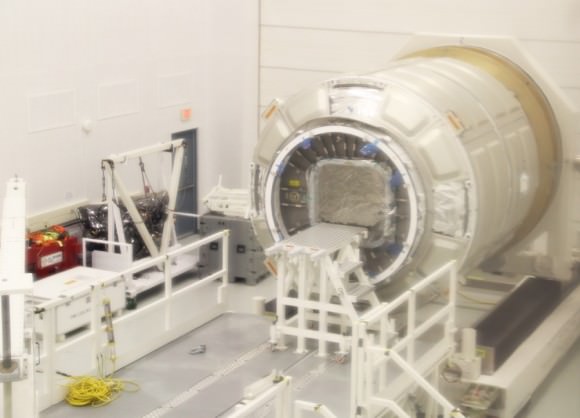
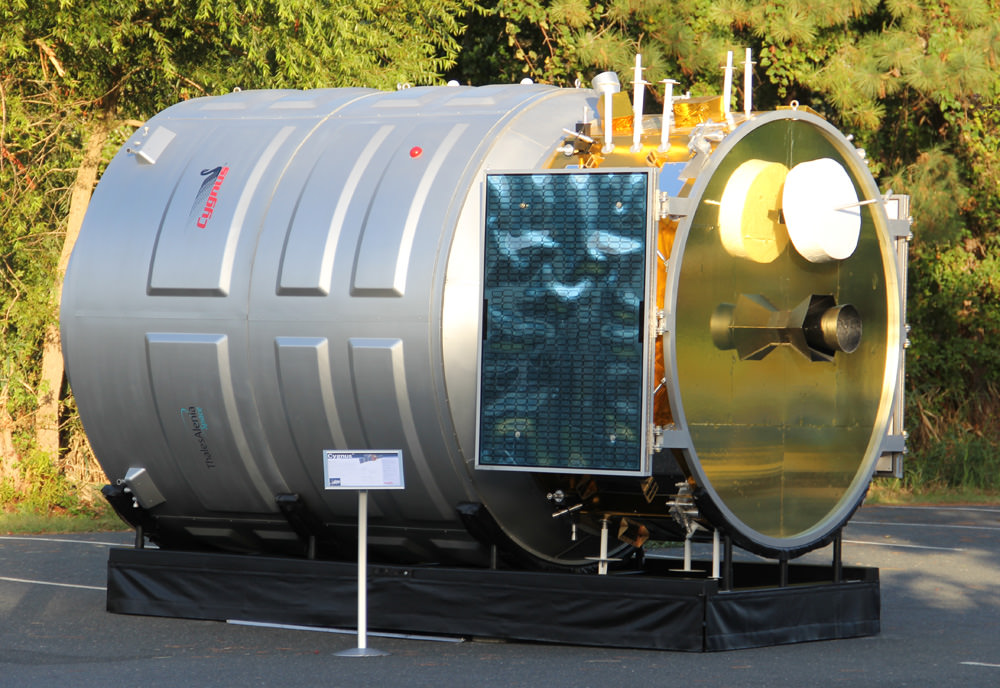
After launching to orbit atop the Antares rocket on Sept. 18, the first ever Cygnus cargo spacecraft is chasing the ISS and set to dock on Sept 22. Until then you have the opportunity to track it in the night skies. This full scale, high fidelity mockup of the Orbital Sciences/Thales Alenia Cygnus gives a feel for it being similar in size to a small room. Credit: Ken Kremer (kenkremer.com)
Story Updated: Further details and photos – and NASA TV link to Live Docking Coverage [/caption]
WALLOPS ISLAND, VA – Following Wednesday morning’s (Sept. 18) spectacular blastoff of the Antares rocket with the commercial Cygnus resupply spacecraft, sky watchers now have a very limited window of opportunity to spot the maiden Cygnus chasing down the International Space Station (ISS) in the early morning skies before it arrives for the historic 1st rendezvous and docking on Sunday morning, Sept 22.
So between now and early Sunday you have the chance to gaze skywards and see and photograph history’s first Earth orbiting Cygnus hunting the ISS and gradually close in for the delicate coupling maneuver.
Here’s our guide on ‘How to Spot Cygnus’.
Sighting opportunities are available worldwide from at least North and South America, Europe, Asia and Africa according to NASA’s ‘Spot the Station’ website – here. See more websites listed below.
Update 4 a.m. Sunday Sept 22– Cygnus Rendezvous Delayed 48 Hours due to communications glitch
Update Sept 23: delayed to no earlier than Saturday due to Soyuz launch on Wednesday. Thus more chances to view!
Time is of the essence! So don’t delay to check this out!
Since the successful separation of the first Cygnus – built by Orbital Sciences and Thales Alenia – from Antares, the Earth orbiting vehicle has been successfully firing its hydrazine fueled thrusters to move ever closer to the massive orbiting lab complex – at a rate of 82 statute miles per orbit..

If all of the ten on orbit maneuvering tests proceed satisfactorily, Cygnus will reach the vicinity of the station on Sunday early morning (US East Coast time).
“There are some ‘goodies’ stowed on board for the crew’s enjoyment,” Alan Lindenmoyer, NASA’s program manager for commercial crew and cargo, told Universe Today at NASA Wallops.
ISS astronauts Karen Nyberg (NASA) and Luca Parmitano (ESA) are scheduled to grapple Cygnus with the station’s Canadian built robotic arm between 7:15 and 7:30 a.m. EDT, if all goes well.
Nyberg and Parmitano, working at a robotic work station in the Cupola module, are due to install the cargo carrier at an earth facing docking port on the Harmony pressurized module as early as 9 a.m. EDT, Sept 22.

