Image Caption: Curiosity Scans ‘Yellowknife Bay’ on Sol 130. NASA’s Curiosity rover celebrated her 1st Christmas on the Red Planet at ‘Yellowknife Bay’ and is searching for her 1st rock target to drill into for a sample to analyze. She snapped this panoramic view on Dec. 17 which was stitched together from navigation camera (Navcam) images. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
Today (Dec. 25) Curiosity celebrates her 1st Christmas on Mars at a spot called ‘Yellowknife Bay’. It’s Sol 138 and nearly 5 months since the pulse pounding landing on Aug. 6, 2012 inside Gale Crater. The robot is in excellent health.
Meanwhile her older sister Opportunity will soon celebrate an unfathomable 9 Earth years on Mars in a few short weeks on Jan. 24, 2013 – on the other side of the planet.
NASA’s Curiosity rover reached the shallow depression named ‘Yellowknife Bay’ on Sol 130 (Dec. 17, 2012) after descending about 2 feet (0.5 m) down a gentle slope inside a geologic feature dubbed ‘Glenelg’. See our panoramic mosaics from Yellowknife Bay – above and below for a context view.
The science team is searching for an interesting rock for the inaugural use of the high powered hammering drill.
According to a new report in SpaceRef, the drilling has been delayed due to concerns that frictional heating may potentially cause liquification of the rock to a gooey “Martian Honey” that could potentially clog and seriously damage the sample handling sieves and mechanisms. So the team is carefully re-evaluating the type of rock target and the drilling operation procedures before committing to the initial usage of the percussive drill located on the turret at the terminus of the robotic arm.
The team chose to drive to ‘Yellowknife Bay’ because it features a different type of geologic terrain compared to what Curiosity has driven on previously. The ‘Glenelg’ area lies at the junction of three different types of geologic terrain and is Curiosity’s first extended science destination.
Curiosity arrived at the lip of Yellowknife Bay on Sol 124 and entered the basin on Sol 125 (Dec. 12) and snapped a scouting panoramic view peering into the inviting locale. The rover is also using the APXS X-ray mineral spectrometer, ChemCam laser and MAHLI hand lens imager to gather initial science characterization data.

Curiosity peaks around Yellowknife Bay on Sol 125, Dec 12, 2012. The rover continued driving inside the basin in search of 1st rock drill target. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
So far the rover has traversed a total driving distance of some 0.43 mile (700 meters).
Most of the science and engineering team is getting a much needed break to spend time with their families after uploading 11 Sols worth of activities ahead of time to keep the robot humming during the Christmas holiday season. A skeleton crew at JPL is keeping watch to deal with any contingencies.
One of the top priorities is acquiring a high resolution 360 degree Mastcam color panorama. This will be invaluable for selection of the very 1st rock target to drill into and acquire a sample from the interior – a feat never before attempted on Mars.
“We decided to drive to a place with a good view of the outcrops surrounding Yellowknife Bay to allow good imaging of these outcrops before the holiday break,” says rover science team member Ken Herkenhoff. “As the images are returned during the break, we can use them to help decide where to perform the first drilling operation.”
The team expects to choose a drill target sometime in January 2013 after a careful selection process.
The 7 foot (2 m) long robotic arm will deliver that initial, pulverized rock sample to inlet ports on the rover deck for analysis by the high powered duo of miniaturized chemistry labs named Chemin & SAM.

Image Caption: Curiosity deploys robotic arm on Sol 129 and examines rock with APXS and MAHLI science instruments to characterize rock and soil composition. This composite mosaic was stitched from Navcam images from Sol 129 (Dec. 16) and earlier sols- and shows the location of the Chemin sample inlet port on the rover deck. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
Curiosity will spend at least another month or more investigating Glenelg before setting off on the nearly year long trek to her main destination – the sedimentary layers of the lower reaches of the 3 mile (5 km) high mountain named Mount Sharp.

Image caption: Scanning Mount Sharp from Yellowknife Bay on Sol 136. This photo mosaic assembled from Mastcam 100 camera images was snapped by Curiosity on Sol 136 (Dec. 23) – from her current location. It shows a portion of the layered mound called Mount Sharp, her main destination. Acquiring a 360 high resolution color panorama from Yellowknife Bay is a high priority task for the rover during the Christmas holiday season. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer
As the Martian crow flies, the breathtaking environs of Mount Sharp are some 6 miles (10 km) away.
The mission goal is to search for habitats and determine if Mars ever could have supported microbial life in the past or present during the 2 year primary mission phase.
Ken Kremer
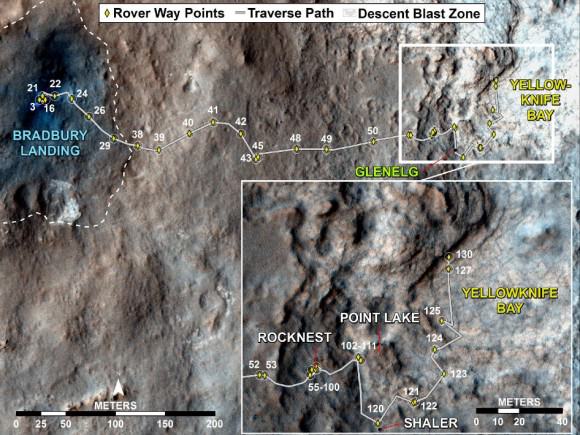
Image Caption: Curiosity Traverse Map, Sol 130. This map traces where Curiosity drove between landing at a site named “Bradbury Landing,” and the position reached during Sol 130 (Dec. 17, 2012) at a spot named “Yellowknife Bay” which is inside an area called “Glenelg”. The inset shows the most recent legs of the traverse in greater detail. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona