
According to recent statements and images from their facilities, SpaceX is making progress and will have big news for us on August 24th!
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

A meteorite recently was spotted in the Great Lakes region and could have left fragments in the area around Bancroft, Ontario.
Continue reading

The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter recently spotted a boulder that had rolled downhill inside the Antoniadi crater, very nearly landing in another, smaller crater.
Continue reading

Continue reading

A new study has shown that the building blocks of life (amino acids) may have come together more easily than we thought
Continue reading
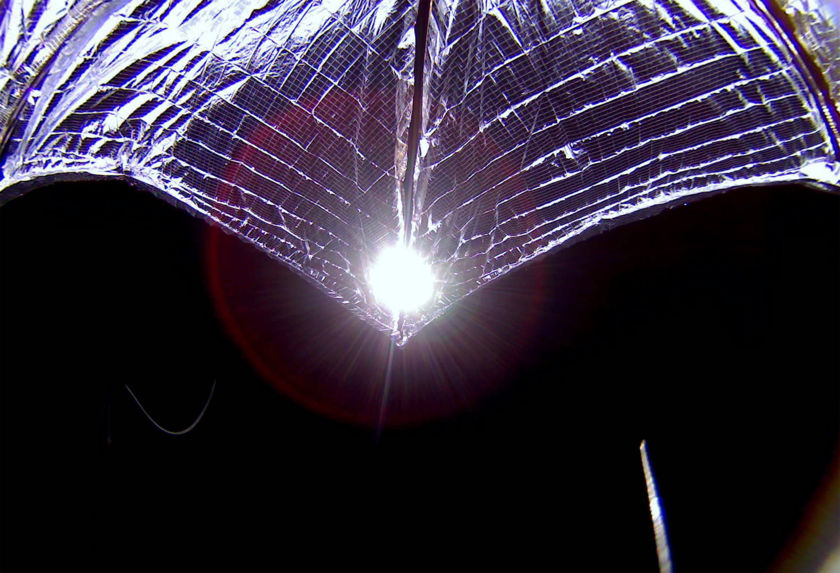

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Located in the constellation Virgo, about 63 million light-years from Earth, is the barred spiral galaxy known as Messier 91.
Continue reading
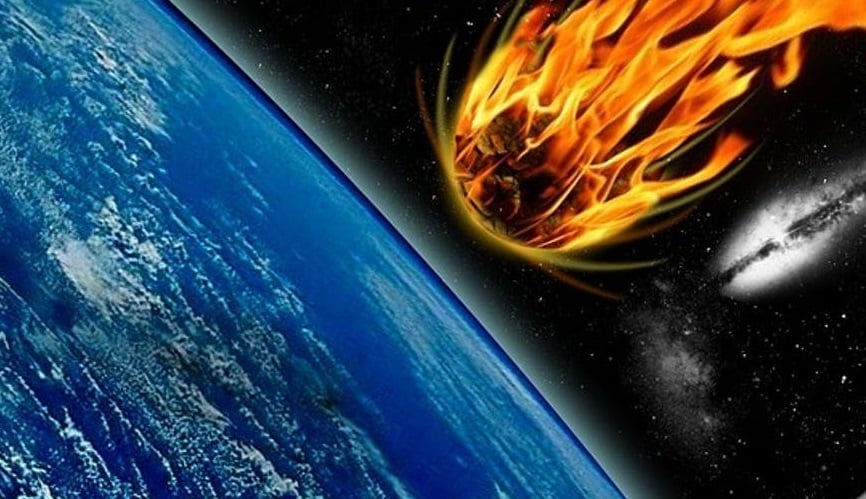

A new study reveals why many meteors, when they enter Earth's atmosphere, become cone-shaped as they heat up.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
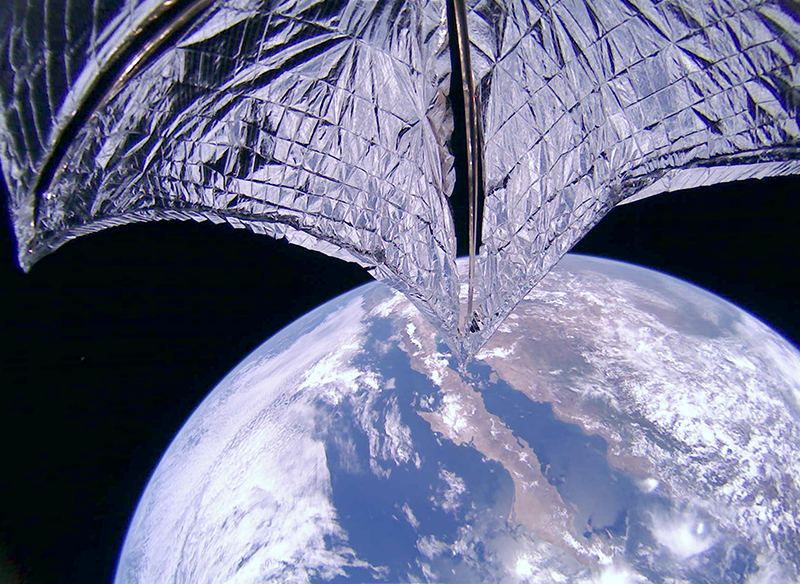

Continue reading

Last night, after multiple delays, SpaceX's Starhopper test vehicle has completed its first untethered test flight.
Continue reading

SpaceX was forced to abort its first free flight test of the Starhopper yesterday (and again today) due to fires breaking out.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

China recently successfully conducted a controlled deorbit of its second orbital laboratory, Tiangong-2.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

To mark the 50th Anniversary of the Moon Landing, VP Pence recently unveiled the the Orion capsule that will take astronauts back to the Moon in 2024.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Despite the fireball that engulfed the Starshopper this past week, both the vehicle and its Draco engine appear to be unscathed.
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

The latest discovery to come from Gaia's years of observing the Milky Way is the first 3D measurements of our galaxy's central bar structure.
Continue reading

Continue reading

SpaceX has revealed the cause of the accident that took place back in April, attributing it to a leak that took place just prior to the final tactic engine fire test.
Continue reading

A research team from the University of Glasgow has, for the first time ever, captured an image of entangled photons.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Engineers at NASA JPL are busy developing next-generation robotic missions that will allow astronauts to explore harder-to-reach places in the search for life.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Happen to be in Europe, Africa, Asia or Australia on Tuesday night with clear skies? I July weather cooperates, you'll have a good view of the final lunar eclipse for 2019.
Continue reading

Located in the Virgo constellation, roughly 50 million light years from Earth, is the elliptical galaxy known as Messier 89.
Continue reading

Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today













































