As we’ve recently learned, the ATLAS3D project was able to study 260 individual galaxies and do some very amazing things. By imaging in both red and blue shift, astronomers were able to take stellar measurements and give us a clear picture of galaxy rotation. But looking at a computer generated image gives a picture just like you reading the text in this article – no dimension. By superimposing the velocity of the stars over the plane of the image, a new breakthrough in simulation can be made. And it’s coming straight on for you… Continue reading “3D Galaxies – Coming Straight On For You”
A Glitch in Pulsar J1718-3718
[/caption]
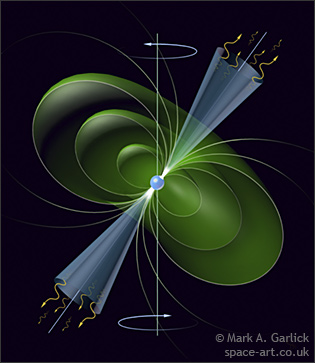
Pulsars are noted as being some of the universe’s best clocks. Their highly magnetized nature gives rise to beams of high energy radiation that sweep out across the universe. If these beams pass Earth, they can rival atomic clocks in their precision. So precise are these timings, that the first extrasolar planet was discovered through the effects it had on this heartbeat. But in September of 2007, pulsar J1718-3719 appears to have had a seizure.
These disjunctions aren’t unprecedented. While not exactly frequent, such “glitches” have been noted previously in other pulsars and magnetars. These glitches are often displayed as a sudden change in the period of the pulsar suddenly drops and then slowly relaxes back to the pre-glitch value at a characteristic rate dependent on the previous value as well as how large the jump was. Behavior like this has been seen in other pulsars including PSR B2334+61 and PSR 1048-5397.
The size of a glitch is measured as a ratio of the change in speed due to the glitch as compared to that of the pre-glitch speed. For past glitches, these have generally been changes that are around a hundredth of a percent. While this may not sound like a large change, the stars on which they act are exceptionally dense neutron stars. As such, even a small change in rotational energy means a large amount of energy involved.
Previously, the largest known glitch was 20.5 x 10-6 for PSR B2334+61. The new glitch in PSR J1718-3718 beats this record with a frequency change of 33.25 x 10-6. Aside from being a record setter, this new glitch does not appear to be following the trend of returning to previous values. The changed period persisted for the 700 days astronomers at the Australia Telescope National Facility observed it. Pulsars tend to have a slow braking applied to them due to a difference between their rotational axes and their magnetic ones. This too generally returns to a standard value for a given pulsar following a glitch, but PSR J1718-3718 defied expectations here as well, having a persistently higher braking effect which has continued to increase.
Currently, astronomers know precious little about the effects which may cause these glitches. There is no evidence to suggest that the phenomenon is something external to the body itself. Instead, astronomers suspect that there are occasional alignments of the stars internal superfluid core which rotates more quickly, with the star’s crust that cause the two to occasionally lock together. Models of neutron stars have had some success at reproducing this odd behavior, but none have suggested an event like PSR J1718-3718. Instead, the authors of the recent study suggest that this may have been caused by a fracturing of the crust of the neutron star or some yet unknown internal reaction. The possibilities currently are not well constrained but studying future events like these will help astronomers refine their models.
Magnetic Ropes Skip To Solar Storms
[/caption]
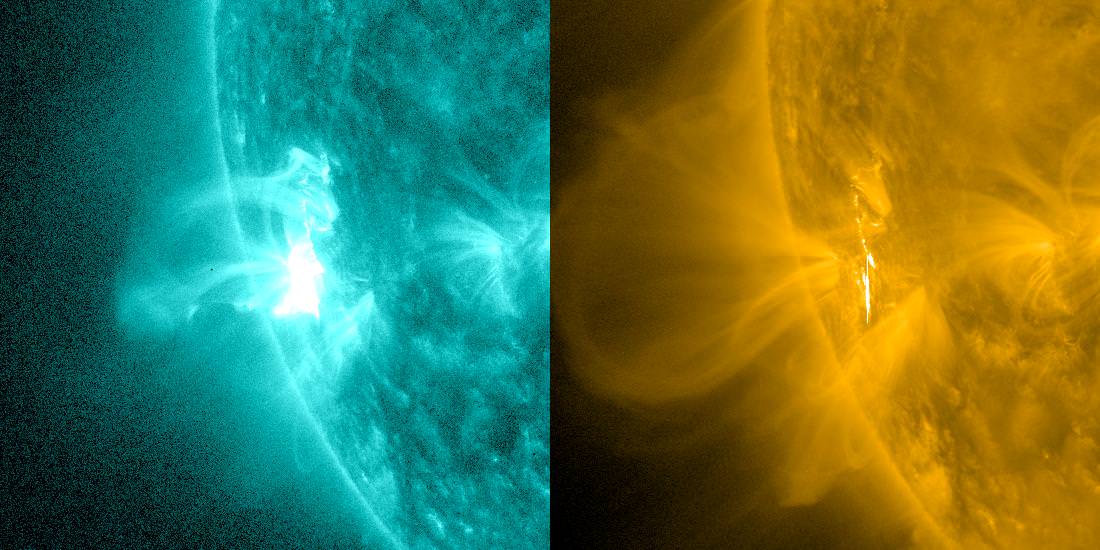
It is our current understanding that the Sun’s magnetic fields and field lines are the cause of solar storms. However, there is no solid evidence as to what form magnetic field lines may take ahead of an energetic outbreak. We know there can be loops connected to the surface – but normally they take the sting off an eruption, rather than cause one. Thanks to a discovery made by associate professor Jie Zhang and his graduate student Xin Cheng using images from the NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) spacecraft, we’re shedding a little light on a solar mystery.
An event called a magnetic rope is assumed to be the progenitor of solar storms – but its existence was far from certain. The phenomena may consist of many magnetic field lines wrapping around a center axis – possibly twisting around each other – and producing an electric current. The current might then be able to generate enough electromagnetic force to overpower the withholding magnetic field lines and cause the rope to move outward at speeds we so far haven’t been able to document… Until now.
Thanks to the images taken by the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) telescope on board the SDO, Zhang was able to isolate an area of the Sun where a magnetic rope was forming. What the images provided was a unique look at an active region ahead of an eruption. Revealed was a long and low-lying channel which produces temperatures up to 10 million degrees – and continues heating. When it reaches a critical point this “hot channel” reveals a never before seen feature unlike the surrounding magnetic field lines… possibly the theoretical magnetic rope.
“The magnetic rope triggers a solar eruption. Scientists have been debating whether or not this magnetic rope exists before a solar eruption. I believe that the result of this excellent observation helps finally solve this controversial issue,” says Zhang.
As we’re all aware, it would be a boost to understand and predict solar storms. While our Earth’s “magnetic shield” protects us from the majority of direct exposure, we have satellites, astronauts and terrestrially-based power sources which could benefit from an early warning scenario.
“Understanding the eruption process of these storms will definitely help us better predict them,” says Zhang. “We cannot prevent solar storms, just like we cannot prevent earthquakes or volcanoes. But the development of prediction capacity can help mitigate adverse effects. For instance, satellite operators can power-down key systems to prevent the possible damage to the systems.”
Original Story Source: MSNBC.
Space Junk Forces ISS Crew to Takes Shelter in Soyuz

[/caption]
The six crewmembers on board the International Space Station were told to take shelter in the two Russian Soyuz spacecraft early Tuesday because Space Command predicted a piece of space junk could make a close approach to the station. Radar tracking indicated the debris would make its close pass at 8:08 a.m. EDT (12:08 UTC), coming within about 243 meters (800 feet) of the station and well within the “pizza box” -shaped area around the ISS, but when no impact was detected the crew was told they could reenter the station and resume normal operations.
NASA’s Chief Scientist for Orbital Debris Nicholas L. Johnson told Universe Today during a previous “conjuction” of space debris and the ISS that on average, close approaches to ISS occur about three times a month. An approach of debris is considered “close” only when it enters an imaginary “pizza box” shaped region around the station, measuring 0.75 kilometers above and below the station and 25 kilometers on each side( 2,460 feet above and below and 15.6 by 15.6 miles).
Johnson said that small pieces of debris have already collided with ISS on many occasions, but these debris to date have not affected the safety of the crew or the operation of the mission. “The dedicated debris shields on ISS can withstand particles as large as 1 cm in diameter,” he said.
The piece of space junk was detected too late for the station to perform an evasive maneuver, so the crew was told to “shelter in place” on the two Soyuz spacecrafts. The crew on board is commander Andrey Borisenko, Alexander Samokutyaev and Ronald Garan, who took shelter aboard the Soyuz TMA-21 spacecraft docked to the Poisk module, and Sergei Volkov, Michael Fossum and Furukawa who went on to the Soyuz TMA-02M spacecraft docked to the Rassvet module.
Satellite Looks Down the Eye of Erupting Nabro Volcano
[/caption]
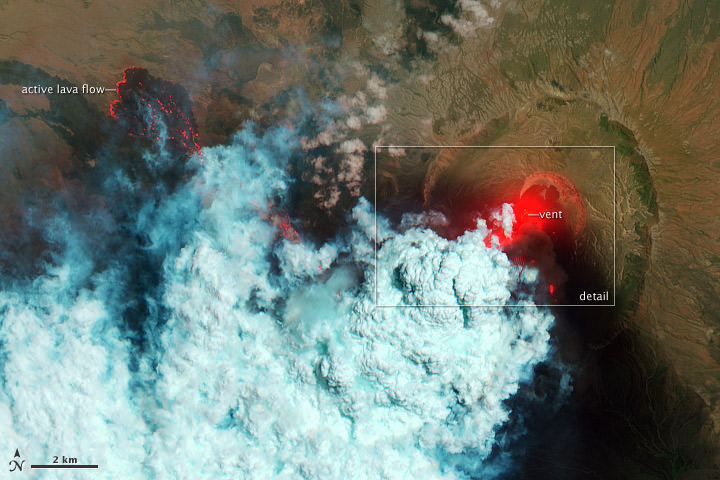
Wow! What an amazing and detailed top-down view of an active volcano! This is the Nabro Volcano, which has been erupting since June 12, 2011. It sits in an isolated region on the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia and satellite remote sensing is currently the only reliable way to monitor the ongoing eruption, according to the NASA Earth Observatory website. The bright red portions of the false-color image (above) indicate hot surfaces. See below for a zoomed-in look. Both images were taken by the Advanced Land Imager (ALI) aboard the Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite.

Robert Simmon of the NASA Earth Observatory website describes the scenes:
Hot volcanic ash glows above the vent, located in the center of Nabro’s caldera. To the west of the vent, portions of an active lava flow (particularly the front of the flow) are also hot. The speckled pattern on upstream portions of the flow are likely due to the cool, hardened crust splitting and exposing fluid lava as the flow advances. The bulbous blue-white cloud near the vent is likely composed largely of escaping water vapor that condensed as the plume rose and cooled. The whispy, cyan clouds above the lava flow are evidence of degassing from the lava.
The natural-color image (lower) shows a close-up view of the volcanic plume and eruption site. A dark ash plume rises directly above the vent, and a short, inactive (cool) lava flow partially fills the crater to the north. A gas plume, rich in water and sulfur dioxide (which contributes a blue tint to the edges of the plume) obscures the upper reaches of the active lava flow. Black ash covers the landscape south and west of Nabro.
Limited reports from the region say that at least 3,500 people and up to 9,000 that have been affected by the eruption, with at least 7 deaths caused by the erupting volcano. The ash plume has also disrupted flights in the region.
For more information see NASA’s Earth Observatory website, and BigThink
Burt Rutan’s Race To Space: A Primer For Things To Come

[/caption]
Voyager, Proteus and SpaceShipOne have become aerospace legends. As has the man who established them all – Burt Rutan. Zenith Press has released a chronicle of the man and his machines entitled Burt Rutan’s Race to Space: The Magician of Mojave and His Flying Innovations. The book provides a chronicle of all the air and spacecraft that have soared off of Rutan’s blueprints and into reality.
The book’s first main segment is a large section which is essentially a catalog of the numerous craft that Rutan has produced over the decades. Many of the flying machines have their unique characteristics highlighted within the 160 pages of this book. Fear not, this tome is wallpapered with images – most of which are color (175 color images to 55 black and white).
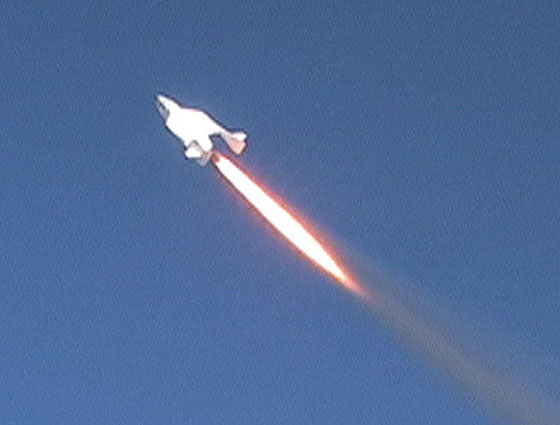

Some of the most interesting of these images are not the glossy stills of air or spacecraft in action but rather the simple drawings that are done by the man himself. These sketches, some little more than cartoons others just simplistic line-drawings, highlight the genius that is Rutan and provide an insight into how his mind works.
The nature of the book changes somewhat when one reaches the chapter entitled, “The Scaled Composites Years.” From this point on, the book’s focus narrows to concentrate on Rutan’s X-PRIZE efforts – and beyond.

The book was written by Dan Linehan and is his second detailing the efforts of Rutan and Scaled Composites (the first was SpaceShipOne: An Illustrated History). In short, the freelance writer is steeped in all things Rutan. Whereas his first work on the subject covered the history-making flight of SpaceShipOne, this effort is a general overview of Rutan and his legacy. But be forewarned, there are many projects that span the entire realm of aerospace that Rutan and company have been involved with that might surprise you.
Given that the Mojave “magician” has retired recently – this book is timely, enjoyable and acts as a wonderful window into the mind of the man that has revolutionized flight. SpaceShipTwo continues to successfully complete test after test – making Burt Rutan’s Race to Space a primer for things to come. The book retails for $30, and it is well-worth the price and will be a welcome addition to any space buff’s collection.

