[/caption]
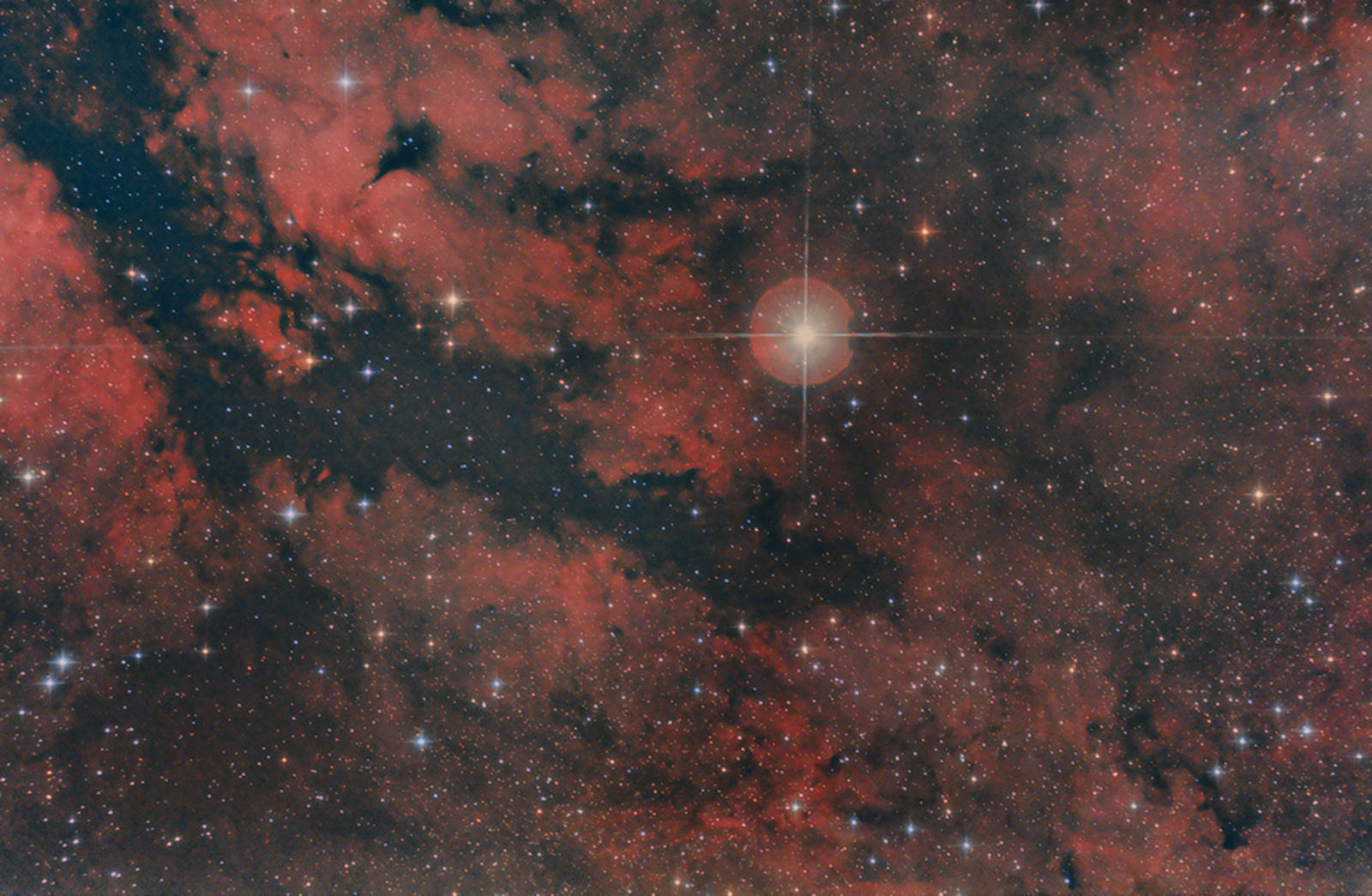
Poor sky condition is just one of the challenges astrophotographers encounter when taking a shot of astronomical bodies and events. But this did not stop Matthew Dieterich from capturing a great image of the the central region of the constellation Cygnus, also known as the Sadr Region.
“Sky conditions were very poor, high humidity and poor transparency mixed with severe light pollution caused difficult color, which is still present in this final image,” Matthew said on his website. He took the image from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
This wide-field image around the star Sadr (middle right of the image) shows the diffuse emission nebula surrounding Sadr or Gamma Cygni (also known as IC 1318). Sadr lies at an estimated distance of 1,500 light years from Earth. Throughout the image is emission nebulae (seen as the red) and dark nebulae (seen as the dark black filamentous regions).
Matthew explained that “the emission nebulae are dominated by hydrogen gas that when excited by electromagnetic radiation emits the color red. On the other hand, the dark nebulae are composed of dust and gas, which due to the density of these objects blocks the light from passing through them, so we observe them as black clouds.”
He also provided us with the camera and equipment specs he used:
Image details: 30 x 2 minutes unguided ISO 800
Mount: Astrotroniks performance tuned Atlas EQ-G
Optics: 8″ Powernewt Astrograph at F/2.8
Camera: Modified Canon Xsi
Calibration: Dark and flat frames applied in ImagesPlus
Aligned and combined in ImagesPlus with final processing in Photoshop
Want to get your astrophoto featured on Universe Today? Join our Flickr group, post in our Forum or send us your images by email (this means you’re giving us permission to post them). Please explain what’s in the picture, when you took it, the equipment you used, etc.