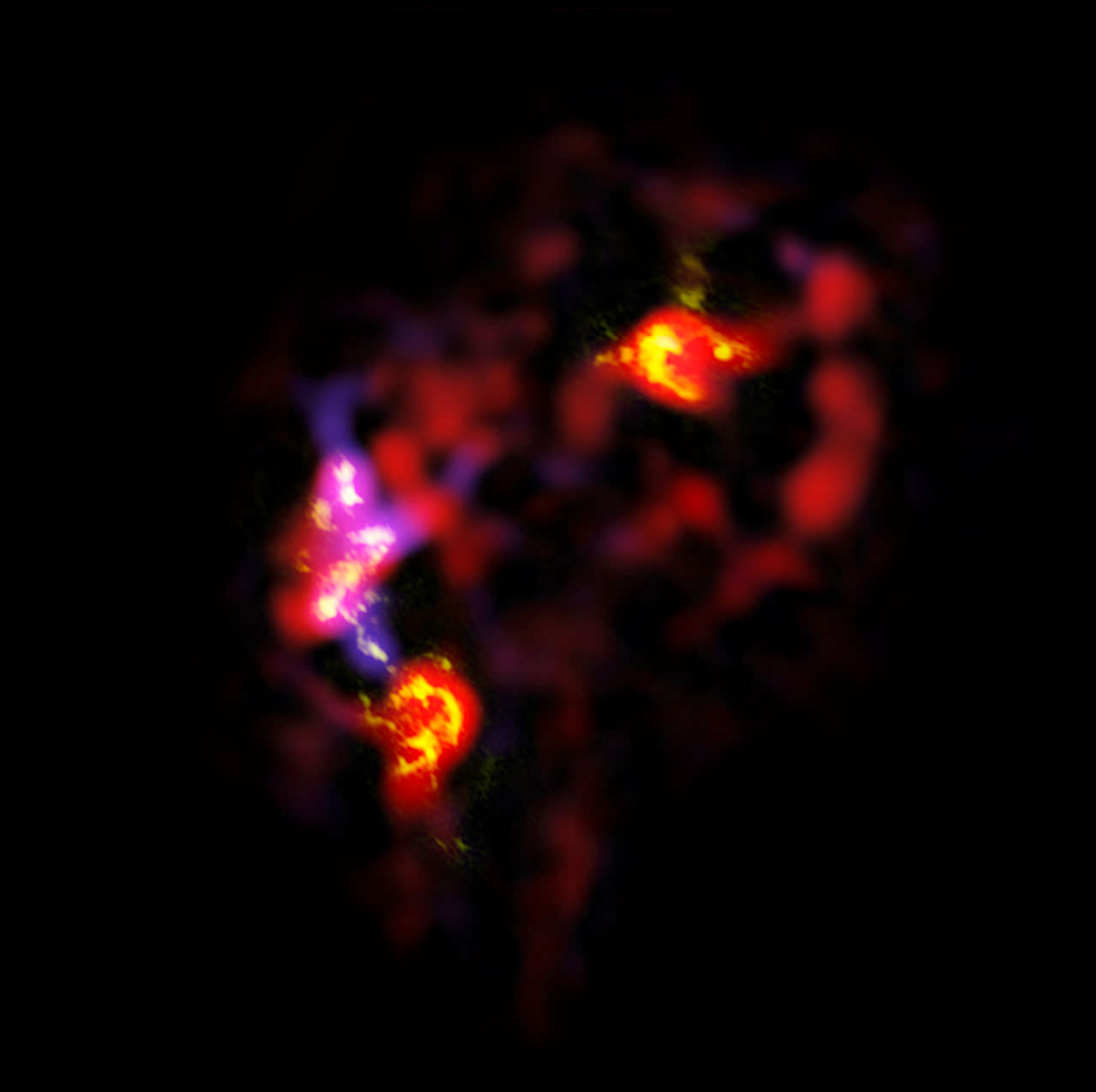
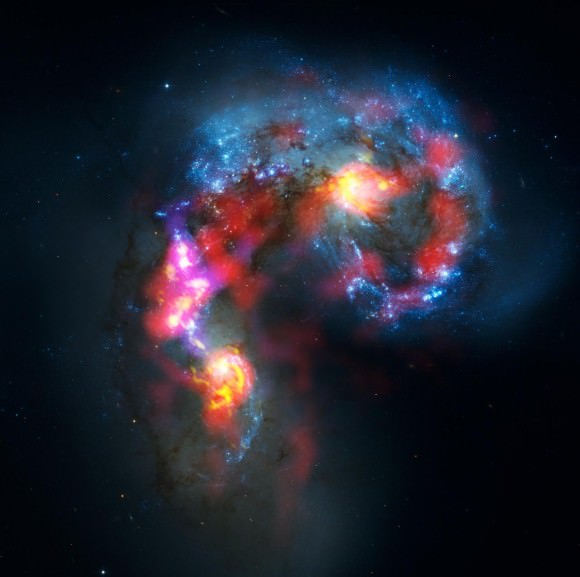
There’s a new telescope in town that just opened up for business. It’s the long awaited ALMA, the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array. Although it is still under construction, the science teams have released the first “early science” image, showing a pair of interacting galaxies called the Antenna Galaxies. ALMA’s view reveals a part of the Universe that just can’t be seen by visible-light and infrared telescopes. “From the formation of the first galaxies, stars, and planets to the merging of the first complex molecules, the science of ALMA is a vast spectrum of investigation,” said Tania Burchell, the ALMA Public Information Officer at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, on today’s 365 Days of Astronomy podcast.

Currently, about one third of ALMA’s eventual 66 radio antennas are built and operational. The antennas are positioned just 125 meters apart on the Chajnantor plateau in northern Chile. This extremely dry and high desert sits over 5,000 meters (16,500) feet above sea level. This puts ALMA higher than any other telescope array on Earth. At this elevation, the temperatures hover around freezing all year round, and the air pressure is half that at sea level. Cold temperatures combined with little air is perfect for telescopes like ALMA.
“Even in this very early phase ALMA already outperforms all other submillimetre arrays,” said Tim de Zeeuw, Director General of ESO, the European partner in ALMA. “Reaching this milestone is a tribute to the impressive efforts of the many scientists and engineers in the ALMA partner regions around the world who made it possible.”
Historically, collecting, focusing, and imaging millimeter and submillimeter waves has been very tricky, Burchell said.
“These waves are so large that mirrors cannot focus them, and their frequencies are too high for off-the-shelf receiver technologies to process,” said said. “The warmth of a telescope’s own electronics is enough to ruin the weak cosmic mm signals that, by the time they reach us, sputter in at about a billionth of a billionth the power of a cell phone call. And as an added torment, humidity itself broadcasts at these frequencies, turning most skies into a glare of millemeter/submillimeter light.”
But ALMA is radically different from visible-light and infrared telescopes. It is an array of linked antennas acting as a single giant telescope, and it detects much longer wavelengths than those of visible light. Its images therefore look quite unlike more familiar pictures of the cosmos.
Compare images of the Antenna Galaxies, from ALMA and the Very Large Telescope:

ALMA’s view reveals the clouds of dense cold gas from which new stars form. This is the best submillimeter-wavelength image ever made of the Antennae Galaxies.
Massive concentrations of gas are found not only in the hearts of the two galaxies but also in the chaotic region where they are colliding. Here, the total amount of gas is billions of times the mass of our Sun — a rich reservoir of material for future generations of stars. Observations like these open a new window on the submillimetre Universe and will be vital in helping us understand how galaxy collisions can trigger the birth of new stars. This is just one example of how ALMA reveals parts of the Universe that cannot be seen with visible-light and infrared telescopes.
Learn more about AlMA in this video:
Sources: ESO, 365 Days of Astronomy, NRAO