Close Approach: Images and Animations of Asteroid 2011 MD
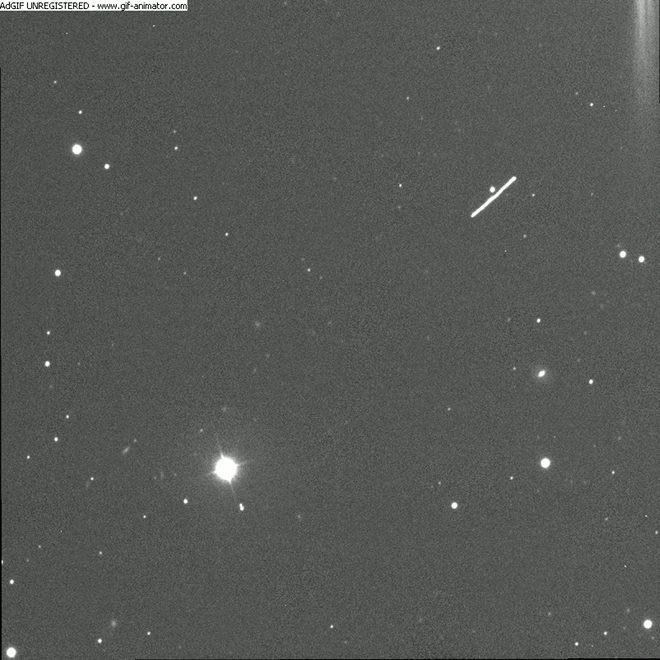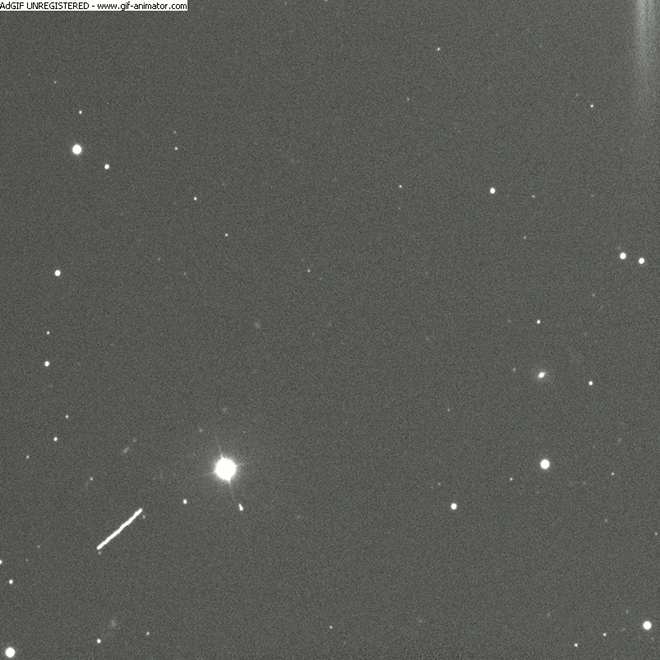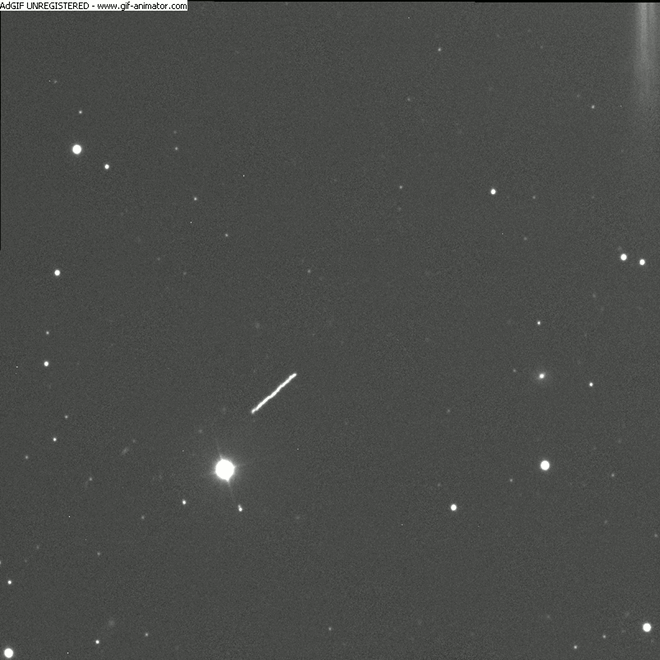
[/caption]
Today, Monday June 27 at about 17:00 UT, asteroid designated as 2011 MD will pass only 12,300 kilometers (7,600 miles) above the Earth’s surface. Here are some images and an animation of the asteroid’s close approach taken around 09:30 UT taken by Ernesto Guido, Nick Howes and Giovanni Sostero at the Faulkes Telescope South through a 2.0-m f/10.0 Ritchey-Chretien and a CCD. The trio of astronomers say that at the time these images were taken, the asteroid had a magnitude of about 14.5. At the moment of its close approach, 2011 MD will be bright as magnitude ~11.8.
The animation above shows the object’s movement in the sky. Each image was 20-second exposure.
See more below from Guido, Howes and Sostero.
Below is a single 20-second exposure also taken by the 2 meter telescope at Faulkes Telescope South, and just below that is another image using a RGB filter.
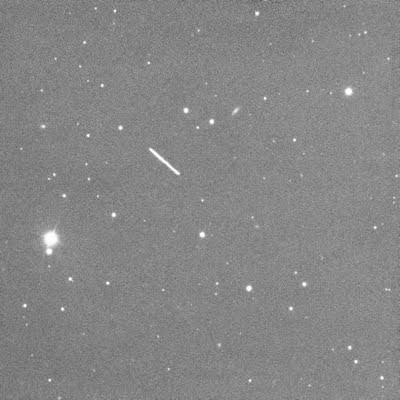
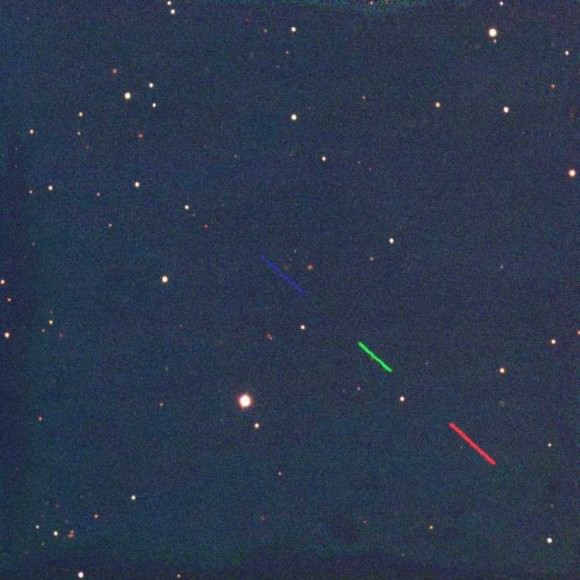


Some early observers have suggested that 2011 MD — which is only 5-20 meters in diameter — could possibly be a piece of space junk, such as a rocket booster. However, additional observations and further calculations show that this asteroid could not have been close enough to Earth any time during the space age to have started off as a rocket booster.
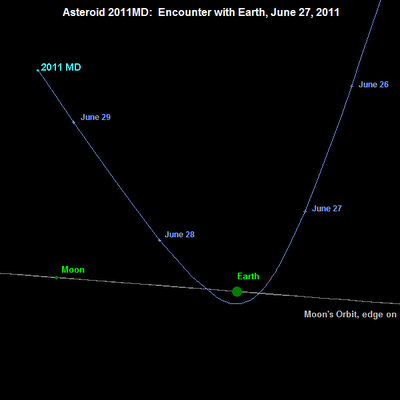
Thanks to Ernesto Guido, Nick Howes and Giovanni Sostero for sharing their image with Universe Today. See more of their work, as well as more information about asteroid 2011 MD at their Remanzacco Observatory website. See here for more information on the Faulkes Telescope.
Again, scientists at NASA’s Asteroid Watch program at JPL say there is no danger of the asteroid hitting Earth. “There is no chance that 2011 MD will hit Earth but scientists will use the close pass as opportunity to study it w/ radar observations,” they said on the the @AsteriodWatch Twitter feed. “Asteroid 2011 MD measures about 10 meters. Stony asteroids less than 25 m would break up in Earth’s atmosphere and not cause ground damage.”
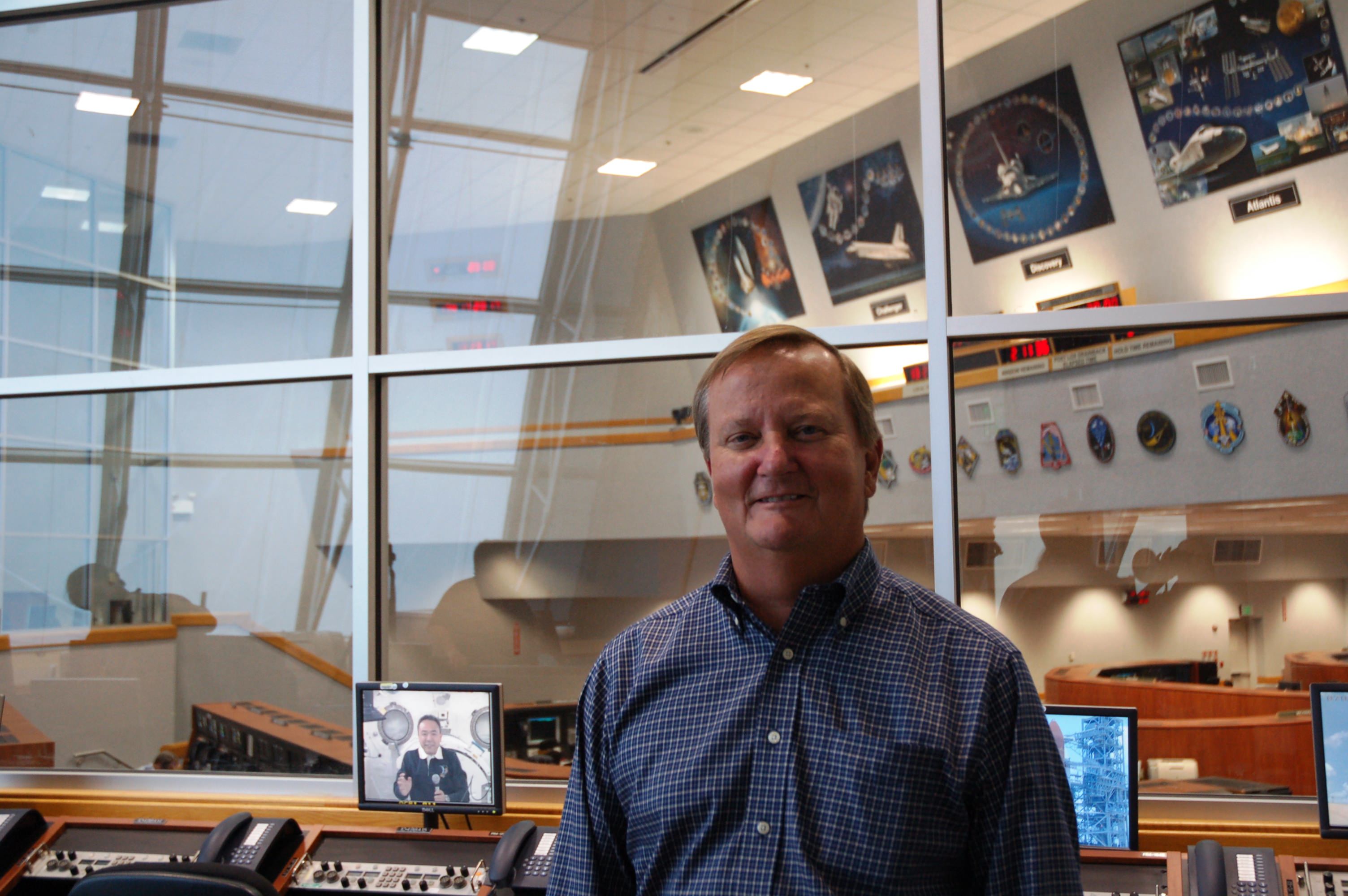
End of the Shuttle Era: Q & A With Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach

[/caption]
CAPE CANAVERAL Fla. – He has been with the shuttle program for the past three decades and has witnessed both its tragedies and its triumphs. NASA’s Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach reflected on the end of the shuttle era when interviewed this week. He talked a bit about his plans for the future as well as what he thinks people can expect from both him and his team on launch day.
Q: The Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for STS-135 has just wrapped up, is this is a period of accelerated work for you and your team or is this a time when you can catch your breath?
Leinbach: “This TCDT was a little different; we had a very busy period getting the crew
ready for this mission. On July 4 we’ll have a bit of a break and then things
will pick right back up again as we get ready for launch.”
Q: What do you think you will be feeling when that final launch occurs?
Leinbach: “I don’t know, I mean I have thought a lot about this…I don’t know what it’s
going to be like. For the last flight of Discovery we had one more launch for
both Endeavour and Atlantis, well now this really and truly the last flight of
the shuttle program… so it’s going to be a very reflective time.”

Q: Do you think anything will be special about this mission?
Leinbach: “The launch itself will be very much any other launch. When the guy’s are
working on the consoles they are very serious about what they are doing.
They won’t be distracted by the fact that it is the last one.
Q: Speaking of your job – it keeps you very busy, have you had any time to reflect?
Leinbach: “For the moment I still have a lot to do concluding TCDT, but this Saturday I
am planning on driving out to the launch pad and just looking up at Atlantis
and just soaking it all in, all by myself.”
Leinbach started working for NASA as a structural engineer in 1984, his words are softly spoken which tends to lend them even more weight. His first mission as launch director was STS-114. This was the first shuttle launch after the loss of the space shuttle Columbia in 2003. Leinbach led the recovery team searching for Columbia’s debris in Texas. A year later in 2004 Leinbach was awarded the Presidential Rank Award, which is given in recognition of long-term accomplishments.
Atlantis will carry the four person crew of STS-135 to the International Space Station on a resupply flight designed to keep the orbiting outpost well stocked after the shuttles are decommissioned. The mission is scheduled to last twelve days, launching on July 8 at 11:26 a.m. EDT. The crew consists of Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim.

Final Shuttle Voyagers Conduct Countdown Practice at Florida Launch Pad

[/caption]
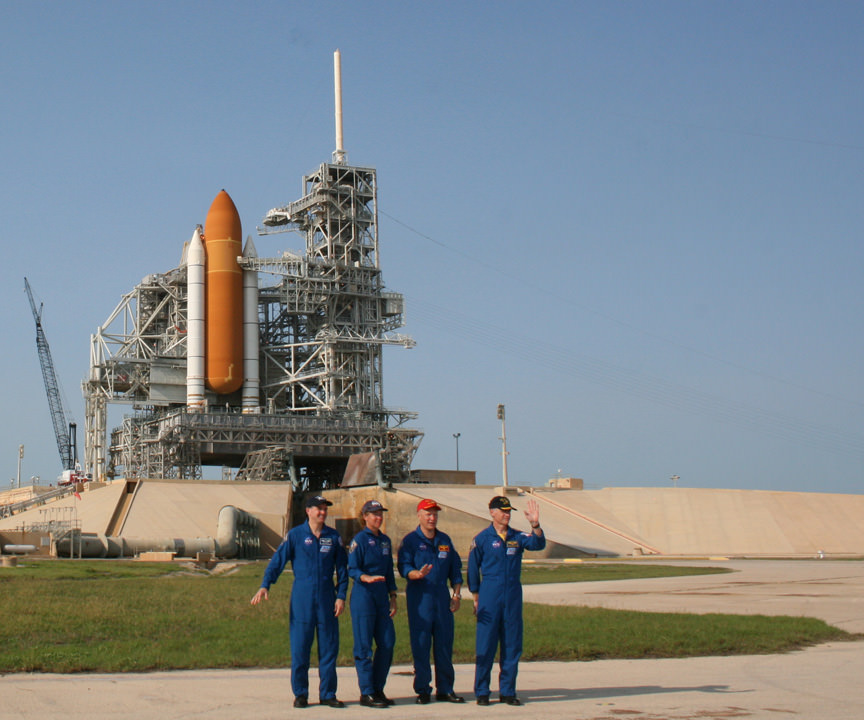
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER – The “Final Four” shuttle astronauts who will ever voyage to Earth orbit aboard a NASA Space Shuttle Orbiter jetted into the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) this week for their final simulated countdown training at the seaside Florida Launch Pad.
The all veteran crew for the STS-135 mission arrived at Kennedy’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) on twin T-38 jets for four days of comprehensive flight training for what’s known as the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). Along with all other shuttle flight related activities, it’s the very last time this training will ever occur.
The TCDT is part of the ritual of training for all shuttle crews that takes place in the last few weeks preceding a liftoff and that concludes with a full countdown dress rehearsal from inside Atlantis at the launch pad.

Chris Ferguson is leading the STS-135 mission and he will be recorded in history as the final Space Shuttle Commander. This will be Ferguson’s third shuttle flight and second one as Commander. Also aboard are Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim.
The quartet of space flyers are due to blast off aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on July 8 at 11:26 a.m. EDT for the “Grand Finale” of NASA’s thirty year old Space Shuttle Program. If all goes according to plan the end of the Shuttle Era is less than 1 month away.
It’s a bittersweet moment for everyone working on the shuttle program. Proud to be part of a magnificent adventure with the most complicated machine ever built by humans, but simultaneously sad that the program is ending well before its true flight time is up and with no concrete timetable to replace the trio of majestic spaceships.
“We are incredibly proud to represent this, the final flight,” said STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson after touchdown to dozens and dozens of journalists gathered at the shuttle landing strip to greet the astronauts.
“I speak on behalf of the crew, everyone in the astronaut office, and I’m sure everybody here at KSC in saying that we are just trying to savor the moment,” Ferguson added. “As our children and our children’s children ask us, we want to be able to say, ‘We remember when there was a space shuttle.”
The first order of business for Ferguson and Hurley was to practice shuttle landings in the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA), which is a modified Gulfstream II jet.
During the TCDT period, the crew engaged in mission briefings at the Launch Control Center which is the brain of shuttle launch operations, payload familiarization and training at the Space Station Processing Facility, fire suppression training, range safety and security briefings and emergency escape training in an M113 armored personnel carrier near Launch Pad 39A. Read more in my upcoming features.
On the last day of TCDT, the astronauts donned their orange launch and entry suits, journeyed to the pad in the Astrovan and were strapped to their assigned seated inside the orbiter exactly as will occur on launch day for a full dress rehearsal of the launch countdown.
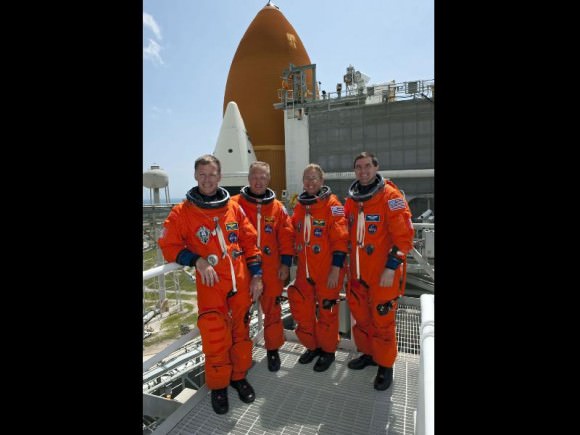

The crew also met with over 100 reporters for a Q & A session at the base of Launch Pad 39A which was back dropped by a thrilling view of Shuttle Atlantis atop the Mobile Launch Platform and the gigantic Flame Duct which directs the rocket exhaust way from the shuttle stack during launch.
“We’re very honored to be in this position,” Ferguson said to reporters at the foot of the pad. “There are many people who could be here. When the dice fell our names were facing up. We consider ourselves fortunate and lucky.”
“I think each of us feels a little extra burden to make sure we put on the best possible face forward for the last go around of this. The crew’s very prepared and we’re going to do a fantastic job.”
“I don’t think that the full magnitude of the moment will really hit us until the wheels have stopped on the runway,” said Ferguson, reflecting on the significance of the grand finale of all shuttle missions. “I’m not sure words will really be able to capture for the crew and for the entire shuttle workforce just how much the shuttle program has meant to us for the last 30 years.”
“TDCT is very comprehensive, hands on and invaluable training at the place you’re going to do it,” said Hurley. “Everything is a just a little bit different when you are in the real vehicle so this is a great way to get you ready for launch day – when it counts!”
Tucked inside Atlantis cargo bay is the Italian- built “Raffaello” logistics module, the primary payload. Raffaello is loaded full with some five tons of critical spare parts, crew supplies and science experiments that will be delivered to the International Space Station (ISS) during the 12 day flight.
The secondary payload is the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) which will demonstrate tools and techniques to refuel satellites in orbit.

“Sandy Magnus is our ‘transfer czar’ in charge of emptying and filling Raffaello,” said Ferguson. Magnus is an ideal choice for the mission since she lived for months aboard the orbiting outpost and is familiar with its nook and crannies.
“We feel very honored to be on this flight and are very focused to perform it well,” said Magnus. “We are just the tip of the iceberg of a huge group of people who plan and get the hardware ready and prepare all our procedures.”
“I often think about how we will launch from the exact same launch pad that Apollo 11 launched at to go to the moon. It gives you goose bumps,” said Walheim.

Watch the TDCT Launch Pad press conference here:
Read my prior features about the Final Shuttle mission, STS-135, here:
Final Payload for Final Shuttle Flight Delivered to the Launch Pad
Last Ever Shuttle Journeys out to the Launch Pad; Photo Gallery
Atlantis Goes Vertical for the Last Time
Atlantis Rolls to Vehicle Assembly Building with Final Space Shuttle Crew for July 8 Blastoff
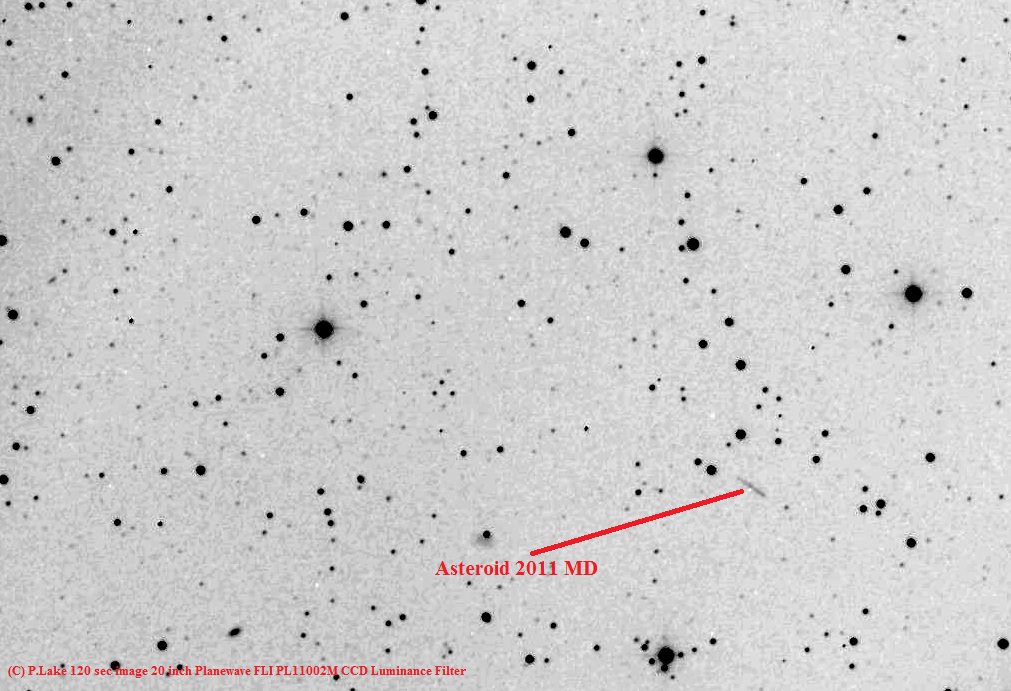
Getting Closer: Images, Video of Asteroid 2011 MD
[/caption]
Accomplished amateur astronomer and blogger Peter Lake, a.k.a “AstroSwanny” from Australia captured some of the first images of what will be a very close pass of Earth by asteroid 2011 MD. He actually took the image at 07:00 UTC on June 26th with a 20 inch telescope in New Mexico controlled via his iPhone, through the Global Rent-A-Scope program. Ahh, the wonders of technology! As Peter says, “Its not every day, that an asteroid misses by less than 3-5 earth Radii.”
The asteroid, which was only detected last week, is about 25 to 55 feet (8 to 18 m) across, is expected to pass less than 8,000 miles above Earth’s surface around 1 p.m. EDT (17:00 UT) on Monday, June 27th. The time of closest approach will be observable from South Africa and parts of Antarctica, but the approach will be visible across Australia, New Zealand, southern and eastern Asia, and the western Pacific.
Below is a video he compiled of the his observations of the pass, and used ten 120-second images for the video.
Peter also noted that “Its close approach is being followed with great interest, more for honing the skills and techniques of the Minor Planet Center and the network of asteroid hunting astronomers, rather than because it poses any real danger.”
Thanks to Peter and his Aartscope Blog for sharing these views with Universe Today.