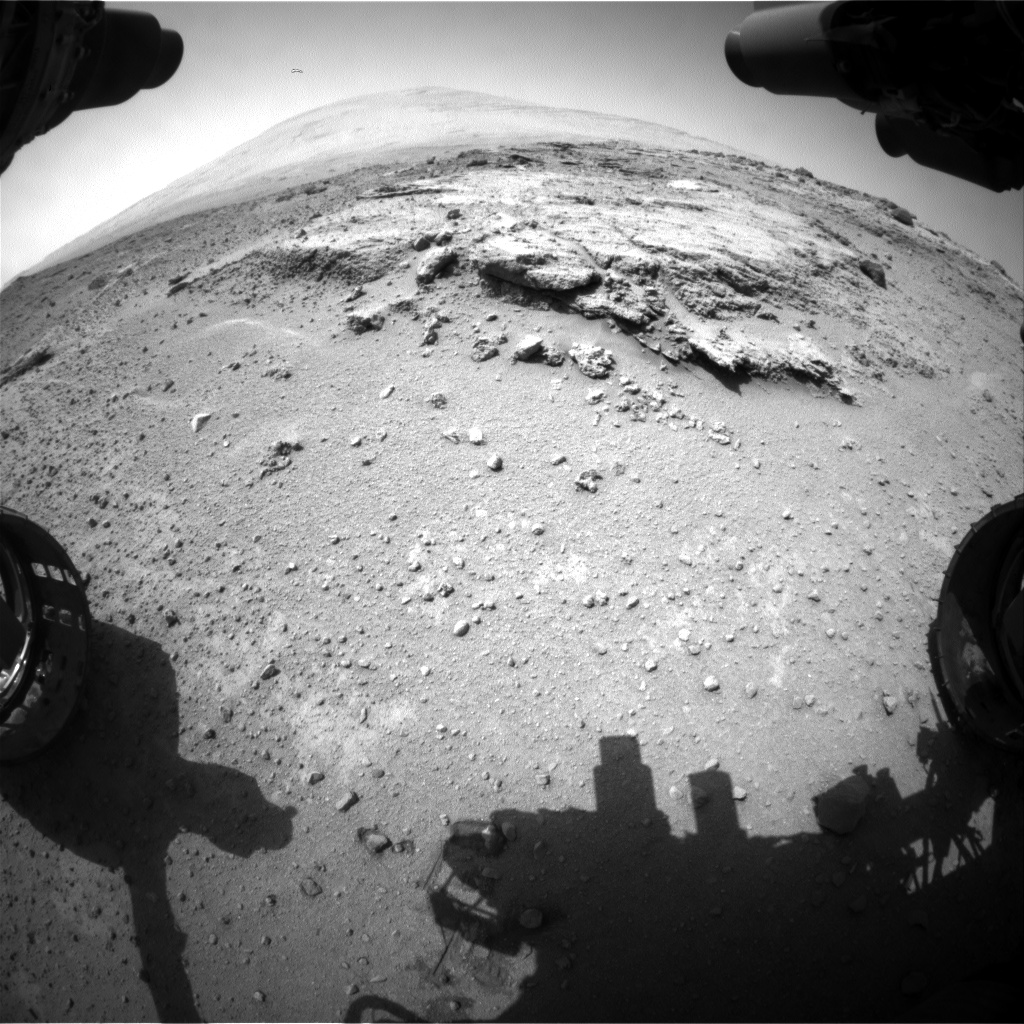
Curiosity’s views a rock outcrop at ‘Darwin’ after arriving for a short stay at ‘Waypoint 1’ on Sept 12 (Sol 392) – dramatically back dropped by her primary destination, Mount Sharp. Front hazcam camera image from Sol 393 (Sept 13, 2013). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Story updated – see close up mosaic views of Darwin outcrop below[/caption]
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover has just rolled into an intriguing site called ‘Darwin’ at ‘Waypoint 1’- having quickly picked up the driving pace since embarking at last on her epic trek to mysterious Mount Sharp more than two months ago. Did life giving water once flow here on the Red Planet?
Because the long journey to Mount Sharp – the robots primary destination – was certain to last nearly a year, the science team carefully choose a few stopping points for study along the way to help characterize the local terrain. And Curiosity has just pulled into the first of these so called ‘Waypoints’ on Sept 12 (Sol 392), the lead scientist confirmed to Universe Today.
“Curiosity has arrived at Waypoint 1,” project scientist John Grotzinger, of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, told Universe Today.
“Darwin is named after a geologic formation of rocks from Antarctica.”
She has now driven nearly 20% of the way towards the base of the giant layered Martian mountain she will eventually scale in search of life’s ingredients.
Altogether, the team selected five ‘Waypoints’ to investigate for a few days each as Curiosity travels in a southwestward direction on the road from the first major science destination in the ‘Glenelg’ area to the foothills of Mount Sharp, says Grotzinger.
“We’ll stay just a couple of sols at Waypoint 1 and then we hit the road again,” Grotzinger told me.

‘Waypoint 1’ is an area of intriguing outcrops that was chosen based on high resolution orbital imagery taken by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) circling some 200 miles overhead. See route map herein.
In fact the team is rather excited about ‘Waypoint 1’ that’s dominated by the tantalizing rocky outcrop discovered there nicknamed ‘Darwin’.
Although Curiosity will only stay a short time at each of the stops, the measurements collected at each ‘Waypoint’ will provide essential clues to the overall geologic and environmental history of the six wheeled rover’s touchdown zone.
“Waypoint 1 was chosen to help break up the drive,” Grotzinger explained to Universe Today.
“It’s a chance to study outcrops along the way.”
The images from MRO are invaluable in aiding the rover handlers planning activities, selecting Curiosity’s driving route and targeting of the most fruitful science forays during the long trek to Mount Sharp – besides being absolutely crucial for the selection of Gale Crater as the robots landing site in August 2012.
The ‘Darwin’ outcrop may provide more data on the flow of liquid water across the crater floor.
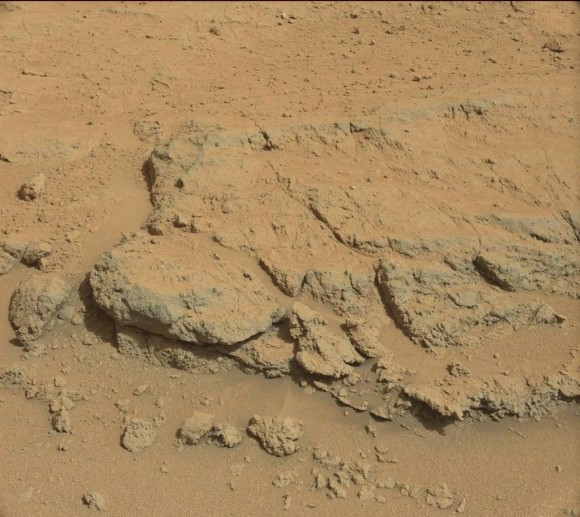

The scientists goal is to compare the floor of Gale Crater to the sedimentary layers of 3 mile high (5 kilometer high) Mount Sharp.
Waypoint 1 is just over 1 mile along the approximately 5.3-mile (8.6-kilometer) route from ‘Glenelg’ to the entry point at the base of Mount Sharp.
Curiosity spent over six months investigating the ‘Yellowknife Bay’ area inside Glenelg before departing on July 4, 2013.
What’s the origin of Darwin’s name?
“Darwin comes from a list of 100 names the team put together to designate rocks in the Mawson Quadrangle – Mawson is the name of a geologist who studied Antarctic geology,” Grotzinger told me.
“Recently we left the Yellowknife Quadrangle, so instead of naming rocks after geological formations in Canada’s north, we now turn to formation names of rocks from Antarctica, and Darwin is one of them.
“That will be the theme until we cross into the next quad,” Grotzinger explained.
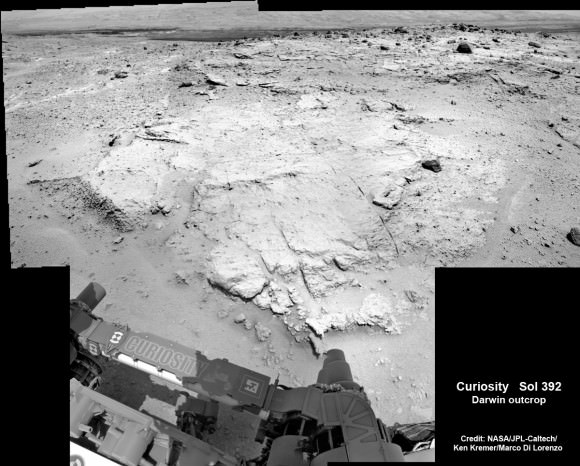

Inside Yellowknife Bay, Curiosity conducted the historic first interplanetary drilling into Red Planet rocks and subsequent sample analysis with her duo of state of the art chemistry labs – SAM and CheMin.
At Yellowknife Bay, the 1 ton robot discovered a habitable environment containing the chemical ingredients that could sustain Martian microbes- thereby already accomplishing the primary goal of NASA’s flagship mission to Mars.
“We want to know how the rocks at Yellowknife Bay are related to what we’ll see at Mount Sharp,” Grotzinger elaborated in a NASA statement. “That’s what we intend to get from the waypoints between them. We’ll use them to stitch together a timeline — which layers are older, which are younger.”
On Sept. 5, Curiosity set a new one-day distance driving record for the longest drive yet by advancing 464 feet (141.5 meters) on her 13th month on the Red Planet.
As Curiosity neared Waypoint 1 she stopped at a rise called ‘Panorama Point’ on Sept. 7, spotted an outcrop of light toned streaks informally dubbed ‘Darwin and used her MastCam telephoto camera to collect high resolution imagery.
Curiosity will use her cameras, spectrometers and robotic arm for contact science and a “full bore science campaign” involving in-depth mineral and chemical composition analysis of Darwin and Waypoint 1 for the next few Sols, or Martian days, before resuming the trek to Mount Sharp that dominates the center of Gale Crater.

She will not conduct any drilling here or at the other waypoints, several team members have told me, unless there is some truly remarkable ‘Mars-shattering’ discovery.
Why is Curiosity now able to drive longer than ever before?
“We have put some new software – called autonav, or autonomous navigation – on the vehicle right after the conjunction period back in March 2013,” Jim Erickson, Curiosity Project Manager of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), told Universe Today.
“This will increase our ability to drive. But how much it helps really depends on the terrain.”
And so far the terrain has cooperated.
“We are on a general heading of southwest to Mount Sharp,” said Erickson. See the NASA JPL route map.
“We have been going through various options of different planned routes.”
As of today (Sol 394), Curiosity remains healthy, has traveled 2.9 kilometers and snapped over 82,000 images.
If all goes well Curiosity could reach the entry point to Mount Sharp sometime during Spring 2014, at her current driving pace.
…………….
Learn more about Curiosity, Mars rovers,LADEE, Cygnus, Antares, MAVEN, Orion and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Sep 17/18: LADEE Lunar & Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA
Oct 3: “Curiosity, MAVEN and the Search for Life on Mars – (3-D)”, STAR Astronomy Club, Brookdale Community College & Monmouth Museum, Lincroft, NJ, 8 PM
Oct 8: LADEE Lunar & Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Princeton University, Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton (AAAP), Princeton, NJ, 8 PM