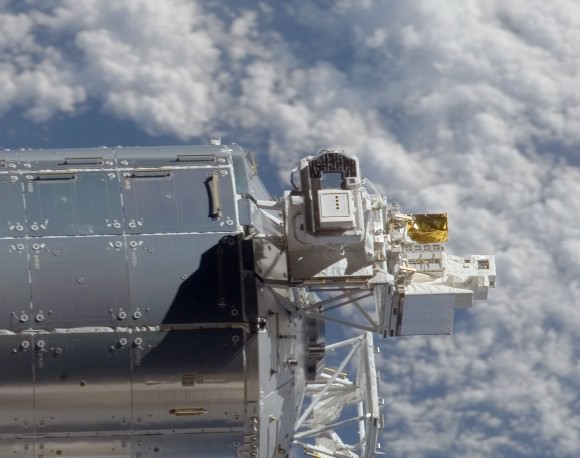
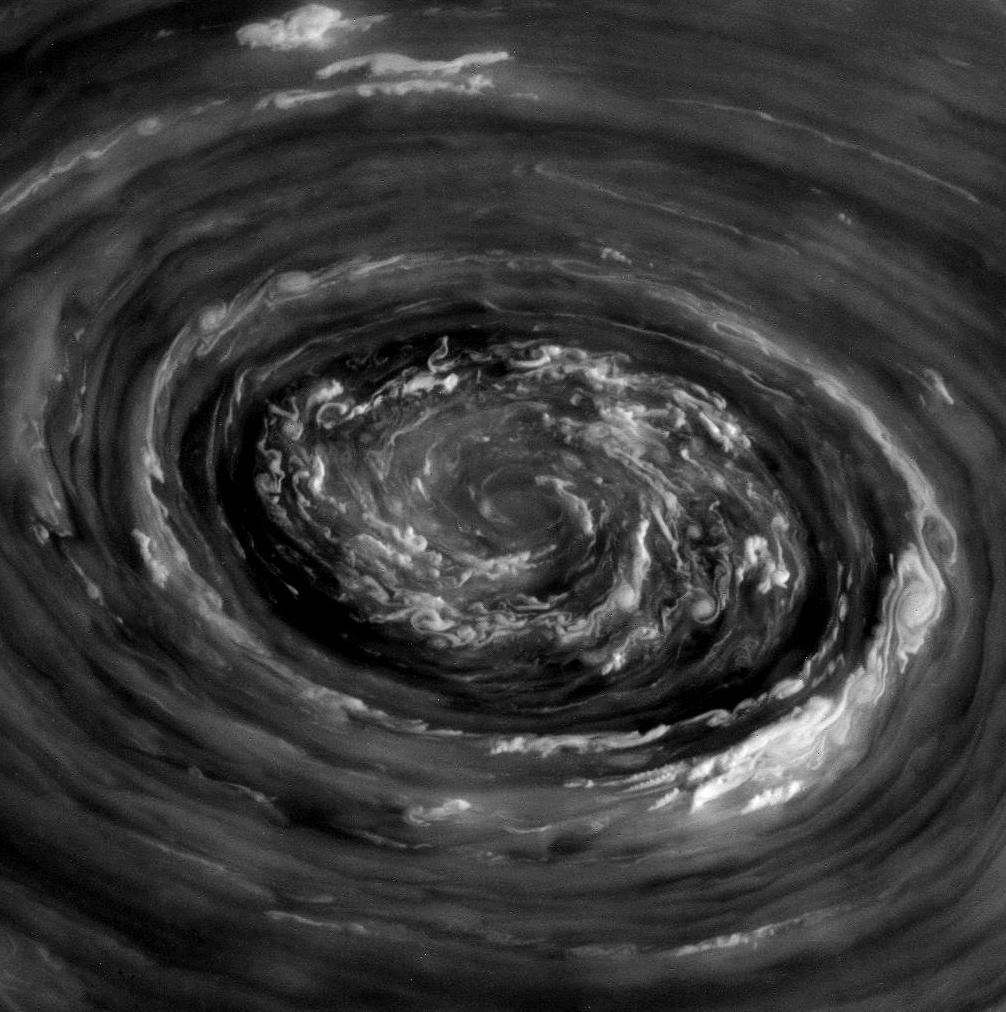
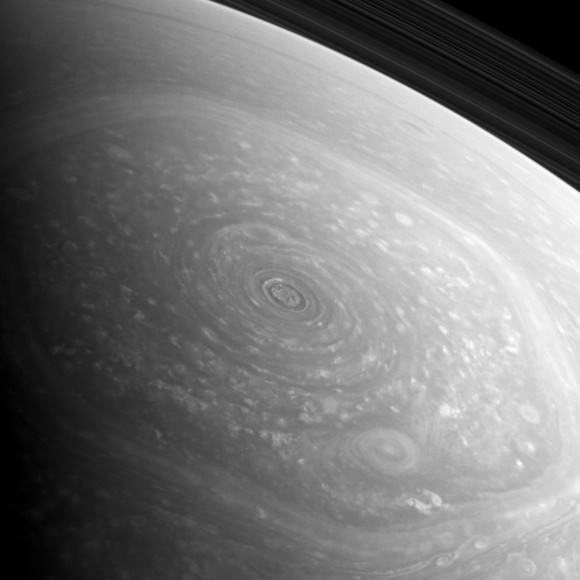
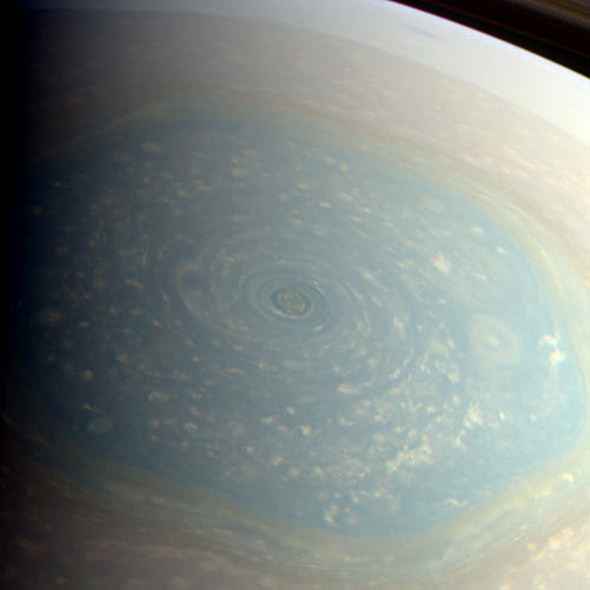
Image of lenticular galaxy NGC 1277 taken with Hubble Space Telescope. (NASA/ESA/Andrew C. Fabian)
It’s thought that at the heart of most if not every spiral galaxy (as well as some dwarf galaxies) there’s a supermassive black hole, by definition containing enormous amounts of mass — hundreds of millions, even billions of times the mass of our Sun packed into an area that would fit inside the orbits of the planets. Even our own galaxy has a central SMBH — called Sgr A*, it has the equivalent of 4.1 million solar masses.
Now, astronomers using the Hobby-Eberly Telescope at The University of Texas at Austin’s McDonald Observatory have identified what appears to be the most massive SMBH ever found, a 17 billion solar mass behemoth residing at the heart of galaxy NGC 1277.
Located 220 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus, NGC 1277 is a lenticular galaxy only a tenth the size of the Milky Way. But somehow it contains the most massive black hole ever discovered, comprising a staggering 14% of the galaxy’s entire mass.
“This is a really oddball galaxy,” said Karl Gebhardt of The University of Texas at Austin, a team member on the research. “It’s almost all black hole. This could be the first object in a new class of galaxy-black hole systems.”
