
Our Guide to Space's official page on Soviet and Russian space missions
Continue reading

Musk recently announced that SpaceX will begin deploying the first batch of its internet satellites next year and continuing until 2024.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
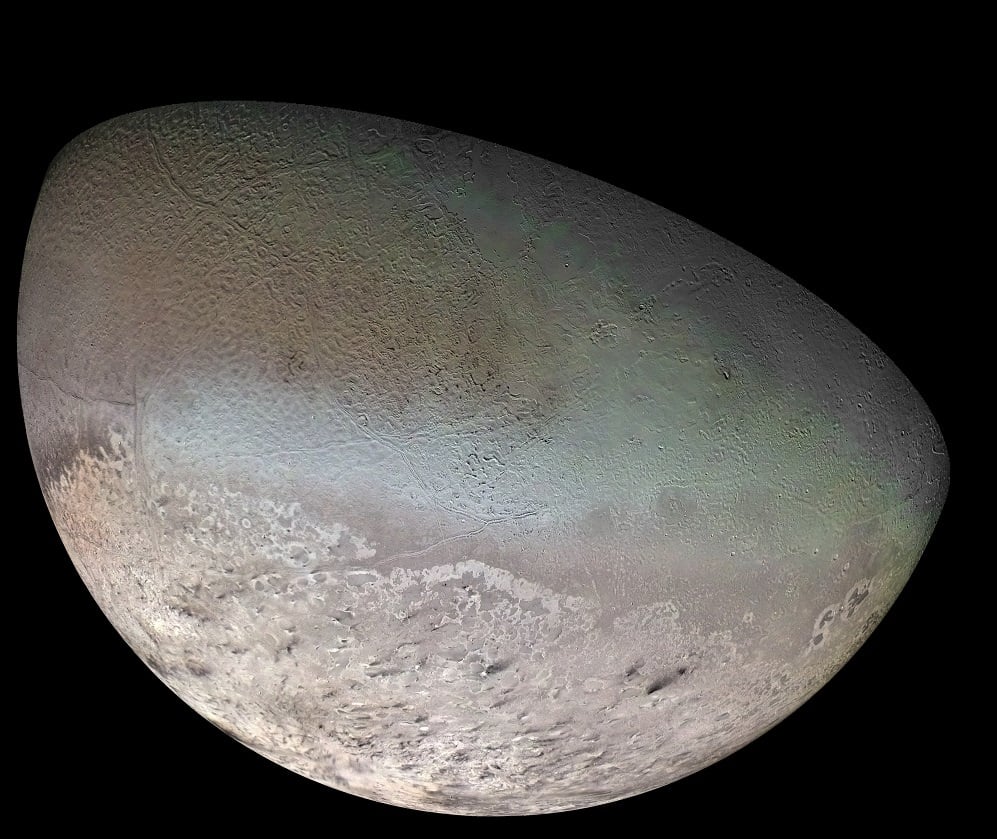
A team of researchers from NASA and the Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) recently proposed a low-cost mission to explore Neptune's largest moon, Triton.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

A new study by a team from the Carl Sagan institutes shows how life could survive the harsh radiation on neighboring exoplanets like Proxima b.
Continue reading

This week, SpaceX conducted the first commercial launch of the Falcon Heavy (and second launch overall) and managed to bring all the boosters back, and even the payload fairings!
Continue reading

A new study takes a look at where the Voyager and Pioneer probes might one day venture to as they make their way through our galaxy
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

The Curiosity rover recently witnessed eclipses involving the moons of Phobos and Deimos from the Martian surface.
Continue reading

Continue reading

A high-flying space telescope is shedding light on where some of the basic building blocks for life may have originated from. A recent study led by astronomers currently at the University of Hawaii, including collaborators from the University of California Davis, Johns-Hopkins University, the North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences, Appalachian State University, and several international partners, including funding from NASA, looked at a lingering mystery in planet formation: the chemical pathway of the element sulfur, with implications for its role in the formation of planets and life.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Located in the direction of the Hydra constellation, over 15 million light years from Earth, is the barred spiral galaxy known as Messier 83.
Continue reading
Japan's Hayabusa2 spacecraft recently struck the asteroid Ryugu with an explosive payload, which will help it collect samples that could teach us more about how the Solar System and life came to be.
Continue reading
Continue reading

A new study by an international team of scientists has tested Hawking's theory of dark matter, and ruled out that it is not likely to be made up of tiny black holes.
Continue reading

Continue reading

After a minor delay, SpaceX has conducted the first successful hop test of their Starship Hopper, a key step in validating the systems that will go into the full-scale prototype.
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

Last week, India shot down one of its own satellites with a missile. According to NASA, the resulting debris field is an "unacceptable" threat to the ISS.
Continue reading

Continue reading

A technical issue has led to the "hop test" of the miniature version of the SpaceX Starship to be delayed once more. However, the company is still on track with their overall development of the system.
Continue reading

Continue reading

It's always awe-inspiring to see the clockwork motion of the heavens, transpire in real time. In a slow motion Universe, occultations give us the chance to see the cosmos pull off a celestial hat trick. This happen in a blink of an eye type event such as when the Moon, a planet or an asteroid winks out a distant star, or transpire as a leisurely affair as the Moon covers, then uncovers the disk of a planet.
Continue reading

Continue reading

NASA's Terra satellites recently spotted a fiery meteorite in Earth's atmosphere, which exploded above the Bering Sea.
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

SpaceX has released an impressive new image that shows its proposed Starship reentering the atmosphere of Earth.
Continue reading
Continue reading

A new study takes a look at the Fermi Paradox by considering the possibility that alien von Neumann probes could be devouring themselves.
Continue reading

Continue reading

The OSIRIS-REx mission has revealed some interesting things about the asteroid Bennu, which includes the 11 plumes it witnessed in the past 3 months.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Located in the vicinity Ursa Major constellation, roughly 12 million light years from Earth, is the starburst galaxy known as the Messier 82 (aka. the Cigar Galaxy).
Continue reading

Recent observations have revealed a pulsar that appears to have been accelerated by the very supernova explosion that created it.
Continue reading
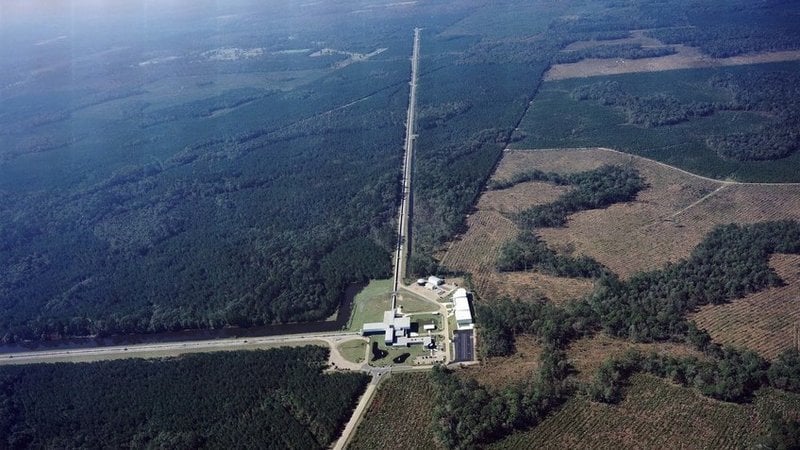

After undergoing upgrades, the LIGO observatory will be going back online this April, with "almost daily" detections of gravitational wave events expected.
Continue reading

Continue reading
Continue reading

The SIRIUS-19 experiment recently kicked off, with six cosmonauts entering a simulated lunar environment (where they will spend the next 122 days conducting experiments).
Continue reading

A new discovery in South America has added further weight to the Young Dryas Impact theory, which states that a sudden shift in its climate 12,800 years ago was due to a comet hitting Earth.
Continue reading









































