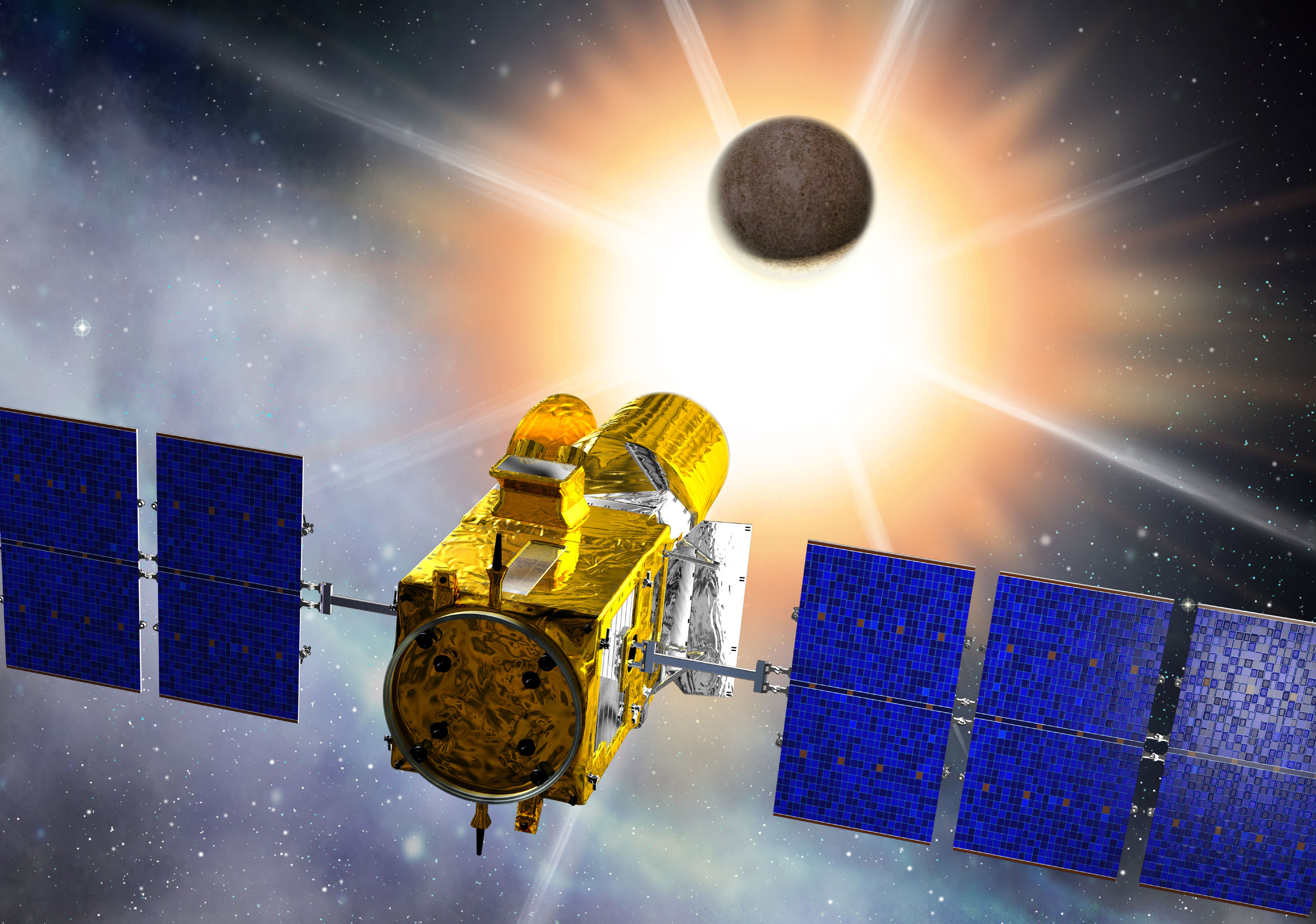
More bad news on the exoplanet-hunting front: While the final fate of the Kepler spacecraft remains unknown, the CoRoT (Convection, Rotation and Planetary Transits) satellite has now been officially shut down. CoRoT suffered a computer failure on November, 2, 2012 and although the spacecraft is capable of receiving navigational commands, the French Space Agency CNES reports it can no longer retrieve data from its 30-centimeter telescope. After a valiant effort to try and restore the computer, CNES announced this week that the spacecraft has been retired. CoRoT’s journey will come to a fiery end as it will be deorbited and it will burn up on re-entry in Earth’s atmosphere.
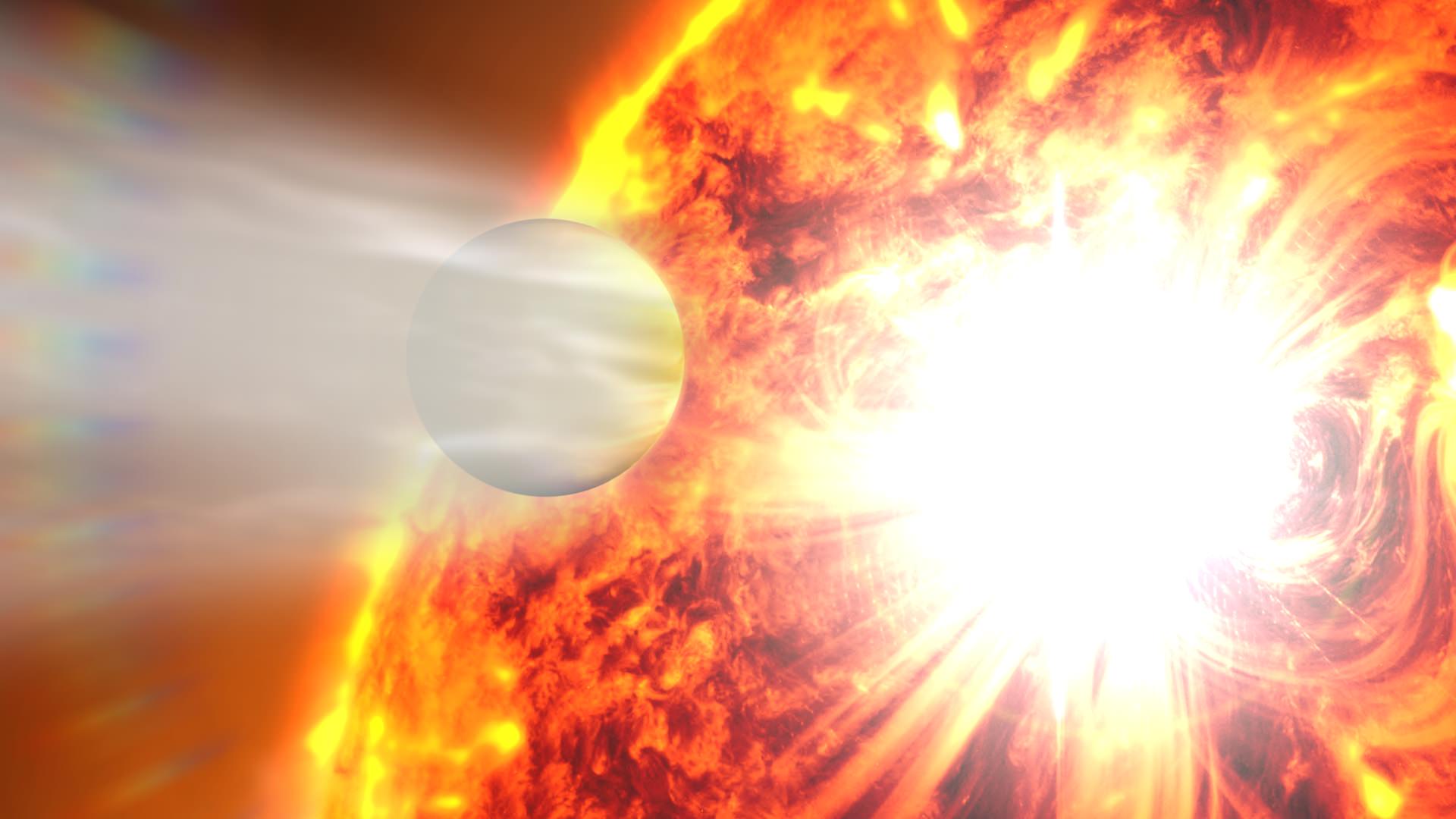
While it’s always hard to see the end of successful mission, we can’t be too sad about CoRoT, however. The mission lasted twice as long as expected and it gathered a remarkable haul of exoplanets. CoRoT looked for planetary transits — a dimming in brightness of the host star as a planet crossed in front. CoRoT was the first mission to find a planet using the transit method.
In all, CoRoT has spotted 32 confirmed planets and at least 100 more are awaiting confirmation. The mission also allowed astronomers to study the stellar physics and the interior of stars.
This is not the first computer failure for the mission. CoRoT launched in December of 2006, and in 2009 the main computer failed and has since been running on the backup computer. When the second computer failed in November, engineering teams have tried to reboot both computers, with no success.
But space radiation is tough on spacecraft, and after enduring 6 years of intense bombardment by high-energy particles in space, both computers have been deemed unrecoverable.
CNES said a series of operations will be performed to lower CoRoT’s orbit and conduct some technology experiments before passivating and deorbiting the satellite. Its journey will end as it burns up on re-entry in Earth’s atmosphere.

CoRoT discovered a diverse array of planets, mostly gas giants. Some of the planets discovered, like CoRoT-7b, orbit their star in less than 24 hours and have a blistering hot surface, while others like CoRoT-9b have an orbital period of 95 days and is one of very few known “warm” transiting exoplanets.
CoRoT was also the first to obtain measurements of the radius of brown dwarves, intermediate objects between a planet and a star, and literally opened up a whole new field of study of temporal analysis of the micro-variability of stars by measuring the frequencies and amplitudes of stellar vibrations with unprecedented precision.
CNES did not provide a timetable for CoRoT’s demise, but we’ll keep you posted.
Source: CNES