
For the first time in history, Einstein's theory of General Relativity was confirmed by observing a star orbiting the supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy
Continue reading

Continue reading

Comets are one of those great question marks in observational astronomy. Though we can plot their orbits thanks to Newton and Kepler, just how bright they'll be and whether or not they will fizzle or fade is always a big unknown, especially if they're a dynamic newcomer from the outer solar system just visiting the inner solar system for the first time.
We had just such a surprise from a cosmic visitor over the past few weeks, as comet C/2017 S3 PanSTARRS erupted twice, brightening into binocular visibility.
Continue reading

The Hubble Space Telescope took advantage of the fact that both Saturn and Mars are at opposition this summer and snapped some of the clearest and most beautiful images of them yet.
Continue reading

A new study led by NASA's Ames Research Center has indicated that microorganisms are not likely to survive in Mars' dry environment, but could be preserved there.
Continue reading

Using 13 years of data obtained by Cassini's Visual and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS), the Cassini imaging team has produced some of the most detailed images of Titan to date.
Continue reading

According to a new study by a European team, the Moon may have been habitable during two periods in the past.
Continue reading

A new analysis of 15 years of data from the Mars Express probe by a team of Italian scientists shows compelling evidence for their being liquid water beneath Mars southern polar region.
Continue reading

According to a new study by a team from the University of Michigan, Andromeda survived a merger with a massive galaxy 2 billion years ago.
Continue reading

One of the top astronomy events of 2018 occurs on the evening of Friday, July 27th, when the Moon enters the shadow of the Earth for a total lunar eclipse. In the vernacular that is the modern internet, this is what's becoming popular as a "Blood Moon," a time when the Moon reddens due to the refracted light of a thousand sunsets falling on it as the pass through the ruddy limb of the Earth.
Continue reading

Thanks to a new study led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, future missions to Europa will be more likely to find spots in the moon's ice sheet where biosignatures still exist.
Continue reading
Continue reading

Using advanced adaptive optics, the ESO's Very Large Telescope was able to capture pictures of Neptune, star clusters and other objects with even greater clarity than Hubble
Continue reading

The ESA recently released stunning photos of a Martian storm front, which were acquired by the Mars Express orbiter in April of 2018.
Continue reading

A new study led by Scott S. Sheppard has discovered 12 more moons around Jupiter, which could scientists a great deal about the history of the Solar System.
Continue reading

Continue reading

When the James Webb Space Telescope is deployed, it will study and characterize the atmospheres of gas giants, with the eventual goal of focusing on potentially-habitable exoplanets.
Continue reading

Have you been checking out Mars this season? Mars reaches opposition on July 27th at 5:00 Universal Time (UT) shining at magnitude -2.8 and appearing 24.3" across—nearly as large as it can appear, and the largest since the historic opposition of 2003. We won't have an opposition this favorable again until September 15th, 2035.
Continue reading

Using data from the Juno spacecraft, a team of scientists found a heat source on Io that could be a previously-undiscovered volcano.
Continue reading

A new study used data from both Hubble and Gaia in order to obtain the most precise measurements of cosmic expansion to date.
Continue reading

A new study by a team from NASA JPL has shown how Europa's interior ocean rises to the surface slowly over time, creating "fossil material" on the surface.
Continue reading

According to a recent study by an international team of researchers, Jupiter's moons of Io and Ganymede leave "footprints" in the planets powerful aurorae.
Continue reading

In recognition of their efforts to communicate the importance of the Cassini mission, NASA's JPL recently received an Emmy nomination for their Cassini Grande Finale campaign.
Continue reading

A new research study conducted by an international team of researchers indicates that life can survive in a variety of cold and briny environments.
Continue reading

The Kepler mission has been put into hibernation prior to downloading data from its 18th campaign and commencing its last.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Eclipse season in nigh... though most of us won't notice. The second eclipse season for 2018 commences with the arrival of New Moon and Brown Lunation number 1182 at 3:01 Universal Time on Friday, July 13th, 2018. This eclipse is a shallow partial, just skimming the southern hemisphere of the Earth between the Australian and Antarctic continents.
Continue reading

NASA is currently partnering with companies to develop technologies for dealing with garbage during long-duration space flights.
Continue reading

A new study by a team of NASA-supported researchers has shown how a giant impact could explain all of Uranus' mysteries.
Continue reading

