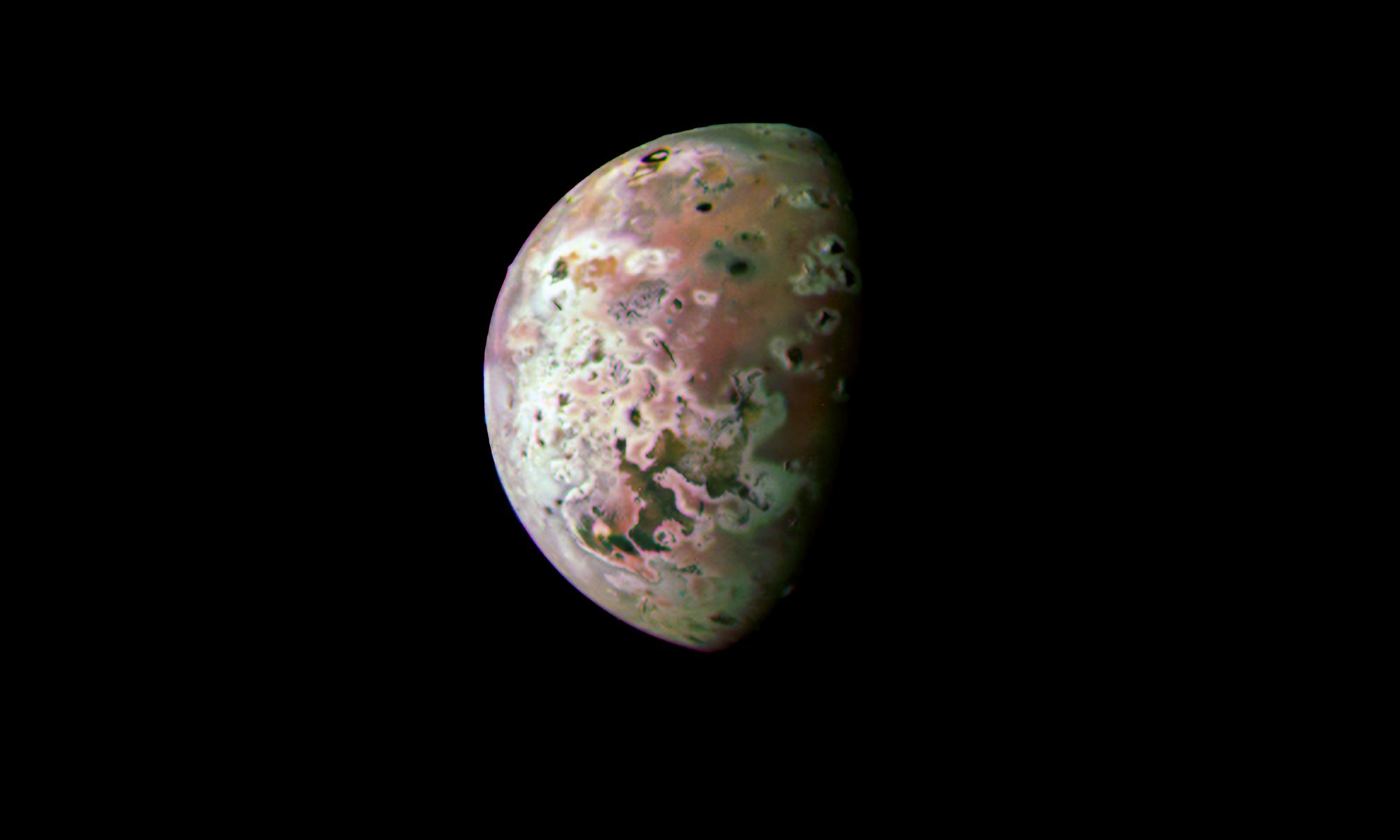
The Galilean Moons, named in honor of Galileo Galileo, who first observed them in 1610, are a fascinating collection of satellites. For decades, scientists have been immensely fascinated by the three icy companions – Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto – which have oceans in their interiors that possibly support life. But Io has also been a focal point of interest lately, owing to the volcanic activity on its surface and lava plumes reaching 300 to 500 km (186 to 310 mi) into space. Since 2016, NASA’s Juno probe has provided stunning images of Io as it continues to orbit its main science objective, Jupiter.
The latest was acquired by the Juno probe’s main camera (JunoCam) on July 31st, 2023, at 05:03 AM UTC (01:03 AM EDT; July 30th, 10:03 PM PDT) and showed Prometheus spewing out lava. This active volcano is located within a 28-km (17-mi) -wide volcanic pit named Prometheus Patera on the hemisphere facing away from Jupiter. Prometheus is known for its regular eruptions, hence its nickname in the astrogeological community, “Old Faithful of Io.” A processed image of the eruption was shared by the NASA Planetary Science Division via Twitter (see below).
Continue reading “Juno Shares Stunning New Images of Jupiter’s Volcanic Moon Io”