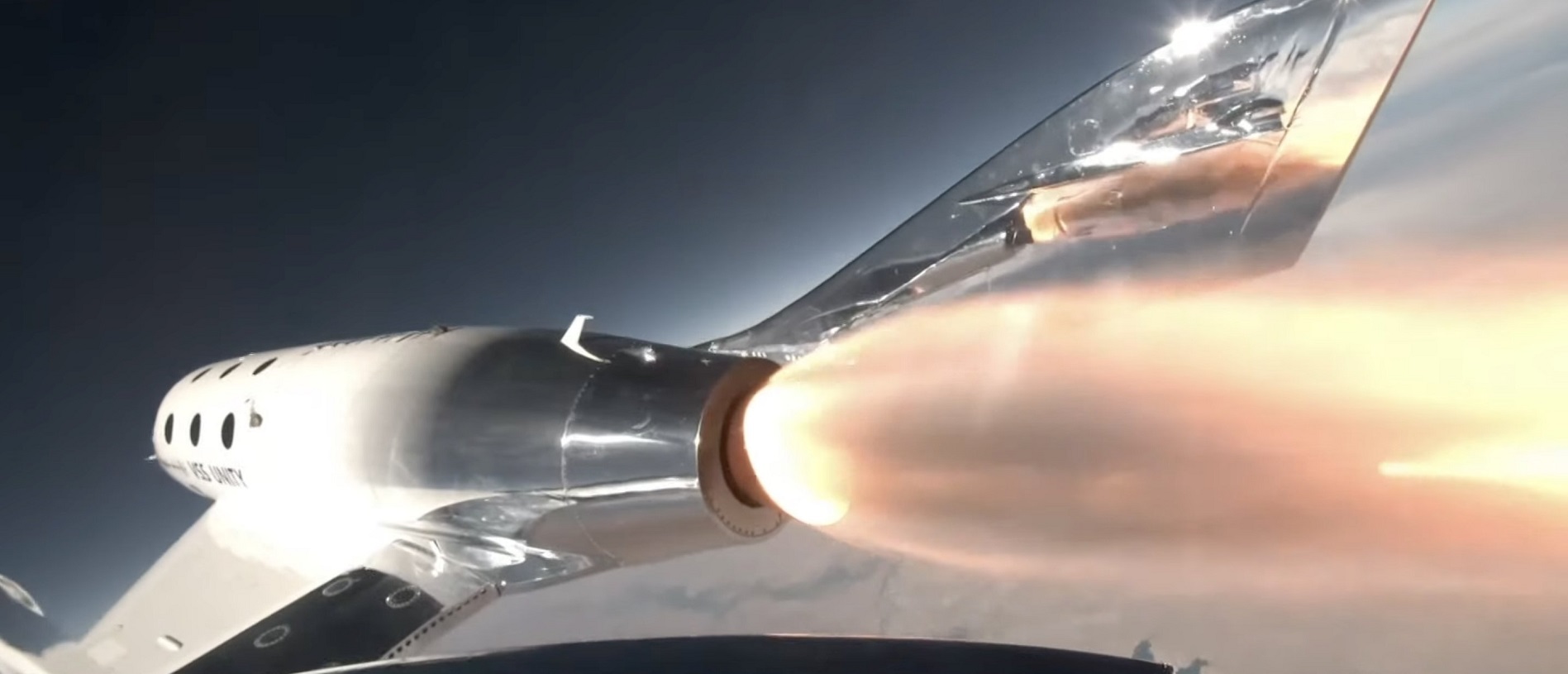
Virgin Galactic sent its first privately funded adventurers — and its first space sweepstakes winners — past the 50-mile space boundary today.
The tourists on the suborbital space trip known as Galactic 02 included Keisha Schahaff, who won two tickets in an online contest organized by the Omaze charity sweepstakes platform and a nonprofit group called Space for Humanity in 2021. She and her daughter, Anastatia Mayers, became the first mother-and-daughter duo to share a spaceflight, and the first spacefliers from the Caribbean island nation of Antigua and Barbuda.
“I kind of feel like I was born in this life for this,” Schahaff, a wellness coach, told NBC’s “Today” show. Her daughter is a college student who aims to become an astrobiologist.
Jon Goodwin — an 80-year-old British adventurer who competed as a canoeist in the 1972 Olympics — also broke barriers on today’s Galactic 02 flight. In 2005, he was one of the first customers to reserve a spot with Virgin Galactic, back when the price was $200,000. Then, almost a decade ago, he was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. Today he became only the second person with Parkinson’s to take a space trip. (The first was NASA shuttle astronaut Rich Clifford.)
Continue reading “Virgin Galactic Flies Its First Privately Funded Space Tourists”