Sometimes, putting things into categories difficult. Witness how many members of the general public are still unhappy that Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet, a decision made by the International Astronomical Union more than seven years ago.
And now we have 3200 Phaethon, an asteroid that is actually behaving like a comet. Scientists found dust that is streaming from this space rock as it gets close to the sun — similarly to how ices melt and form a tail as comets zoom by our closest stellar neighbor.
Phaethon’s orbit puts it in the same originating region as other asteroids (between Mars and Jupiter), but its dust stream is much closer to actions performed by a comet — an object that typically comes from an icy region way beyond Neptune. So far, therefore, the research team is calling Phaethon a “rock comet.” And after first proposing a theory a few years ago, they now have observations as to what may be going on.
Phaethon is not only an asteroid, but also a source of a prominent meteor shower called the Geminids. This shower happens every year around December when the Earth plows into the cloud of debris that Phaethon leaves in its wake. Astronomers have known about the Geminids’ source for a generation, but for decades could not catch the asteroid in the act of shedding its stuff.
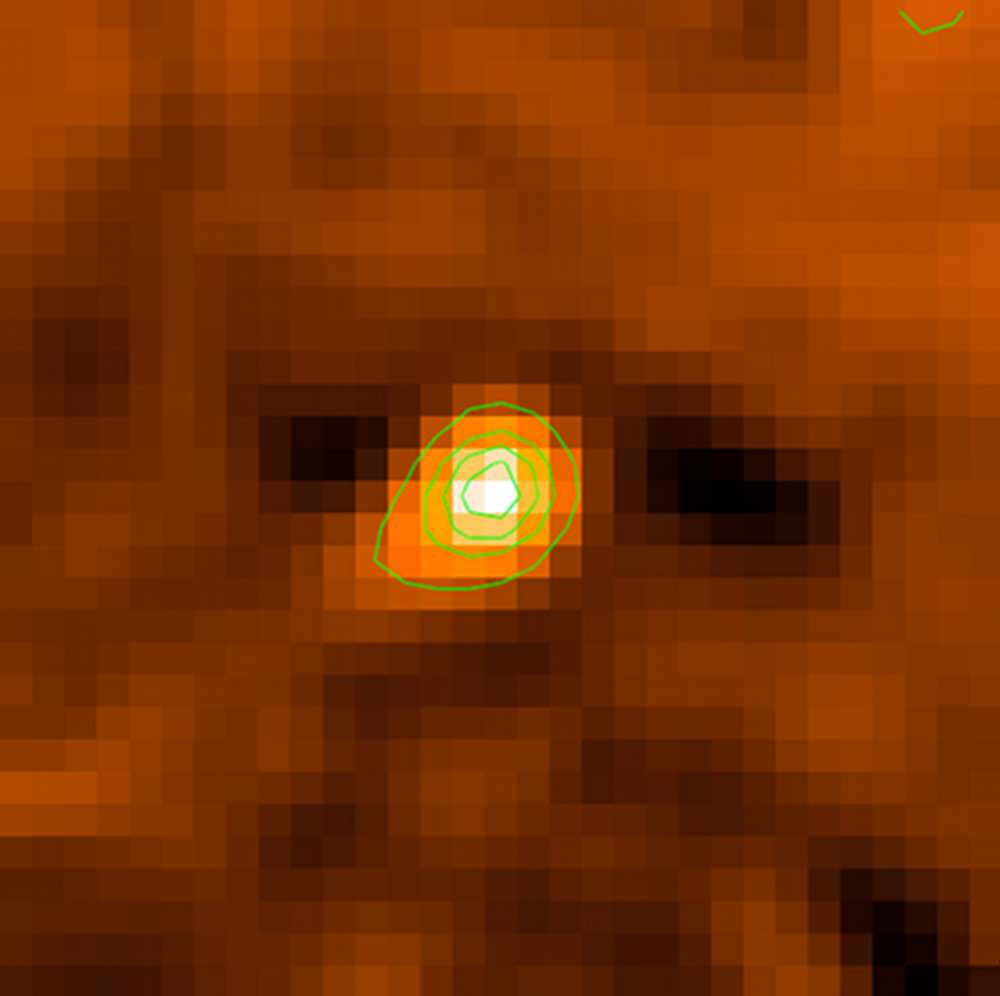
That finally came with images of NASA’s twin sun-gazing Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory (STEREO) spacecraft that were taken between 2009 and 2012. The researchers saw a “comet-like tail” extending from the 3.1-mile (five kilometer) asteroid. “The tail gives incontrovertible evidence that Phaethon ejects dust,” stated David Jewitt, an astronomer at the University of California, Los Angeles who led the research. “That still leaves the question: why?”

The answer lies in just how close Phaethon whizzes past the sun. At perihelion, its closest approach to the sun, it only appears eight degrees (16 solar diameters) away from the sun in Earth’s sky. This close distance makes it all but impossible to study the asteroid without special equipment, which is why STEREO came in so handy.
When Phaethon reaches its closest approach of 0.14 Earth-sun distances, surface temperatures rise above an estimated 1,300 degrees Fahrenheit (700 degrees Celsius). It’ s way too hot for ice, as what happens with a comet. In fact, it’s probably hot enough to make the rocks crack and break apart. The researchers publicly hypothesized this was happening at least as far back as 2010, but this finding provided more evidence to support that theory.
“The team believes that thermal fracture and desiccation fracture (formed like mud cracks in a dry lake bed) may be launching small dust particles that are then picked up by sunlight and pushed into the tail,” a statement from the research team read.
“While this is the first time that thermal disintegration has been found to play an important role in the solar system,” they added, “astronomers have already detected unexpected amounts of hot dust around some nearby stars that might have been similarly produced.”
The results were presented at the European Planetary Science Congress on Tuesday. By the way, STEREO also caught Mercury behaving somewhat like a comet in results released in 2010, although that find was related to the planet’s escaping sodium atmosphere.
Read more about the research in the June 26 issue of Astrophysical Letters. A preprint version is also available on Arxiv.
Source: European Planetary Science Congress