
Using data from multiple telescopes, an international team of astronomers has identified the most distant galaxy group to date - a find which that reveal a great deal about the early Universe.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
A new MIT-led study has shown how the Moon once had a more powerful magnetic field than Earth and why it was lost over time.
Continue reading

According to new research by a team from the LPI, it appears likely that Venus could indeed have active volcanoes on its surface today.
Continue reading

New research by a team of geophysicists has revealed that "snow" could be a regular feature in Earth's core region.
Continue reading

A new study by a team led from the University of Colorado, Boulder, has discovered a rare and unique class of exoplanet that has the density of cotton candy.
Continue reading

The year 2020 is expected to be an exciting one for space exploration. Here are the top stories that are expected to take place
Continue reading

Continue reading

Ready for another amazing year of sky watching? Hard to believe, were already a fifth of the way into the 21st century. 2020 rounds out the final year of the second decade, promising an amazing year of skywatching to come.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Using the ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT), an international team of astronomers observed gas clouds that in the early Universe that could explain how supermassive black holes formed so quickly.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Using data from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, a team of scientists have discovered a new type of solar phenomenon that could lead to breakthroughs in space weather prediction and fusion technology.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Using data from the GALACICNUCLEUS survey, a team of astronomers has determined that star formation occurred in massive bursts in our galaxy, not continuously over time.
Continue reading

Continue reading
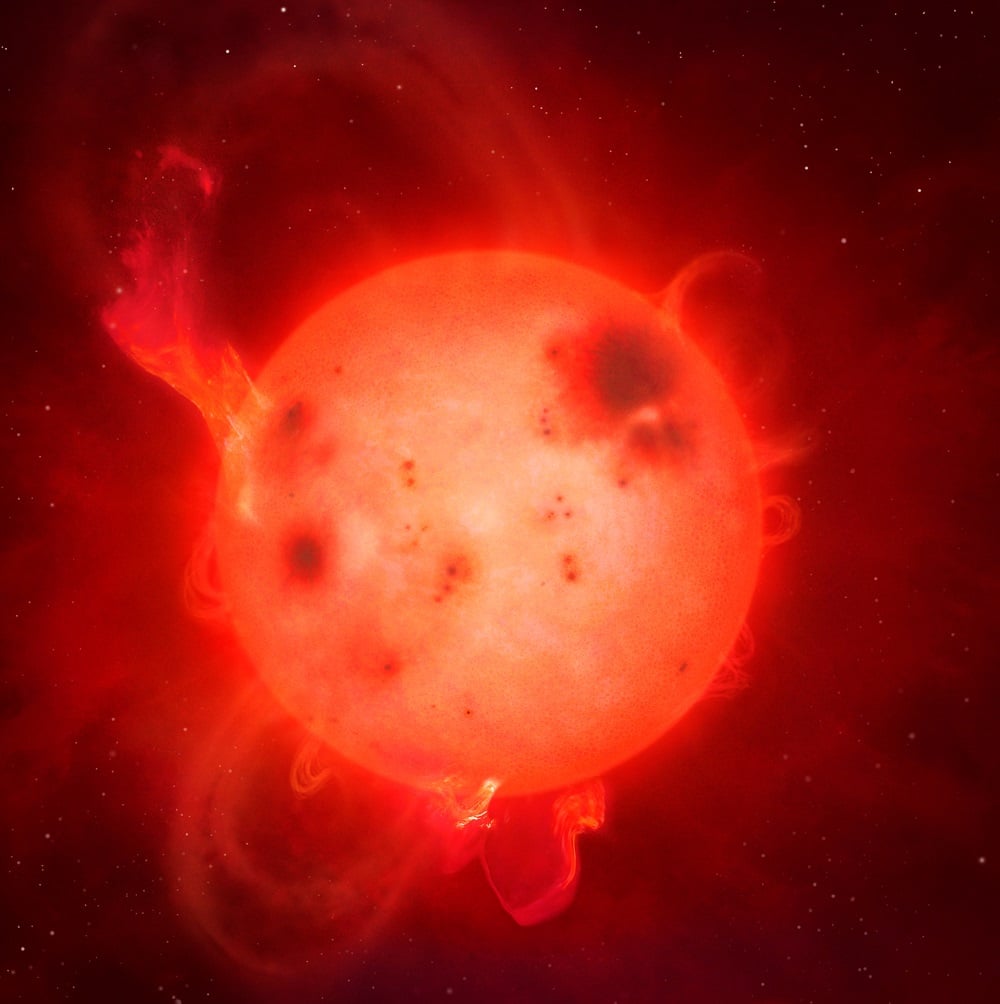

Continue reading

next bright comet? You're not alone. Though we've had a steady string of decent binocular comets over the past few years, we haven't had a good naked eye comet since W3 Lovejoy beat death during its blistering perihelion passage in 2011. But this survivor turned out to be bashful, headed for southern hemisphere skies… Comet P1 McNaught followed suit in 2007, hiding from northern hemisphere observers. And we all remember what happened to Comet S1 ISON—touted as the next great 'Comet of the Century' on Thanksgiving Day 2013. Here it is almost 2020, and you have to go allll the way back nearly a quarter of a century to Comets Hale-Bopp and Hyakutake to remember just how brilliant a good naked eye comet can be.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

Using NICER data, two teams of researchers were able to map the surface of a pulsar for the first time in history!
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

A new study by a team of German physicists and an American biomedical engineer has solved a long-standing problem in how planets form.
Continue reading

The 2020 Spaceport America Cup will be the largest to date, thanks to a new collaboration with crowdsourcing powerhouse HeroX!
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

A specialized spacecraft will be sent to orbit by the ESA in 2025 to remove a piece of space debris, which will pave the way for future cleanup missions.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

A NASA image showcases the beauty of the NGC 5468 galaxy, which has experienced 5 supernovae in the last 20 years (all of which we've witnessed).
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading
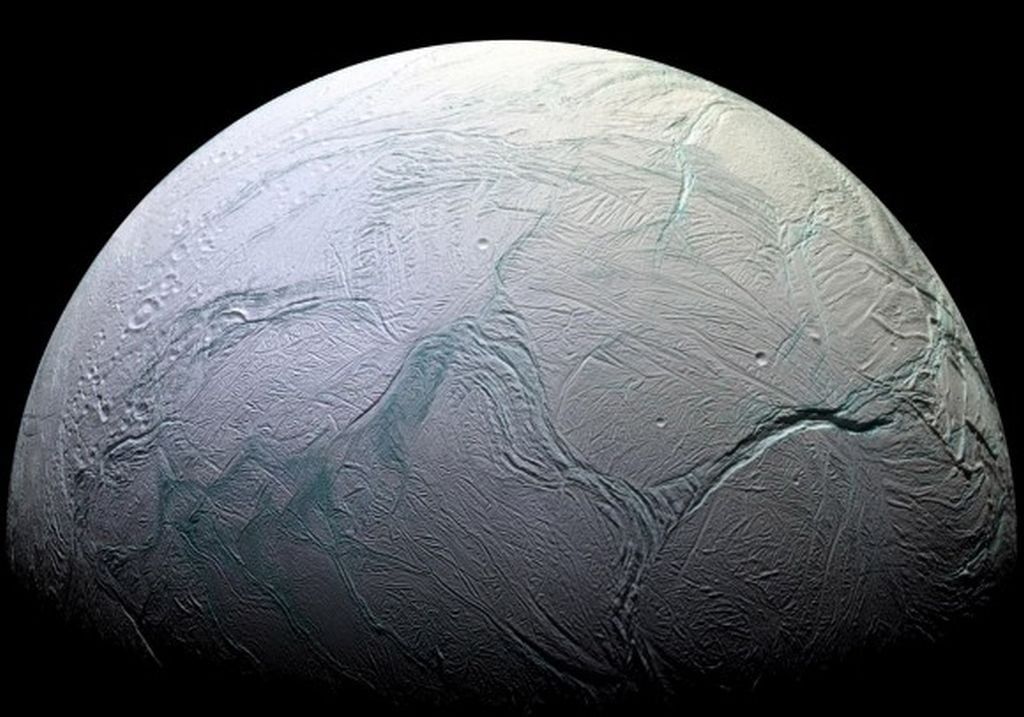

A study led by the Carnegie Institute of Science has determined why Enceladus' has its mysterious Tiger Stripes.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

December means chillier climes for northern hemisphere residents, a time to huddle inside near the campfire, both real and cyber. I've always thought this was a shame, however, as the cold crisp nights of winter offer up sharp clear skies. Over the past decade or so, December gives observers another reason to brave the cold: the Geminid meteors.
Continue reading

Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today








