The study was led by Remco van den Bosch, who is now at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA).
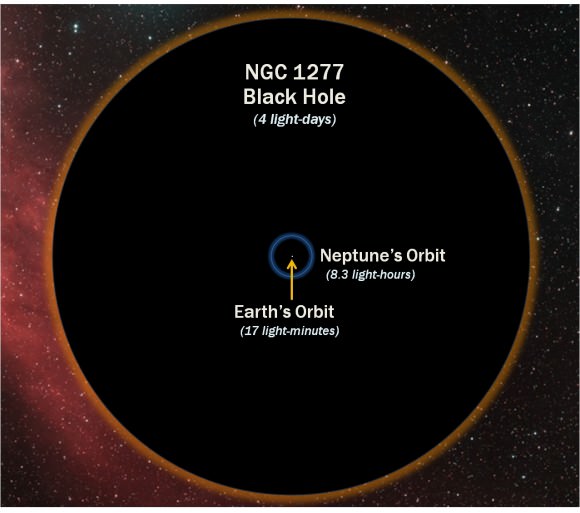
It’s estimated that the size of this SMBH’s event horizon is eleven times the diameter of Neptune’s orbit — an incredible radius of over 300 AU.
How the diamater of the black hole compares with the orbit of Neptune (D. Benningfield/K. Gebhardt/StarDate)
Although previously imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope, NGC 1277’s monster black hole wasn’t identified until the Hobby-Eberly Telescope Massive Galaxy Survey (MGS) set its sights on it during its mission to study the relationship between galaxies and their central black holes. Using the HET data along with Hubble imaging, the survey team calculated the mass of this black hole at 17 billion solar masses.
“The mass of this black hole is much higher than expected,” said Gebhardt, “it leads us to think that very massive galaxies have a different physical process in how their black holes grow.”
To date, the HET team has observed 700 of their 800 target galaxies.
In the video below, Remco van den Bosch describes the discovery of this unusually super supermassive black hole:
Read more on the UT Austin’s McDonald Observatory press release here, or this press release from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy.