[/caption]
Physicists from Fermilab have seen a “bump” in their data that could indicate a brand new particle unlike any ever seen before. If verified, this could re-write particle physics as we know it. “Essentially, the Tevatron has seen evidence for a new particle, 150 times mass of proton, that doesn’t behave like a standard Higgs particle,” said physicist Brian Cox on Twitter. “If this stands up to scrutiny and more data (there is not yet enough data for a “discovery”), then it is RIP Standard Model.”
“It was hard for us to not go crazy when we saw the results,” said Viviana Cavaliere from the University of Illinois (UIUC), one of the 500-member team working with the CDF particle detector at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory in Batavia, Illinois, speaking on a webcast on April 6. “But for now, we need to stay focused on what we do know.”
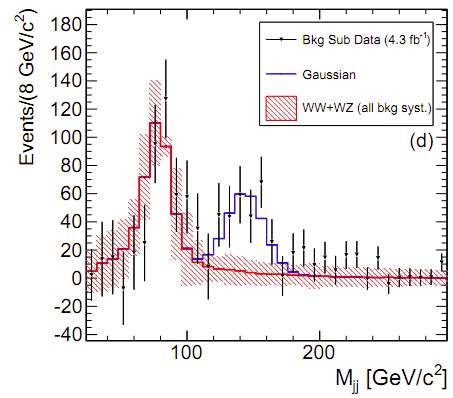
The result comes from CDF’s (the Collider Detector at Fermilab) analysis of billions of collisions of protons and antiprotons produced by Fermilab’s Tevatron collider. In high energy collisions, subatomic particles can be detected that otherwise can’t be seen. Physicists try to identify the particles they see by studying the combinations of more-familiar particles into which they decay, while trying to find new particles, such as the theoretical Higgs Boson which is predicted by the Standard Model of particle physics.
The Standard Model contains a description of the elementary particles and forces inside atoms which make up everything around us. The model has been successful at making predictions that have been subsequently verified. There are sixteen named particles in the Standard Model, and the last particles discovered were the W and Z bosons in 1983, the top quark in 1995, and the tauon neutrino in 2000. But most physicists agree the Standard Model is probably not the final word in particle physics.
The researchers at Fermilab were searching for collisions that produced a W boson, which weighs about 87 times as much as a proton, as well as some other particles that disintegrate into two sprays of particles called “jets,” which are produced when a collision scatters out a particle called a quark.
Instead, they saw about 250 events which indicate a new particle weighing about 150 times as much as a proton, the team said at the webcast from Fermilab and in their paper on arXiv.
The researchers estimate the statistical chances of random jets or jet pairs from other sources producing a fake signal that strong at 1 in 1300.
The Standard Model does not predict anything like what was seen in the CDF experiment, and since this particle has not been seen before and appears to have some strange properties, the physicists want to verify and retest before claiming a discovery.
“If it is not a fluctuation, it is a new particle,” Cox said.
The Tevatron accelerator at Fermilab is scheduled to be shut down later this year, due to lack of funding and because of sentiments that it would be redundant to the Large Hadron Collider.
You can see more complete discussions and interpretations of the results at: