
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

An international team of astronomers recommends creating "Betelgeuse Scope" to monitor this mysterious star find out why it has been acting so strangely of late!
Continue reading

Continue reading

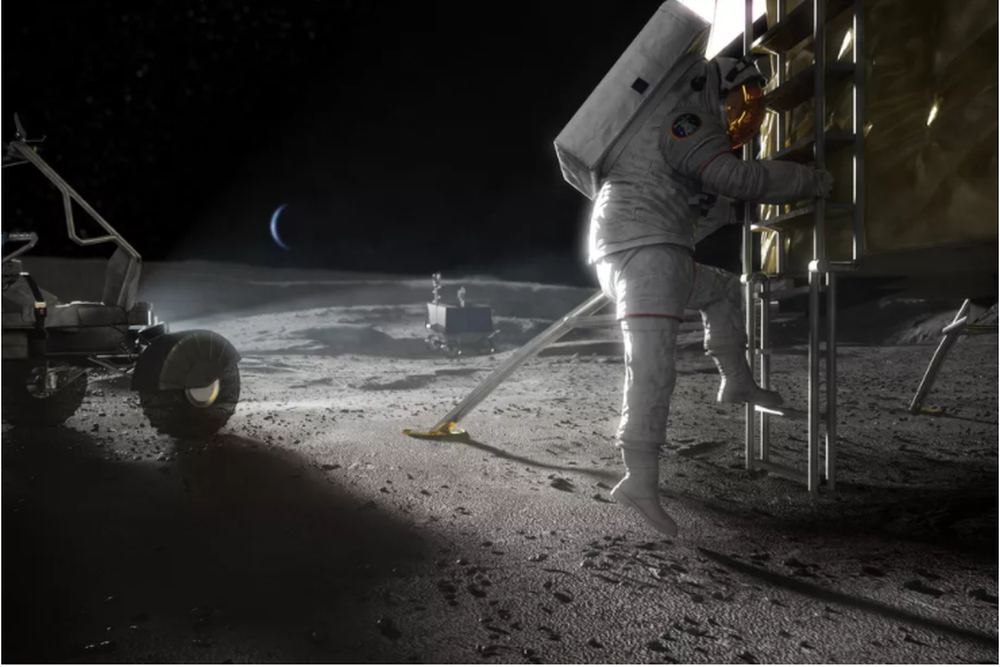
NASA recently awarded contracts to fourteen companies to develop technologies that will help them return to the Moon, and stay there!
Continue reading

The stars at the center of our galaxy could tell us just how fast our closest supermassive black hole is spinning.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

The SN8 Starship prototype just got its three Raptor engines, and is now preparing to test fire them. After that, it's smooth sailing towards the 15 km (50,000 ft) hop test!
Continue reading
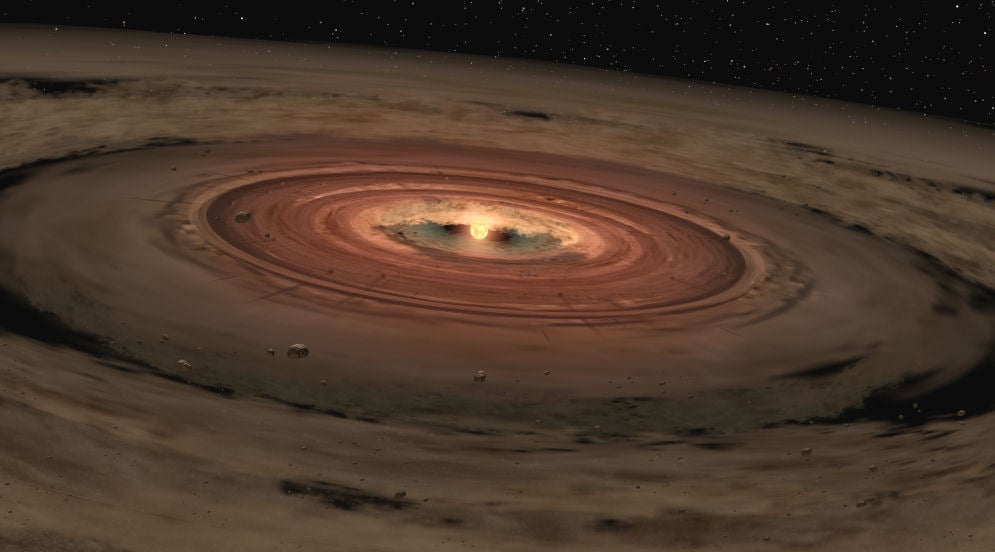
This week we are joined by Dr. Jane Huang and Dr. Jonathan Willams from the Center for Astrophysics, Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA). Dr. Huang, Dr. Williams, and their team recently discovered some surprising information about the size and shape of some protoplanetary disks.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

In a interesting bit of SpaceX news, Starman and his cherry Tesla Roadster made their first flyby of Mars, and will be passing by Earth in less than a month!
Continue reading

Continue reading

Using the largest survey ever conducted, a team of astronomers from the IfA have created the largest 3D catalog of the Universe ever!
Continue reading

The Mercury-bound BepiColombo spacecraft will observe Venus during tonight's pass, on the hunt for phosphine and sulfur-dioxide.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

When a black hole consumes a star, it does so by turning it into spaghetti first. Astronomers have seen it happen.
Continue reading

Continue reading

The Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) caught another intriguing object on August 2, 2020 as part of its extended sky survey mission, as Comet C/2020 P1 NEOWISE is set to become a fine binocular object in late October and early November.
Continue reading

Continue reading

When black holes collide, they emit chirps of gravitational waves even after they have merged.
Continue reading
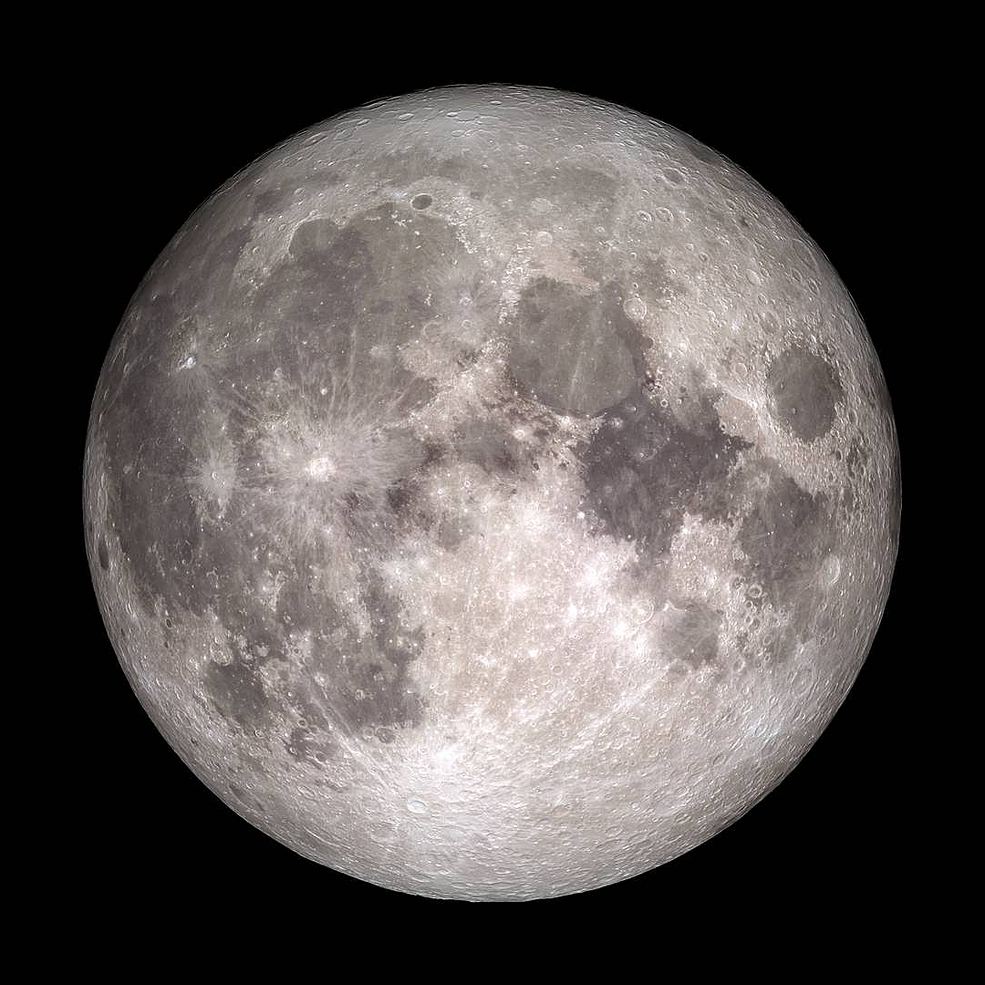

A recent white paper submitted to the PSA Decadal Survey 2023-2032 recommends that a lunar observatory be built that can search the Universe for signs of intelligent life!
Continue reading
A new study from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy shows how a "Sun Diver," a light sail that dives closer to the Sun, could make these promising spacecraft much faster!
Continue reading

With all the satellite constellations heading to space in the near future, there are concerns they will interfere with radio telescopes like the Square Kilometre Array (SKA)
Continue reading
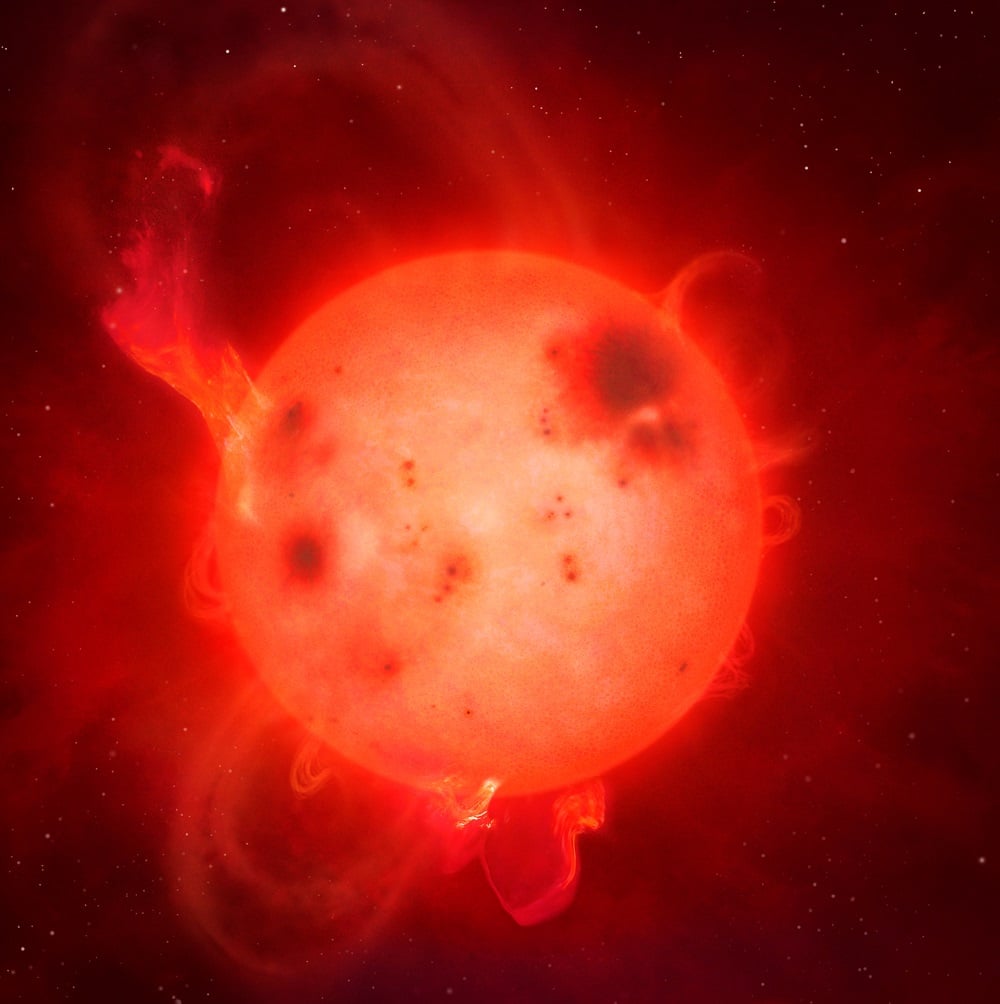

Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Check out this stunning new deep-sky panoramic and new light-weight 'smartscope,' courtesy of Vaonis.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
This week we welcome back to the show Dr. David Warmflash. Since he was last with us, David has been named as Co-Principal Investigator and Medical Director for a new NASA Small Business Innovation Research (SBRI) Phase I study titled "Mixed-Reality Holographic Training System to Enable High-Value Surgical and Complex Medical Procedures by Astronauts."
Continue reading

Because gravitational waves travel at the speed of light, they can be lensed just as light waves are. But observing this effect will be difficult.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
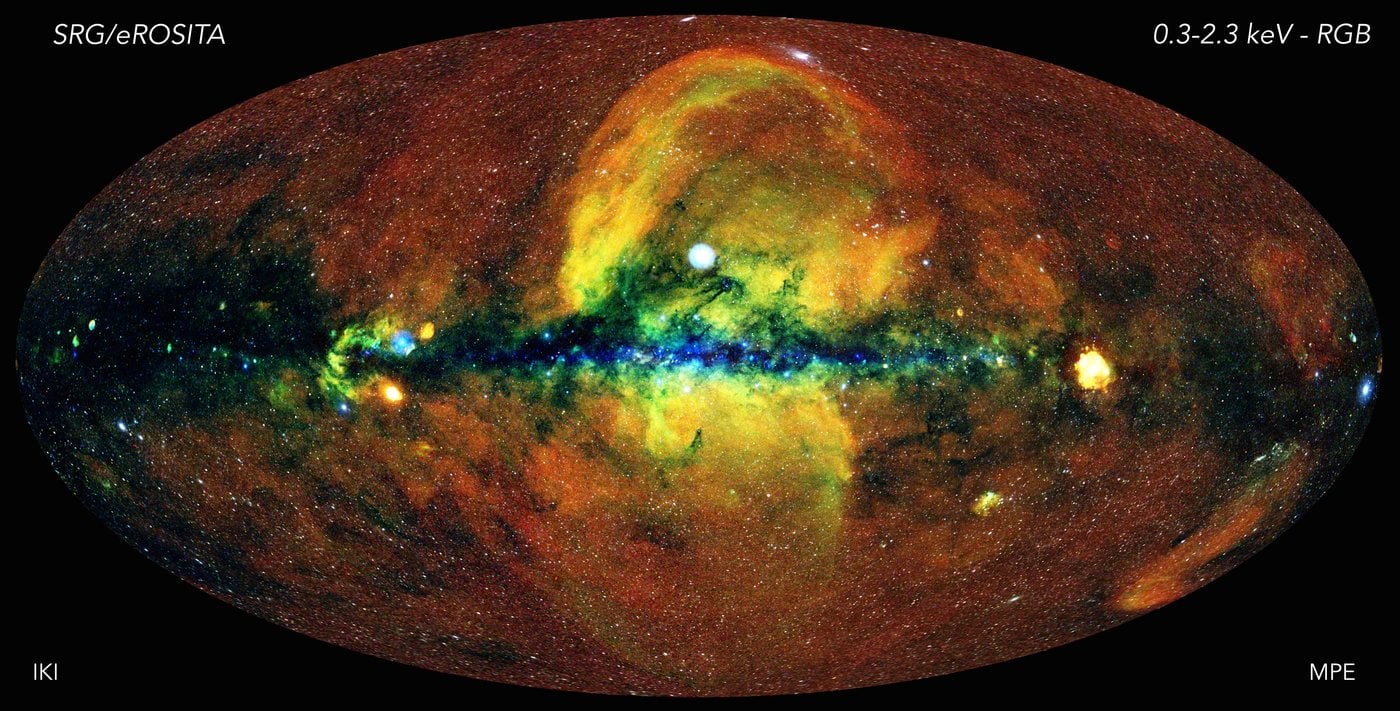

Continue reading
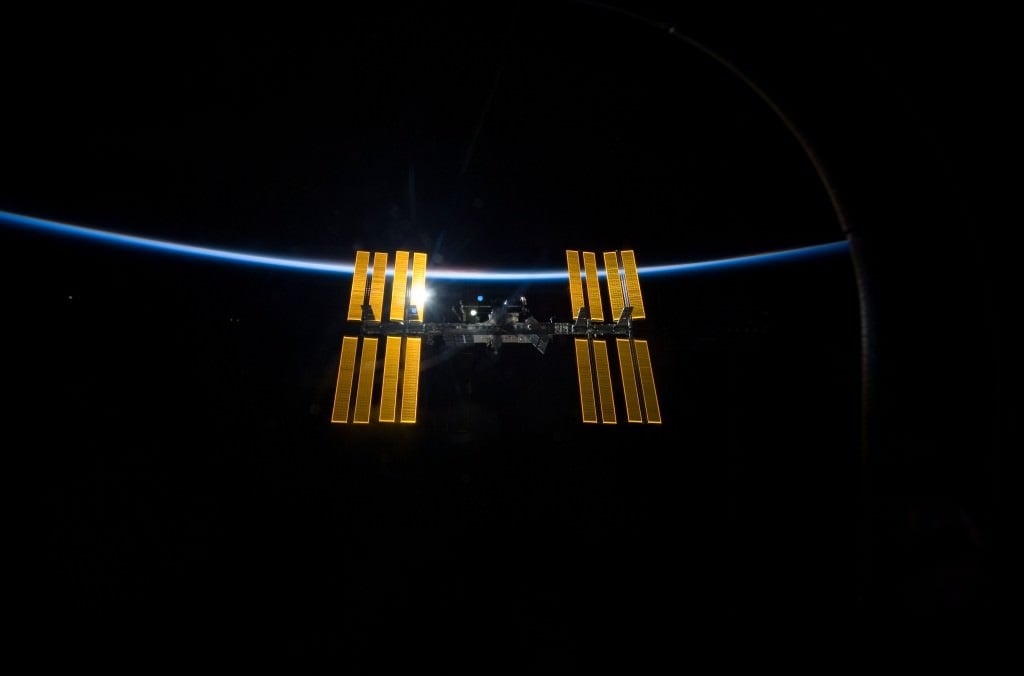

The crew aboard the ISS have managed to narrow the search for the leak, which NASA and Roscosmos both insist does not pose a danger to the crew or their operations
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading















































