[/caption]
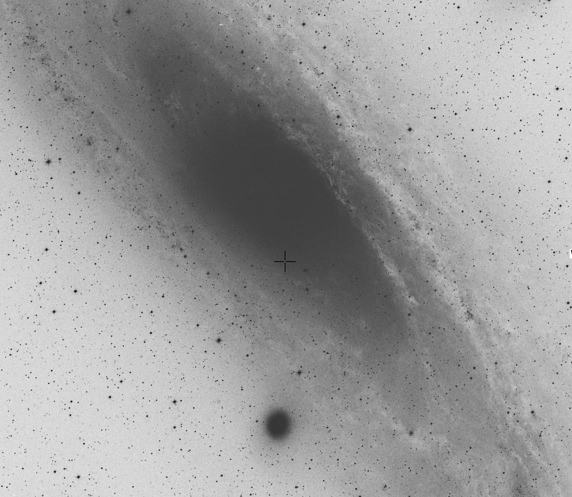
On December 11, 1923, Edwin Hubble discovered a nova in the Andromeda galaxy. Novae occurring in our Milky Way’s sister galaxy have proven to be not that uncommon, as there have been over 800 novae detected in M31 in the last 100 years. Hubble’s 1923 discovery became known as M31N 1923-12c, the third nova discovered in December of 1923.
Fast forward to January 21, 2012, and another nova has been discovered in M31, already the second novae seen in January 2012. K. Nishiyama and F. Kabashima reported the discovery and it has been given the designation, PNV J00423804+4108417. A day later, a spectrum was taken with the 9.2m Hobby-Eberly Telescope using the Marcario Low-Resolution Spectrograph, confirming the new nova in M31, and that it is a member of the He/N spectroscopic class.
What’s even more interesting, however, is that the new nova likely comes from the same progenitor as Hubble’s 1923 nova!

Classical novae are a subclass of cataclysmic variable stars. They are semi-detached binary systems where an evolved, late-type star fills its Roche lobe and transfers mass to its white dwarf companion. If the mass accretion rate onto the white dwarf is sufficiently low, it allows this gas to pile up and become degenerate. Eventually, after thousands to tens of thousands of years, a thermonuclear runaway ensues in this highly pressurized layer of gas, leading to a nova eruption. These eruptions can reach an absolute magnitude as bright as about MV -10, making them among the most luminous explosions in the Universe. Their high luminosities and rates, about 50 per year in a galaxy like M31, make novae very useful to astronomers exploring the properties of close binaries in extragalactic stellar populations.
Comparing its position with the approximately 900 novae in W. Pietsch’s M31 nova catalog revealed that PNV J00423804+4108417 was located about six arc seconds from the cataloged position of M31N 1923-12c, the nova discovered by Edwin Hubble on December 11, 1923. Given that the positions of M31 novae from early photographic surveys were typically reported to a precision of only ten arc seconds, and that He/N spectra are often associated with recurrent novae, astronomers considered the possibility that M31N 1923-12c and PNV J00423804+4108417 represented two outbursts arising from the same nova progenitor. To explore this possibility further, F. Schweizer (Carnegie Observatories) located Hubble’s original plate in the Carnegie Observatories archives and performed an eyeball comparison of the position of Hubble’s nova with that of PNV J00423804+4108417, finding them to match within ~1.5″. You can see the images for yourself here.

After digitally scanning the Hubble plate and comparing the position of the nova relative to those of three nearby USNO reference stars, analysis revealed that M31N 1923-12c was located
at R.A. = 00 42 38.06; Decl. = 41 08 41.0 (J2000). Hubble’s M31N 1923-12c and this year’s PNV J00423804+4108417 are the same object!
88 years and a handful of days later, PNV J00423804+4108417 represents the second recorded outburst of the recurrent nova M31N 1923-12c. Like the telescope named for him, Hubble’s legacy to astronomy and astrophysics continues to grow to this very day. Way to go, Edwin.
This blog post adapted from Astronomer’s Telegram #3914
M31N 1923-12c is a recurrent nova in M31
Authors: A. W. Shafter (SDSU), M. J. Darnley, M. F. Bode (Liverpool JMU, UK), R. Ciardullo (PSU), F. Schweizer (Carnegie Observatories)