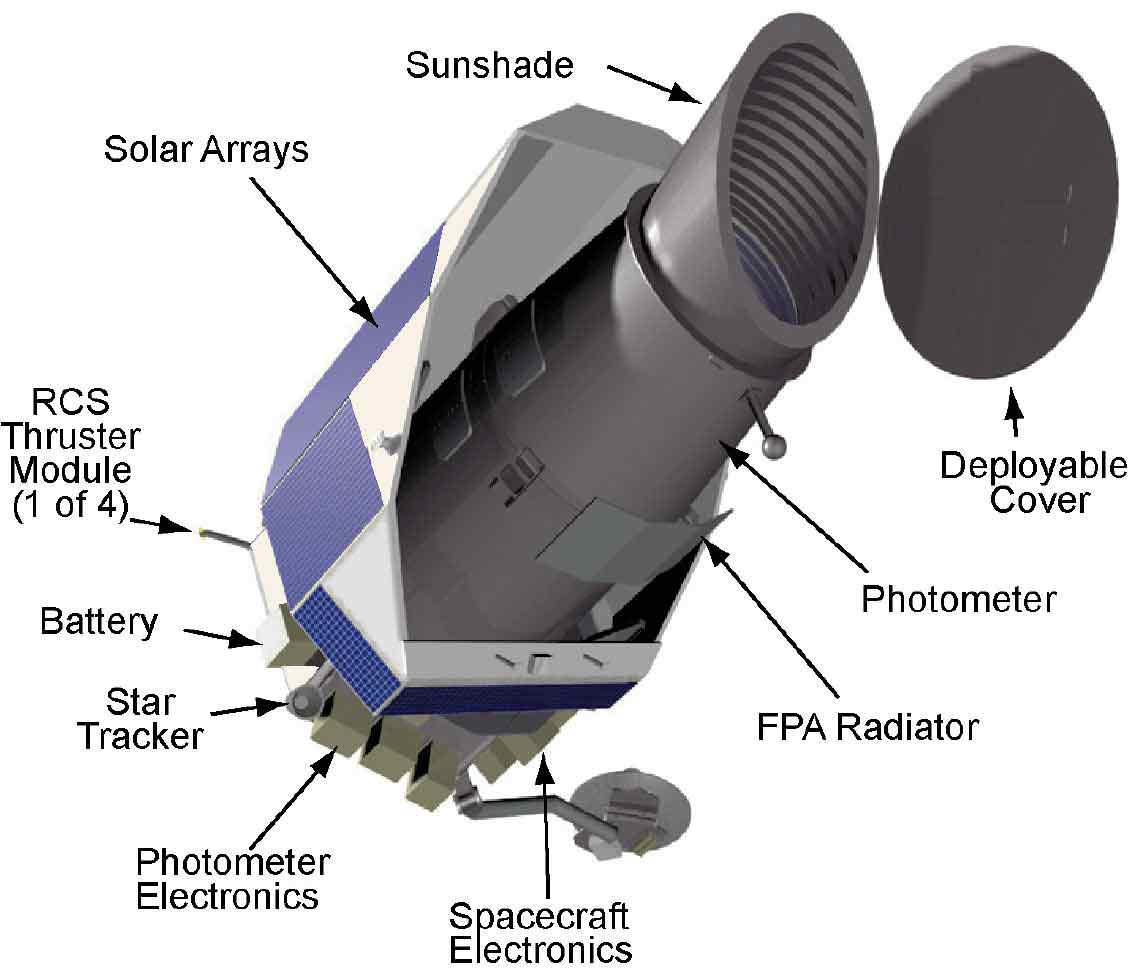
NASA’s Kepler telescope has lost its ability to precisely point toward stars, putting its exoplanet search in jeopardy. One of the reaction wheels –devices which enable the spacecraft to aim in different directions without firing thrusters – has failed. This is of grave concern because last year reaction wheel #2 failed, and now #4 has failed. Kepler scientists say the spacecraft needs at least three reaction wheels to be able to point precisely enough to hunt for planets orbiting distant stars.
“We need three wheels in service to give us the pointing precision to enable us to find planets,” said Bill Borucki, Kepler principal investigator, during a press briefing today. “Without three wheels it is unclear whether we could continue to do anything on that order.”
But the Kepler team said there are still possibilities of keeping the spacecraft in working order, or perhaps even finding other opportunities for different science for Kepler, something that doesn’t require such precise pointing abilities.
“We’re not ready to call the mission down and out just yet,” said John Grunsfeld, NASA’s associate administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, “but by any measure it’s been a spectacular mission.”
Last year, NASA had approved an extended mission for Kepler through 2016, and so a lot is riding on the health of the spacecraft’s reaction wheels.
Yesterday, (May 14, 2013) Kepler went into safe mode, a pre-programmed software mode that if the observatory has trouble with pointing, it puts the spacecraft in a state where the solar panels turn towards the Sun to maintain power to its systems, as well as sending an alert to ground controllers. When engineers looked at telemetry, they saw indication that reaction wheel #4 was not moving, even after they commanded it to speed up.
“Initially, they did see some movement on the wheel,”said Charles Sobeck, Kepler deputy project manager during today’s briefing, “but it quickly went back to zero speed, indicative of internal failure on the wheel. Our next step is to see what we can do to reduce the fuel consumption, as we would like to extend the fuel reserve as long as we can.”
Sobeck said they have a few things to try yet to perhaps get wheel #4 working again, such as “jiggling” it or trying the wheel in reverse.
“We can try jiggling it, like you’d do with any wheel here on Earth, commanding it to move back and forth,” said Sobeck, “so we can try to bring the wheel back in service. Or perhaps since wheel #2 hasn’t been turned on for eight months, it may come back if we turn it on. It will take us awhile to come up with a plan.”
Sobeck explained they are currently using thrusters to stabilize the spacecraft, and in its current mode, the onboard fuel will last for several months. But they hope to soon put the spacecraft into what is called a “Point Rest State,” which would extend the fuel to last a period of several years.
“The Point Rest State is a sort of oasis where we can park the vehicle while we decide what we can do next, or see if there’s another mode we can operate the spacecraft in,” Sobeck said “Once we know how we can operate, we can know what the spacecraft can do in the future.”
The Point Rest State is a loosely-pointed, thruster-controlled state that minimizes fuels usage while providing a continuous X-band communication downlink. Sobeck described it as using the solar pressure from the Sun in conjunction with minimum thruster use to allow for a periodic slow back and forth rocking motion of the vehicle which is very fuel efficient but still keeps the solar arrays pointing towards the Sun and communications antennas pointed towards Earth.
The software to execute that state was loaded to the spacecraft last week, and last night the team completed the upload of the parameters the software will use.
Sobeck also said there is the possibility of the wheel running in the opposite direction, but running the wheel backward would mean they would need to use more thruster fuel. “The reaction wheels try to balance the forces from the solar pressure, that’s what forces a wheel to run,” he told Universe Today. “If you’re running the wheel backward, you don’t balance the forces, but add to it, and spacecraft will start to tip, so you will have to offset that with additional thruster firings.”
Reaction wheels have been a problem with several different missions, and Sobeck said NASA does have a team looking at problems of reaction wheels and trying to find ways to maximize their longevity.
Earlier this year, elevated friction was detected in reaction wheel #4, and so as a precaution for wheel safety, and as a measure to mitigate the friction, the reaction wheels were spun down to zero-speed and the spacecraft was placed in a thruster-controlled safe mode for several days. After that, the wheel was able to be used again and it operated until this week.
But the team stressed that even if the Kepler spacecraft is unable to make more observations, there are still terabytes of data to pore over yet from the mission.
“We have two years of data that has yet to be searched through,” said Borucki, “I’m optimistic that the data we have we’ll be able to accomplish Kepler’s mission of finding another Earth. We believe that in the next couple of years we will have many more exciting discoveries with respect to finding planets.”
Boricki added that while he’s delighted that they have found so many planetary candidates, on the other hand “I would have been even happier if it had continued another four years. That would have been frosting on the cake,” he said, “but we have an excellent cake right now.”
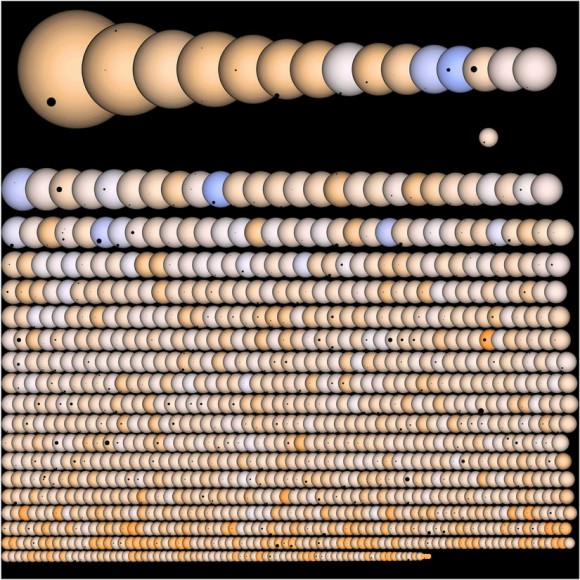
Kepler has found over 2,700 planetary candidates, with 130 confirmed planets, from the size of Earth’s moon to larger than Jupiter.
“We’ll continue to analyze the data to get the science that Kepler was designed to do,” said Paul Hertz, NASA’s astrophysics director. “Even though Kepler is in trouble, it has collected all the data necessary to answer its scientific objectives. Kepler is not the last exoplanet mission, but the first. It has been a great start to our path of exoplanet exploration.”
There’s also the chance that something else could be done with the spacecraft if it no longer can do planet hunting, such as asteroid hunting or other astronomical observations…just something that doesn’t need as precise ability for pointing. If that’s the case, Hertz said they would open up a call for science mission proposals.
Additional info here from the Kepler Mission Manager Update