[/caption]
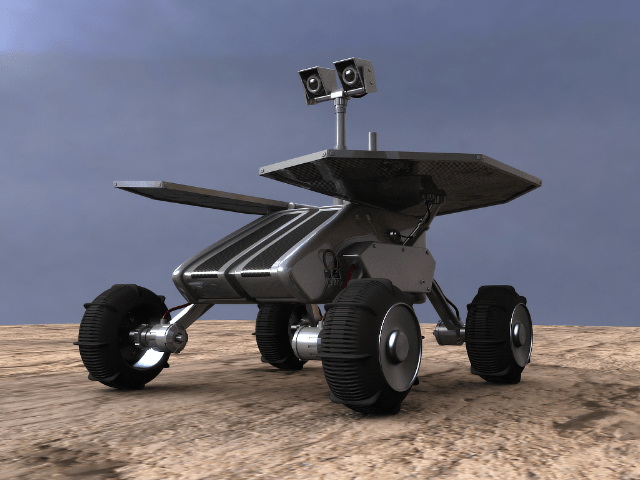
ORLANDO – The Google Lunar X-PRIZE (GLXP) recently announced the 29 official teams that will be vying for the $30 million grand prize. One group in particular stands out amongst the list however – Omega Envoy. This team is comprised primarily by college students from the University of Central Florida, working on engineering and other degrees. However, while they may be relatively young, they have drawn the attention of the media, numerous sponsors, NASA and the space industry.
NASA has inked a deal with the tiny band of potential explorers to purchase data from their spacecraft. The space agency awarded the Innovative Lunar Demonstration Data contract to Omega Envoy. This contract is worth up to $10 million. However, while this contract and the growing list of sponsors is impressive, the feat that the team is trying to accomplish is daunting. What they are attempting to do, only nations have done before.
The GLXP requires that to win, the team must safely land a robot on the lunar surface, have it travel 1,500 feet and send back both images and data to Earth. Given the fact that, to date, only the U.S. and Russia have accomplished this before – this is no small task.

The Google Lunar X-PRIZE is another effort by the X-PRIZE Foundation. The impetus behind this organization is to accelerate space exploration efforts much in the same way that the Orteig Prize accelerated air travel in the 20th Century. That prize was a paltry (by today’s standards) $25,000 for the first person to fly non-stop from New York to Paris (or vice-versa). Its winner, Charles Lindbergh, would go down in history as one of the most famous aviators of all time. It is with this premise in mind that the X-PRIZE Foundation works to inspire today’s explorers and innovators.

For the original Ansari X-PRIZE it took an established (if somewhat outside of the mainstream) aerospace company with years of experience to finally accomplish the objectives laid out. Scaled Composites, renowned for their kit aircraft; successfully sent a manned spacecraft into sub-orbital space, returned safely and then sent the same spacecraft, SpaceShipOne; back into space within the required two weeks.
The non-profit organization that oversees all aspects of Omega Envoy, Earthrise Space Inc. (ESI), works to provide services to private companies, government agencies, as well as educational institutions that currently have the resources to explore space and are looking for low cost products that will accomplish their requirements. They feel that this will enhance the accessibility of technology and increase educational interest amongst the workforce that drives the space.
“Aside from the GLXP, ESI intends to continuously schedule lunar deliveries for scientific payloads and robotics,” said Earthrise Space Institute’s Project Director Ruben Nunez. “Other mission objectives for Omega Envoy entail the visual feedback of a scientific payload that will analyze the lunar terrain.”

Through the Google Lunar X-PRIZE and government contracts such as the contract with NASA, it is hoped that this initiative will enable the creation of a new economic system to support lunar exploration as well as Technology Readiness Level (TRL) advancement of innovative, commercial space systems.
“I am fortunate in that I had the opportunity to witness what Omega Envoy is capable of producing when I field tested their prototype rover during the 2009 FMARS (Flashline Mars Arctic Research Station) Expedition,” said Joseph Palaia 4Frontiers’ Vice President. “There is little doubt in my mind that this team is fully capable of accomplishing the objectives laid out in the GLXP.”