There have been multiple reports about a “weather satellite gap” coming in the United States as many of NOAA’s geostationary and polar-orbiting satellites are nearing the end of their expected lives. The Subcommittees on Oversight and Environment held hearings into this issue in September.
What’s still online?
These are some of the programs that are still happening at NASA and NOAA:

NASA:
- Bare-bones management on programs such as the International Space Station and several robotic missions that are already in operation (such as the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE).
- Certain missions are in critical phases that could be hurt if work stops, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, which is undergoing cryogenic testing on some of its instruments.
- Several missions run out of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Applied Physics Laboratory are still running as usual, according to the Planetary Society, as these receive contract money from NASA; this means Mars Curiosity is still working, for example.
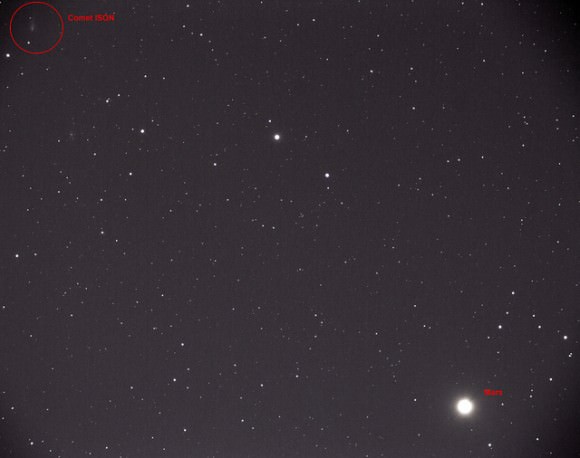
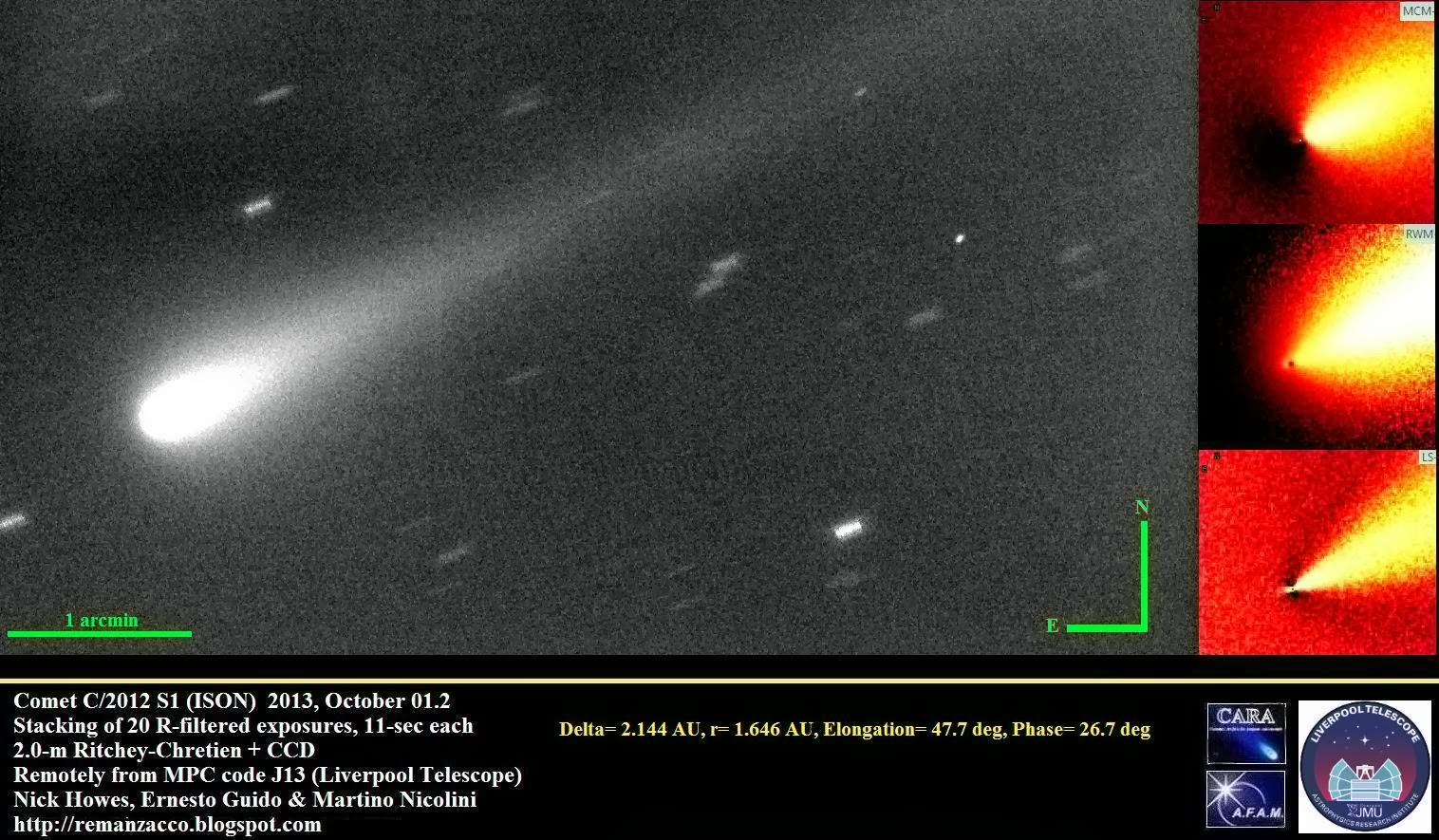
- The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s HiRISE camera is still snapping pictures, its Twitter account reported, which is positive given that it was intended to snap shots of Comet ISON during its closest approach to Mars yesterday.
- The decades-long Landsat Earth observation program is still operating, according to The Atlantic, with data being sent back to Earth as usual. The difference is this information won’t be packaged as usual until government operations restart.
NOAA (all information according to this Department of Commerce document):
- The Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research will keep 73 employees on board “to ensure continuity of crucial long-term historical climate records, and real-time regular research to support ongoing weather and air quality prediction services,” NOAA said.
- 184 employees will stay with the Environmental Satellite and Data Information Service for command and control of several satellites for NOAA and the Department of Defense.
- 474 employees will remain with the National Marine Fisheries Service. 174 are funded in another form besides appropriations. The others are a mix of law enforcement, fisheries management and property protection officials.
- 490 employees are with the Office of Marine and Aviation Operations for observational data collection related to weather forecasting.
- 173 employees are with the National Ocean Service. 17 are funded outside of appropriations, while the 156 remaining “are required to protect against imminent and significant threats to life and property by supporting safe maritime commerce in U.S. waters, including real-time water level data for ships entering U.S. ports, critical nautical chart updates, and accurate position information,” NOAA stated. Some are also monitoring marine health aspects such as algal blooms.
- There are 19 IT-related employees and 20 employees providing support services.
- The large bulk of employees still at work, 3,935 people, are with the National Weather Service to keep up weather forecasting.
There’s no word yet on when government employees could go back to work. Congress representatives are jousting over the implementation of a spending bill to keep the money flowing to government departments. One big issue: whether to include the Affordable Care Act, sometimes dubbed Obamacare, in the bill.
Another deadline is looming, too. Treasury Secretary Jack Lew has warned repeatedly that on Oct. 17, if the debt ceiling is not raised, the United States government may default on some financial obligations.