Looking to the next-generation of telescopes, a pair of astrophysicists propose using swarm robots to conduct observations instead of relying on increasingly large and complex arrays.
Continue reading
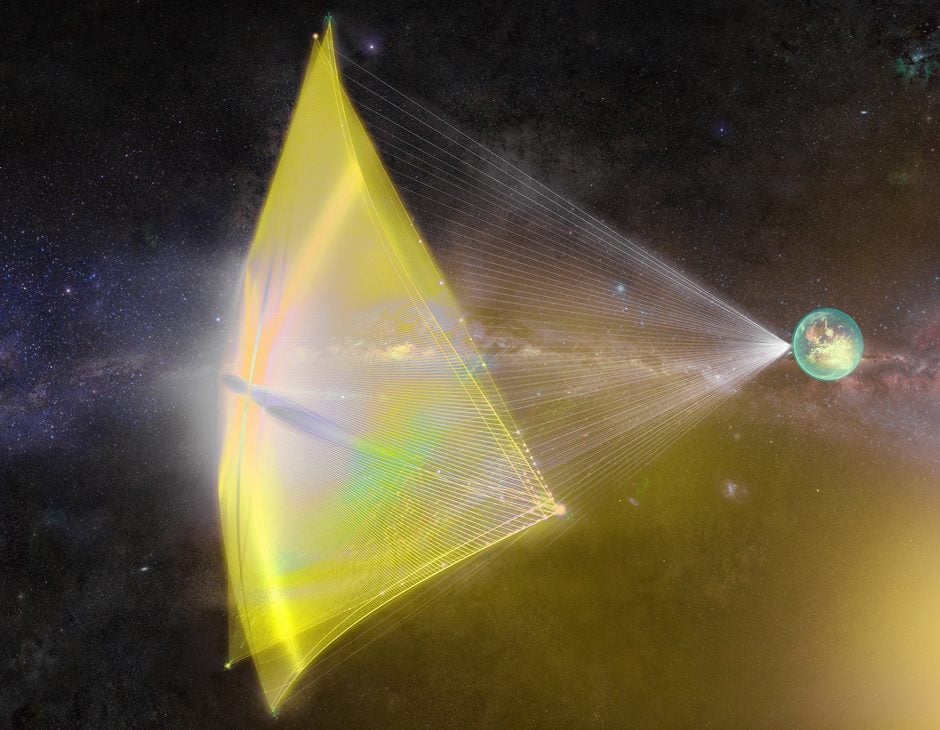
In a recent study, a pair of astrophysicists suggest that Breakthrough Starshot could also test Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity while traveling to Alpha Centauri.
Continue reading

An unusual celestial spectacle unfolds for observers around the Great Lakes region next Tuesday at dawn. The Moon has been faithfully occulting (passing in front of) the bright star Aldebaran for every lunation now since January 29th, 2015. This split second events have touched on nearly every farflung corner of the Earth. Now the United States and Canada get to see the penultimate event, as the waning crescent Moon occults Aldebaran one last time for North America.
Continue reading

Continue reading
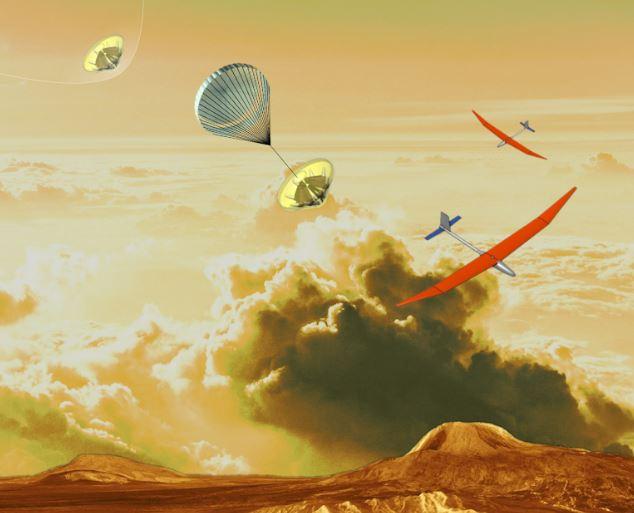

NASA recently partnered with the Boulder-based drone company Black Swift to create an unmanned aerial system to explore Venus' cloud tops for signs of life.
Continue reading
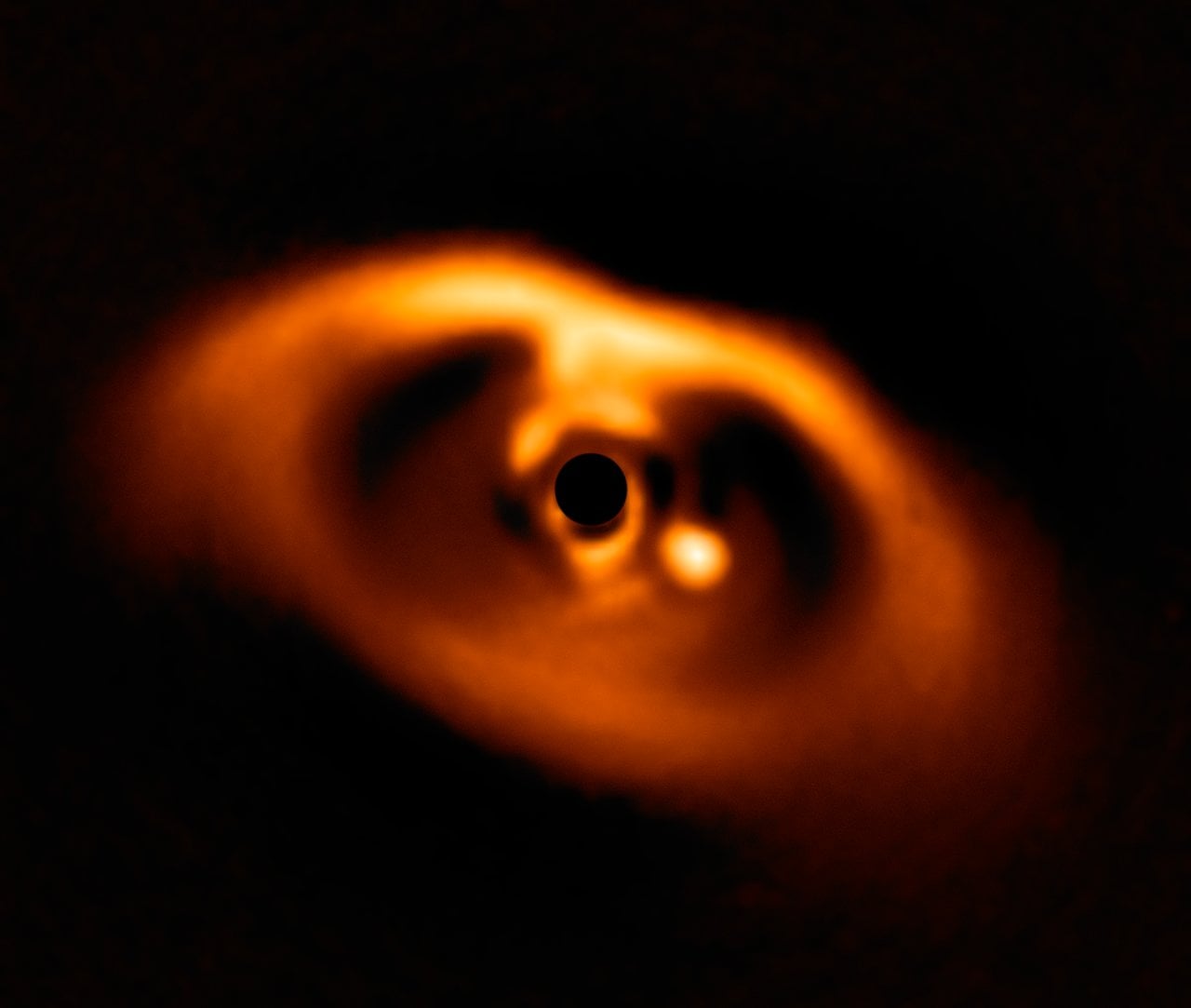
A team of international astronomers recently captured the first image of a newly-formed planet, which will allow astronomers to test models of planetary formation
Continue reading

A new study by a team of astronomers from Australia and Turkey has determined that space is filled with immense amounts of grease-like molecules.
Continue reading

Continue reading

In response to the report issued by an Independent Review Board, NASA has decided to delay the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope to 2021.
Continue reading

Using data from ground-based observatories and the Hubble space telescope, an international team of scientists found evidence that 'Oumuamua is an interstellar comet after all.
Continue reading
Continue reading

While observing a distant galaxy cluster, an image taken by Hubble was photobombed by 22 previously undetected asteroids.
Continue reading

According to the last study based on Cassini data, complex organic molecules exist within Enceladus and are being released through its plumes.
Continue reading

The RemoveDebris satellite, a spacecraft designed to remove junk from orbit, recently deployed from the ISS to begin demonstrating its capabilities.
Continue reading
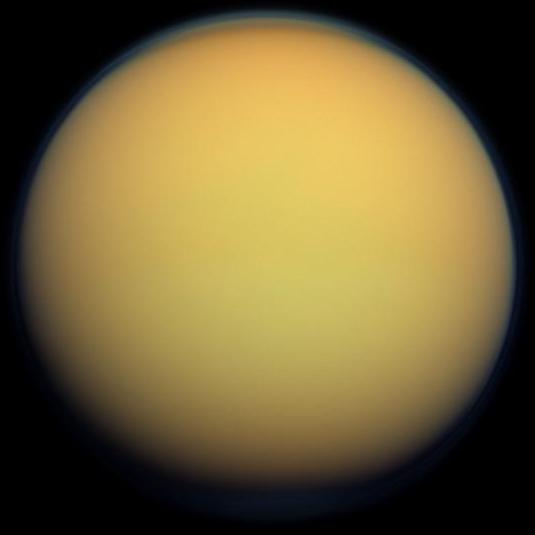