It’s the same docking port already used by the SpaceX Dragon cargo vessel on three successful missions to date since 2012.

At 17 feet (5 meters) long and 10 feet (3 meters) wide, Cygnus is the size of a small room.
In fact, while I was at NASA Wallops this week reporting on the Antares launch for Universe Today, I had a chance to visit a full scale, high fidelity mockup of Cygnus built for Orbital Sciences and on display at the local community center in Chincoteague, VA.
The Cygnus display model gives one a great feel for just how big Cygnus really is- see my photos herein.
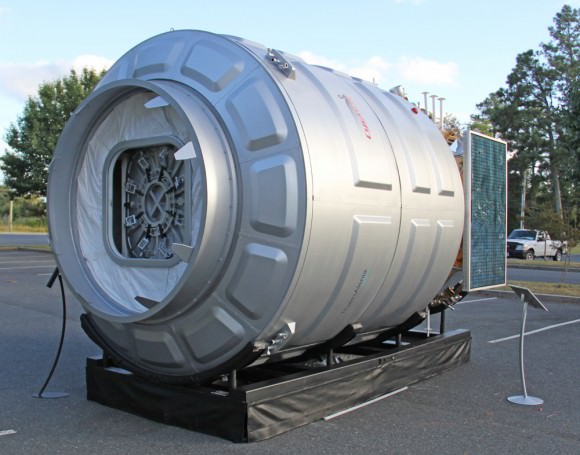

A full size human mannequin standing inside showed that a human can fit comfortably inside.
Thales Alenia Space in Italy designed and constructed the 17 foot ( 5 meter) long Cygnus pressurized module under contract with Orbital.
“Thales Alenia has actually built 50% of the pressurized modules currently comprising the ISS,” said Luigi Quaglino, Thales Alenia Senior Vice President.
“We have built 25 pressurized space modules and learned a lot along the way,” Quaglino told Universe Today at NASA Wallops.
The ISS is the largest manmade object in orbit. It’s the size of a football field and the brightest object in the night sky after the Moon thanks also to the huge, reflecting solar arrays.
Cygnus will be significantly dimmer, but nevertheless should be readily visible.
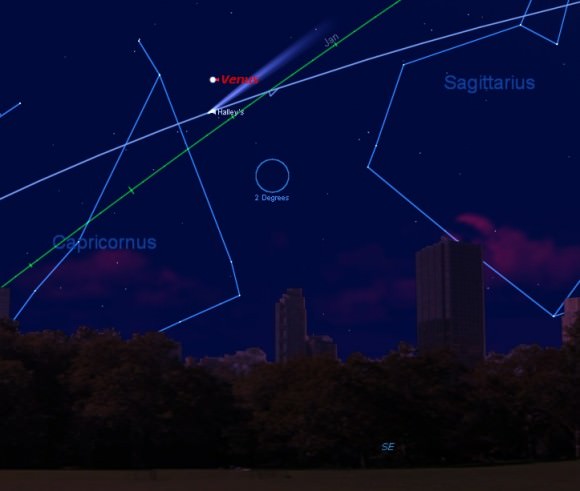
Look for a ‘star’ moving gradually against the backdrop of stars trailing behind the ISS that likewise appears as a bright moving ‘star’.

As Sunday approaches, the gap between the ISS and Cygnus narrows.
On Thursday Cygnus was trailing about 10 minutes behind the ISS. Whereas on Friday and Saturday, the gap narrows down to roughly 4 minutes and then just 1 minute.
You can also try and photograph the ISS and Cygnus trails by mounting your camera on a tripod and leaving the shutter open at least several seconds and longer. Send me any cool time lapse photos to post here at Universe Today.
Many folks have never seen an ISS flyover and this is a fantastic time to start as the dynamic duo speed merrily across the nighttime sky.
To determine if there are any favorable sighting opportunities in your area, check out NASA’s Spot the Station website – here.
Check the NASA website for a detailed listing of the precise times, elevations, direction and durations. It’s an easy to use viewing guide. Just plug in the particulars of the country in which you live.
Another great source is Heaven’s Above – here
Also check Spaceweather.com – here
And Orbital Sciences reports that “AGI has developed a slick interactive 2D/3D simulation that allows you to track the location of Cygnus in real-time.”
I have personally watched the SpaceX Dragon, European ATV and Japanese HTV cargo carriers streaking through the night sky, trailing a few minutes behind the ISS. And it’s always a thrill.
The cargo vessel will deliver about 1,300 pounds (589 kilograms) of cargo, including food, clothing, water, science experiments, spare parts and gear to the Expedition 37 crew.
Cygnus will remain attached to the ISS for about a month. The astronauts will unload the supplies including few goodies starting on Monday. They they’ll pack it with trash. After undocking Cygnus will come to a flaming finale by burning up upon reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere.
So there should be a final opportunity to view it circling Earth.
NASA Television coverage of the arrival and capture of Cygnus will begin at 4:30 a.m. EDT
Streaming video will be available on NASA’s website at http://www.nasa.gov/ntv
Saturday evening Update:
NASA has given the GO for Sunday morning Docking !
Happy Viewing and Clear Skies
…………….
Learn more about Cygnus, Antares, LADEE, Curiosity, Mars rovers, MAVEN, Orion and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Oct 3: “Curiosity, MAVEN and the Search for Life on Mars – (3-D)”, STAR Astronomy Club, Brookdale Community College & Monmouth Museum, Lincroft, NJ, 8 PM
Oct 8: NASA’s Historic LADEE Lunar & Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Princeton University, Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton (AAAP), Princeton, NJ, 8 PM