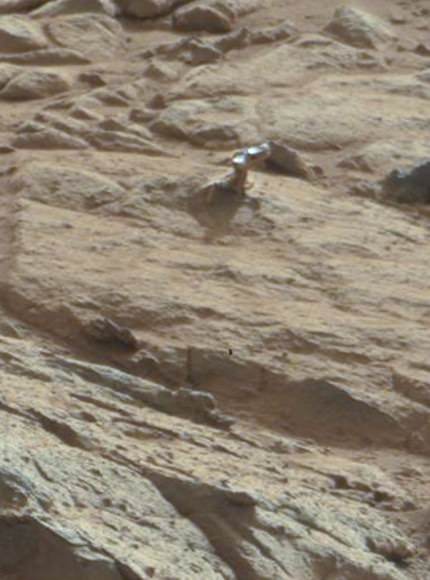
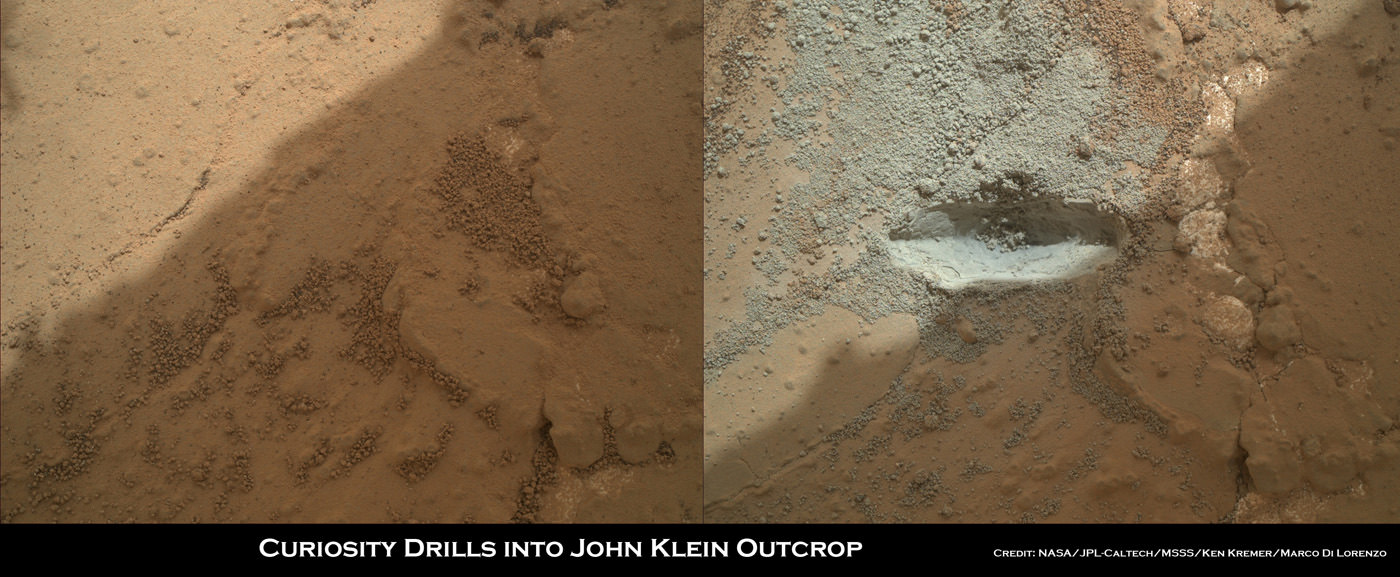
Image caption: Before and after comparison of Curiosity’s 1st ever drill test into Martian rock. Drill bit penetrated several mm and vibrations apparently unveiled hidden, whitish mineral by dislodging thin dust layer at John Klein outcrop in Sol 176 images. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
A robot from Earth has successfully drilled into a Martian rock for the first time ever and exposed pristine alien material for high powered science analysis.
NASA’s car sized Curiosity rover deliberately plunged the drill bit on the end of her 7 foot (2.1 m) robot arm into a flat outcrop of rocks possessing hydrated mineral veins, that is situated inside a shallow basin named Yellowknife Bay where water repeatedly flowed.
“The drill test was done. The mission has been spectacular so far,” said Dr. Jim Green, Director of NASA Planetary Sciences Division at NASA HQ, in an exclusive interview today with Universe Today on the campus of Princeton University. “The area is tremendously exciting.”
And what’s even more amazing is that as Curiosity hammered straight down into the rock outcrop, it appears that the resulting vibrations also simultaneously uncovered a hidden vein of whitish colored material that might be calcium sulfate – as the Martian ground shook and a thin layer of rust colored soil was visibly dislodged.
The robot is working at a place called Glenelg – where liquid water once flowed eons ago across the Red Planet’s surface.
“This area is really rich with all the cracks in the rocks and the veins. It’s really fabulous,” Green told me. “The landing was an engineering feat that enabled us to do all this great science that comes next.”

Image caption: Curiosity views 1st plunge of the hammering drill bit up from raised position, at left, to rock outcrop penetration, at right, on Jan 31, 2014, Sol 174 using the front hazard avoidance camera. 3 mile (5 km) high Mount Sharp ultimate destination offers dramatic backdrop. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
Drill, Baby, Drill !! — Drilling is essential toward achieving Curiosity’s goal of determining whether Mars ever offered an environment favorable for microbial life, past or present
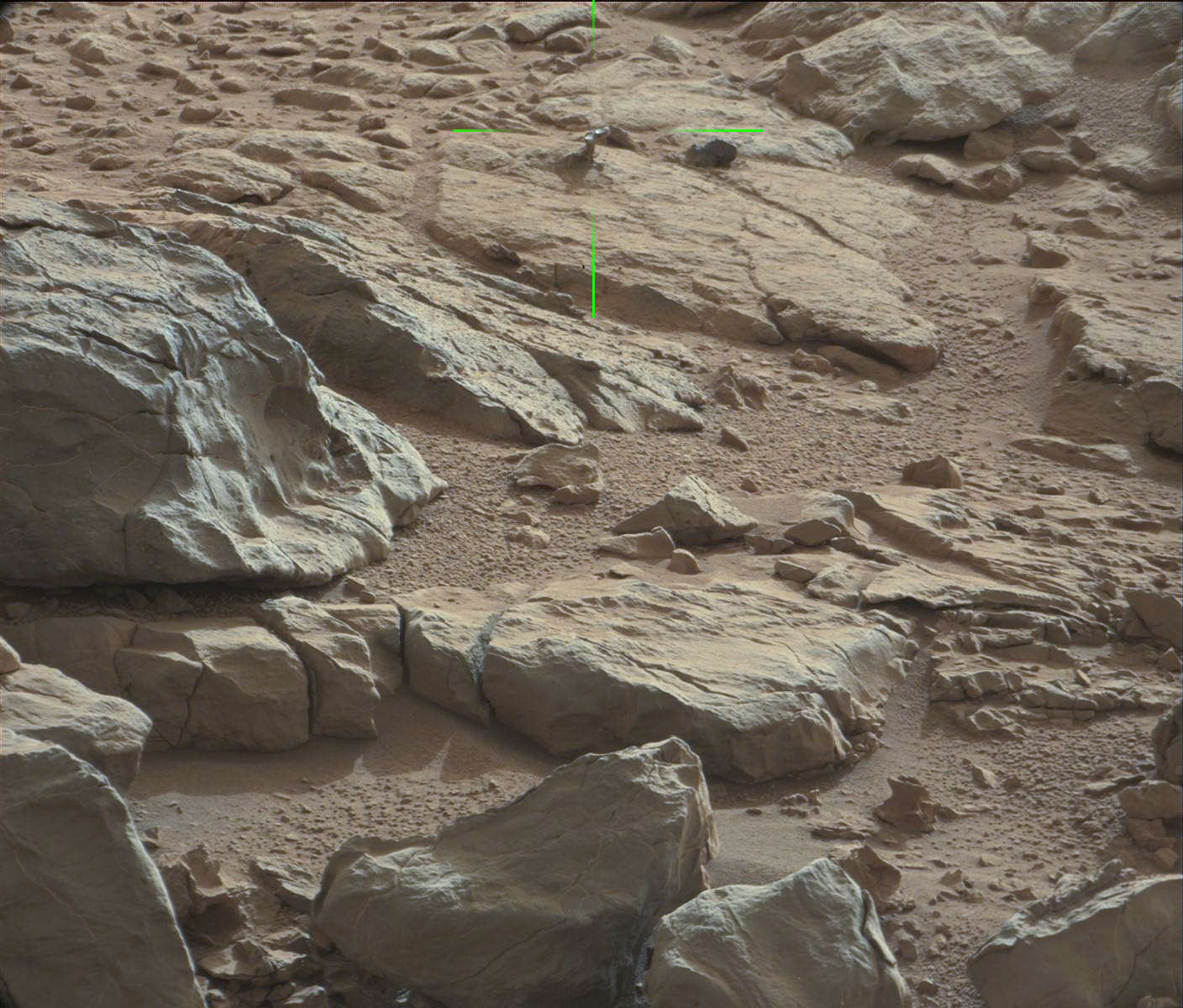
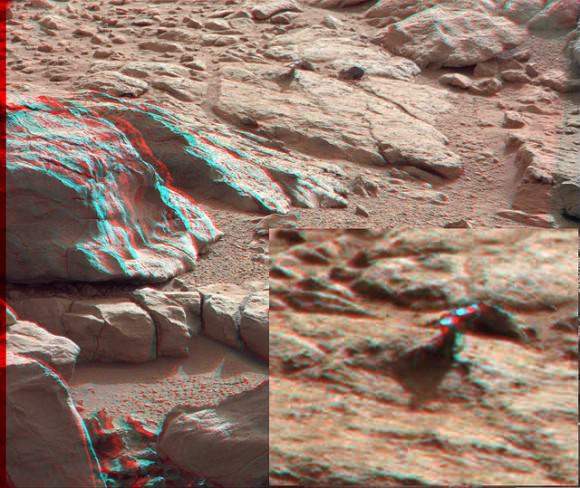
The drill bit penetrated a few millimeters deep into the intriguing outcrop called ‘John Klein’ as planned during the drill tests run on Jan 31 and Feb 2, 2013 (or Sols 174 & 176), Green elaborated. The results were confirmed in new images snapped by Curiosity over the past few days, that trickled back to Earth this weekend across millions of miles of interplanetary space.
Several different cameras – including the high resolution MAHLI microscopic imager on the arm tool turret – took before and after up-close images to assess the success of the drilling maneuver.

Image caption: Curiosity tool turret located at end of robotic arm is positioned with drill bit in contact with John Klein outcrop for 1st hammer drilling into Martian rock surface on Jan 31, 2013. It’s nearby a spot that was brushed earlier. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
The Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS) was also placed in contact with the ground to determine the chemical composition of the rock drill test site and possible calcium sulfate vein and investigate its hydration state.
The drill test marks an historic first time achievement in the annuls of space exploration.
NASA’s Spirit and Opportunity Mars rovers successfully abraded numerous rocks but are not equipped with penetrating drills or sample acquisition and analysis instruments.
During this initial test, Curiosity’s hi-tech drill was used only in the percussion mode – hammering back and forth like a chisel. No tailings were collected for analysis. The 5/8-inch (16 mm) wide bit will be rotated in upcoming exercises to bore several test holes.
Green told me that the Curiosity science and engineering team says that this initial test will soon be following up by more complex tests that will lead directly to drilling into the interior of a rock for the first ever sampling and analysis of fresh, rocky Martian material.
“The drill test results are looking good so far,” Green said. “Depending on the analysis, it’s possible that the initial test bore hole could be drilled as early as tonight. Sampling could follow soon.”
The science and engineering team are wisely being “ultra careful” says Green, in slowly and methodically checking out the highly complex drill.
“We are motivated to work in a stepwise fashion to get it right,” Green elaborated.
“The drilling has got to be done carefully. We are still in checkout mode and the drill is the last instrument of Curiosity’s ten science instruments to be fully checked out.”
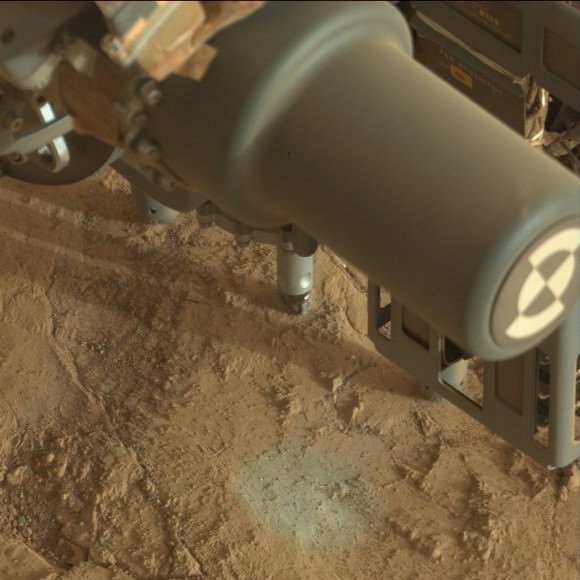

Image caption: Close-up view of Curiosity drill bit penetrating John Klein outcrop during 1st ever drill test into Martian rock on Jan 31, 2013 (Sol 174). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Curiosity can drill to a depth of about 2 inches (5 cm) into rocks. Ultimately a powdered and sieved sample about half an aspirin tablet in size will be delivered to the SAM and CheMin analytical labs on the rover deck.
“The drilling is going very well so far and we’re making great progress with the early steps,” said Curiosity project scientist Prof John Grotzinger to the BBC.
Drilling goes to the heart of the mission. The cored rock samples will be analyzed by the duo of chemical spectrometers to ascertain their elemental composition and determine if organic molecules – the building blocks of life – are present.
The 1 ton robot will spend at least several weeks or more investigating Yellowknife Bay and Glenelg – which lies at the junction of three different types of geologic terrain.
Thereafter, the six-wheeled mega rover will set off on a nearly year long trek to her main destination – the sedimentary layers of the lower reaches of the 3 mile (5 km) high mountain named Mount Sharp.
As the Martian crow flies, the breathtaking environs of Mount Sharp are some 6 miles (10 km) away.
Ken Kremer
Feb 4: Dr Jim Green, Director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, is presenting a free public lecture at Princeton University at 8 PM titled: “The Revolution in Planetary Science.” Hosted by the Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton. Location: Peyton Hall, Astrophysics Dept. on Ivy Lane, Princeton, NJ.

Image caption: Curiosity conducted Historic 1st drilling into Martian rock at John Klein outcrop shown in this context view of the Yellowknife Bay basin where the robot is currently working. The robotic arm is pressing down on the surface at John Klein outcrop of veined hydrated minerals – dramatically back dropped by her ultimate destination; Mount Sharp. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
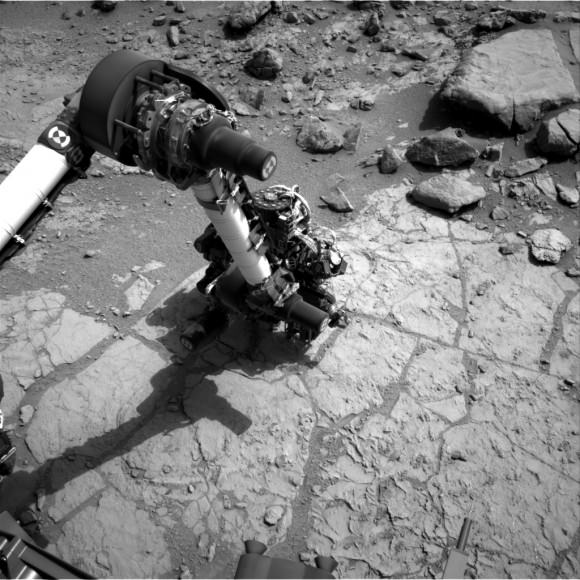

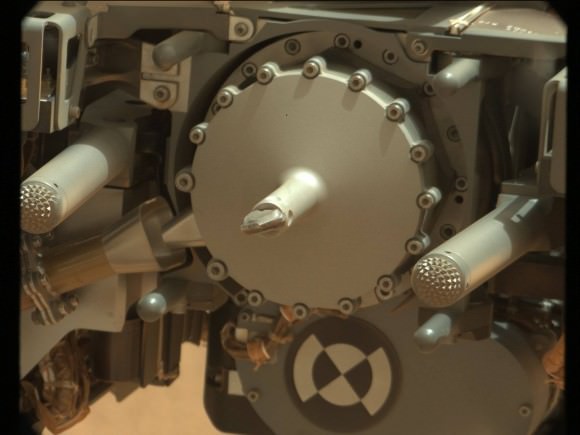
Image caption: Close-up view of Curiosity drill bit. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
CfA astronomers identified 95 planetary candidates circling red dwarf stars. Of those, three orbit within the habitable zone (marked in green) – the distance at which they should be warm enough to host liquid water on the surface. Those three planetary candidates (marked with blue dots) are 0.9, 1.4, and 1.7 times the size of Earth. Credit: C. Dressing (CfA)
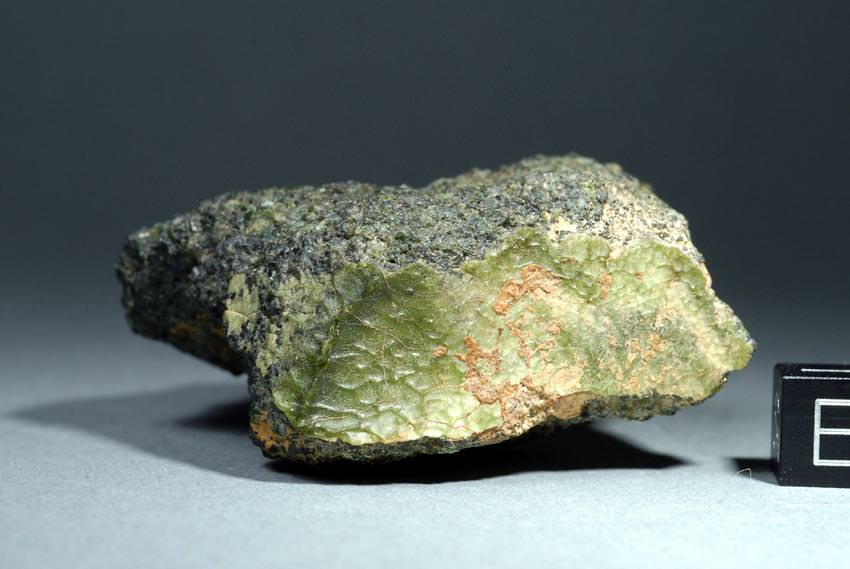


























 And even though the ratio of calcium silicates is higher than what’s found on Mercury today, Irving speculates that the fragments of NWA 7325 could have come from a deeper part of Mercury’s crust, excavated by a powerful impact event and launched into space, eventually finding their way to Earth.
And even though the ratio of calcium silicates is higher than what’s found on Mercury today, Irving speculates that the fragments of NWA 7325 could have come from a deeper part of Mercury’s crust, excavated by a powerful impact event and launched into space, eventually finding their way to Earth.