A new study led by researchers from John Hopkins University tackles the question of where Titan's mysterious sand dunes come from.
Continue reading

Continue reading
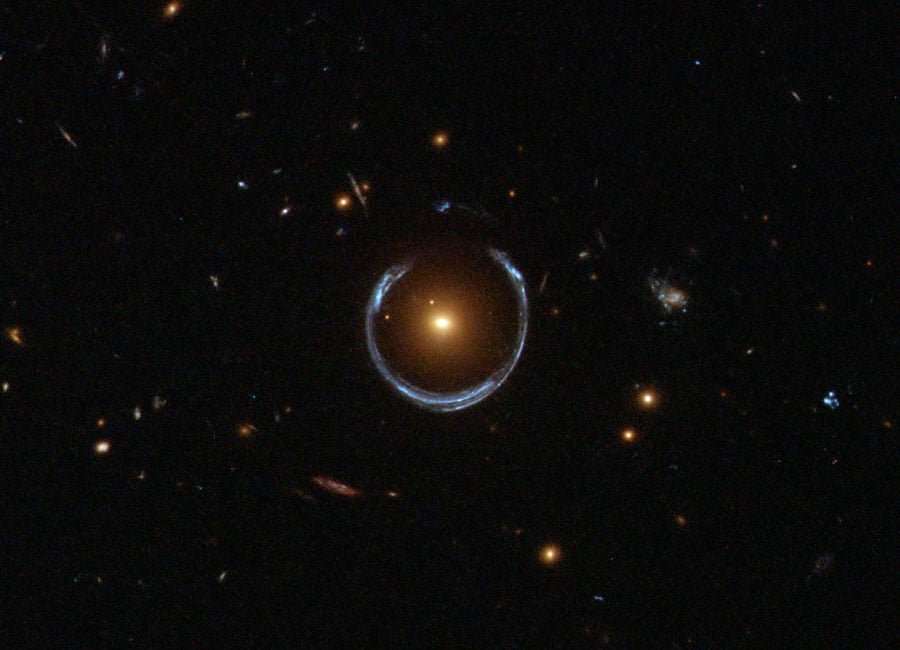

In a recent study, a team of international astronomers used the gravitational lensing technique to study the most distant individual star ever observed.
Continue reading

Thanks to a recent study by an international team of scientists, the remaining missing normal matter of the Universe may finally have been found!
Continue reading

Missed the planets in the dusk sky in early 2018? This summer's astronomical blockbuster sees the return of all the classical naked eye planets in the dusk sky, in a big way.
Continue reading
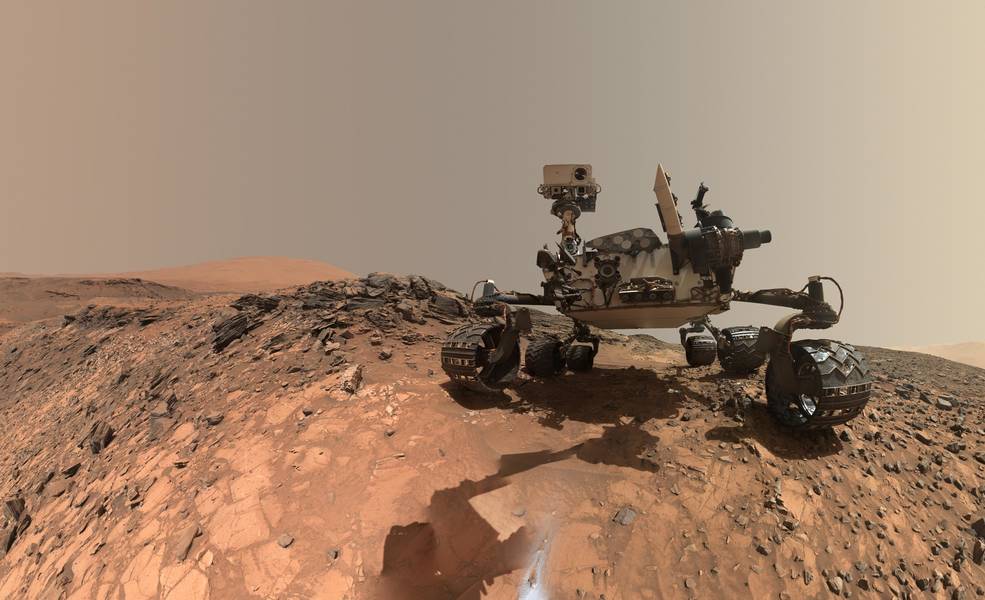

The Martian dust storm that began a few weeks ago has grown to engulf the entire planet, and Curiosity is well-positioned to get it on camera!
Continue reading

Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today











































