When Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers first glimpsed Vesta on March 29, 1807 — this date in history — the asteroid was but a small point of light. Asteroid science was very, very new at the time as the first asteroid (Ceres) had been discovered only six years before.
Fast-forward 200-plus years and we can treat Vesta as a little world in its own right. NASA sent the Dawn spacecraft in orbit for about a year, which has produced a wealth of weird results. (Stay tuned for what happens at Dawn’s next port of call: Ceres.)
Below are five strange things we’ve discovered about Vesta:
1) Vesta has a fresh face.
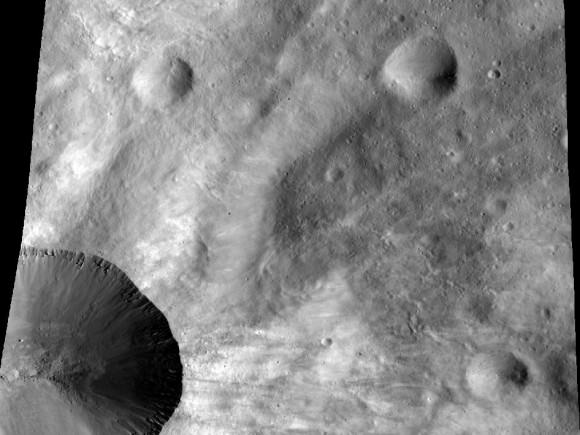

Space “weathering” from tiny particles hitting the Moon has shaped the surface over time. Not so much on Vesta. It turns out the topography on the asteroid (and other factors) allow constant mixing of the surface, making it appear almost new even though the asteroid is several billion years old. “Vesta ‘dirt’ is very clean, well mixed and highly mobile,” said Carle Pieters, one of the lead authors and a Dawn team member based at Brown University, Providence, R.I. when the finding was made public.
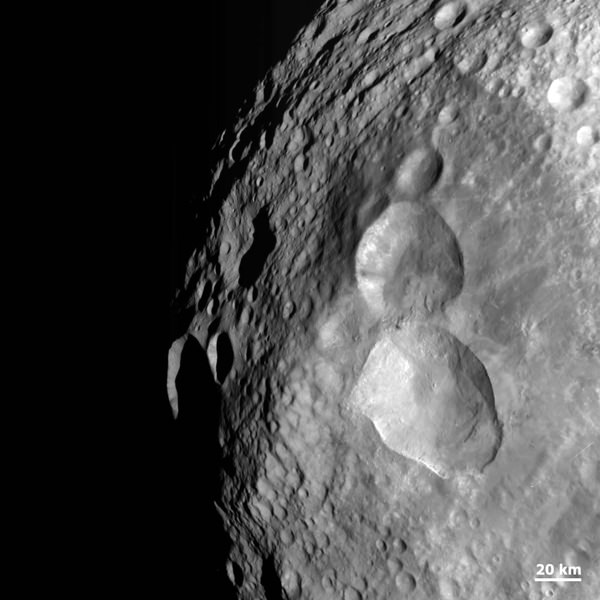
2) Vesta might have stretch marks.
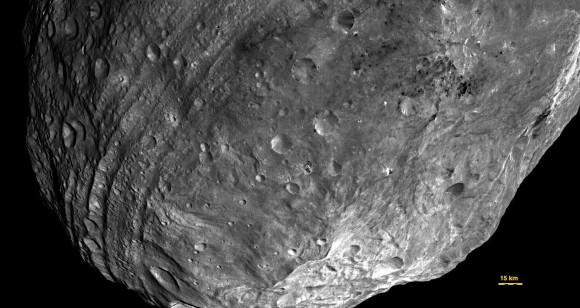
While trying to wrap their mind around fault lines that circle Vesta’s equator, a group of scientists proposed these could be graban — features that show surface expansion. It’s possible these faults came to be after something big smashed into the planet, creating a gigantic crater with a peak that is almost three times as high as Mt. Everest. The expansion occurred as Vesta’s interior differentiated, or experienced a separation of its core, mantle and crust.
3) Vesta kind of looks like a planet.
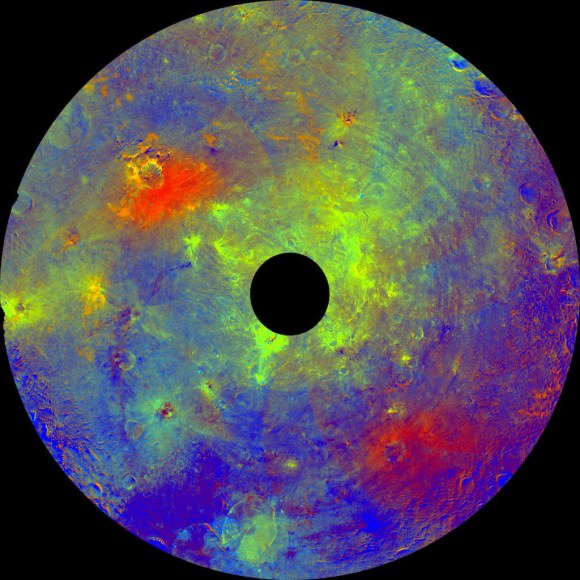
Looking at Vesta in false color — wavelengths that let different kinds of minerals shine — show a veritable cornucopia of different types of stuff. There’s the iron-rich mineral pyroxene, there’s diagenite material (characteristic of stony meteorites), and various particles of different sizes and ages. “Vesta is a transitional body between a small asteroid and a planet and is unique in many ways,” said mission scientist Vishnu Reddy of the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany. “We do not know why Vesta is so special.”
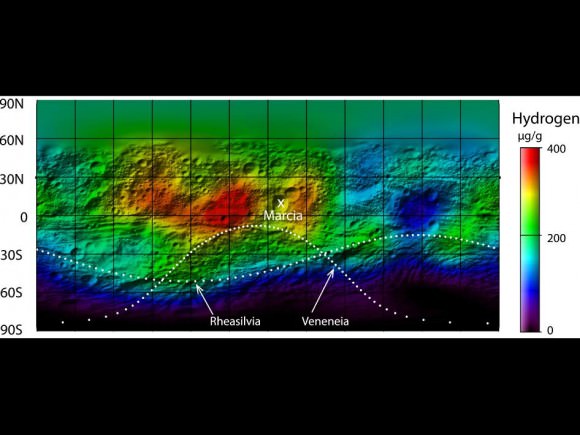
4) Vesta has hydrogen.
Hydrated minerals are circling the equator of the little world. It’s not quite water, but still an interesting find for scientists. “The source of the hydrogen within Vesta’s surface appears to be hydrated minerals delivered by carbon-rich space rocks that collided with Vesta at speeds slow enough to preserve their volatile content,” stated Thomas Prettyman, lead scientist for Dawn’s gamma ray and neutron detector (GRaND) from the Planetary Science Institute.
5) The northern and southern hemispheres look completely different.
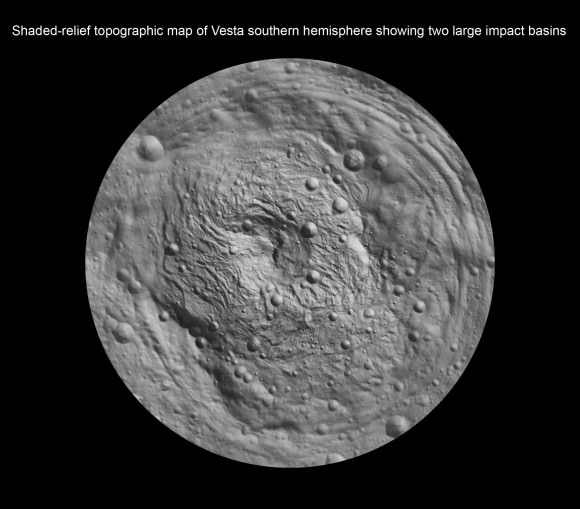
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
It’s fun to get to a new world and end up with something fundamentally surprising. Some of the very first pictures of Vesta showed a vast difference between different regions of the planet, giving scientists a workout in terms of figuring out how that came to be. “The northern hemisphere is older and heavily cratered in contrast to the brighter southern hemisphere where the texture is more smooth and there are lots of sets of grooves. There is a massive mountain at the South Pole. One of the more surprising aspects is the set of deep equatorial troughs,” said Carol Raymond, Dawn deputy principal investigator, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
Here’s a video where you can see that for yourself: