It has been another great year in space, and the European Space Agency has put together a video highlight reel for 2010. They look at the achievements in different areas, including Earth Observation, Science, Human Spaceflight and Telecommunications. From the launch of Cryosat to the Planck sky scan, from Node 3 Cupola completing the ISS to Paolo Nespoli launching on the Soyuz to the ISS, from the Rosetta flyby of asteroid Lutetia to the launch of Hylas providing broadband for Europe.
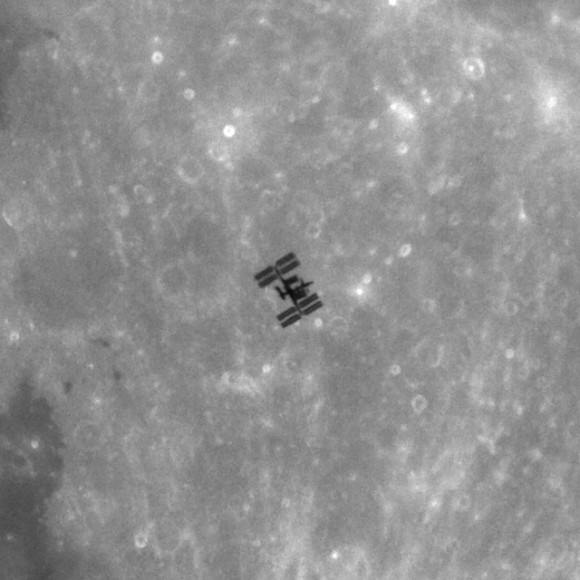
International Space Station on the Moon?

[/caption]
From our vantage point on Earth, it takes just a half second for the International Space Station to fly across the face of the Moon, so catching a transit is tricky. But award-winning French astrophotographer Theirry Legault captured an amazingly sharp and detailed transit image that makes the ISS look like it is sitting on the Moon’s surface! Legault took this image from Avranches (Normandy, France) a few hours before the eclipse, on December 20th at 21:34 UT. He used a Meade 10″ ACF on Takahashi EM400, with a Canon 5D mark II. The transit duration was just 0.55 seconds, as the ISS is traveling at 7.5km/s or 28,0000 km/h (17,500 mph). See below for a close-up crop of the image which shows the amount of detail visible of the space station.

Legault has also taken incredible images of the ISS and a docked space shuttle transiting the Sun, (at least twice), as well as the shuttle Atlantis and Hubble transiting old Sol.
See more of his images at his website, or click the images for larger versions. Legault told us he’ll be traveling for a good view of the solar eclipse on January 4, so we look forward to his images of that event.
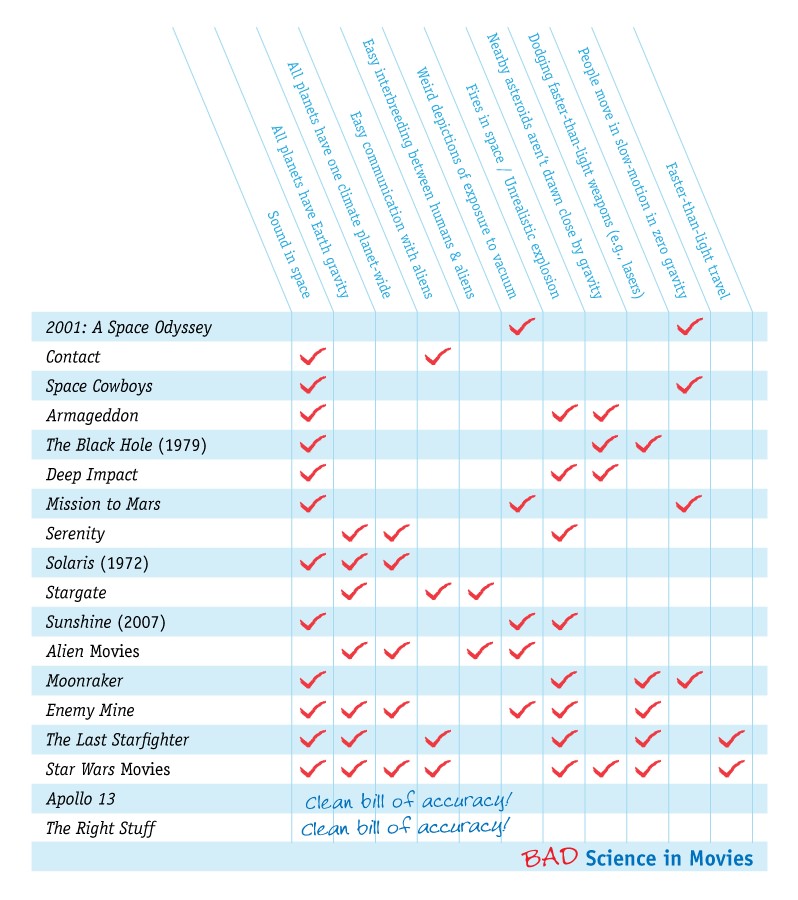
Bad Science in Movies
[/caption]
If you’re finding the time to watch a few movies during the holidays, you might want to make your choices based on this “report card” put together by the website io9 a while back. They rated 18 movies based on how many laws of physics they mangled. Star Trek is not included just because there is too much of it (bad science and movies!) to fit all in one graphic.
Hat tip to Nate!
SOHO Finds Its 2000th Comet
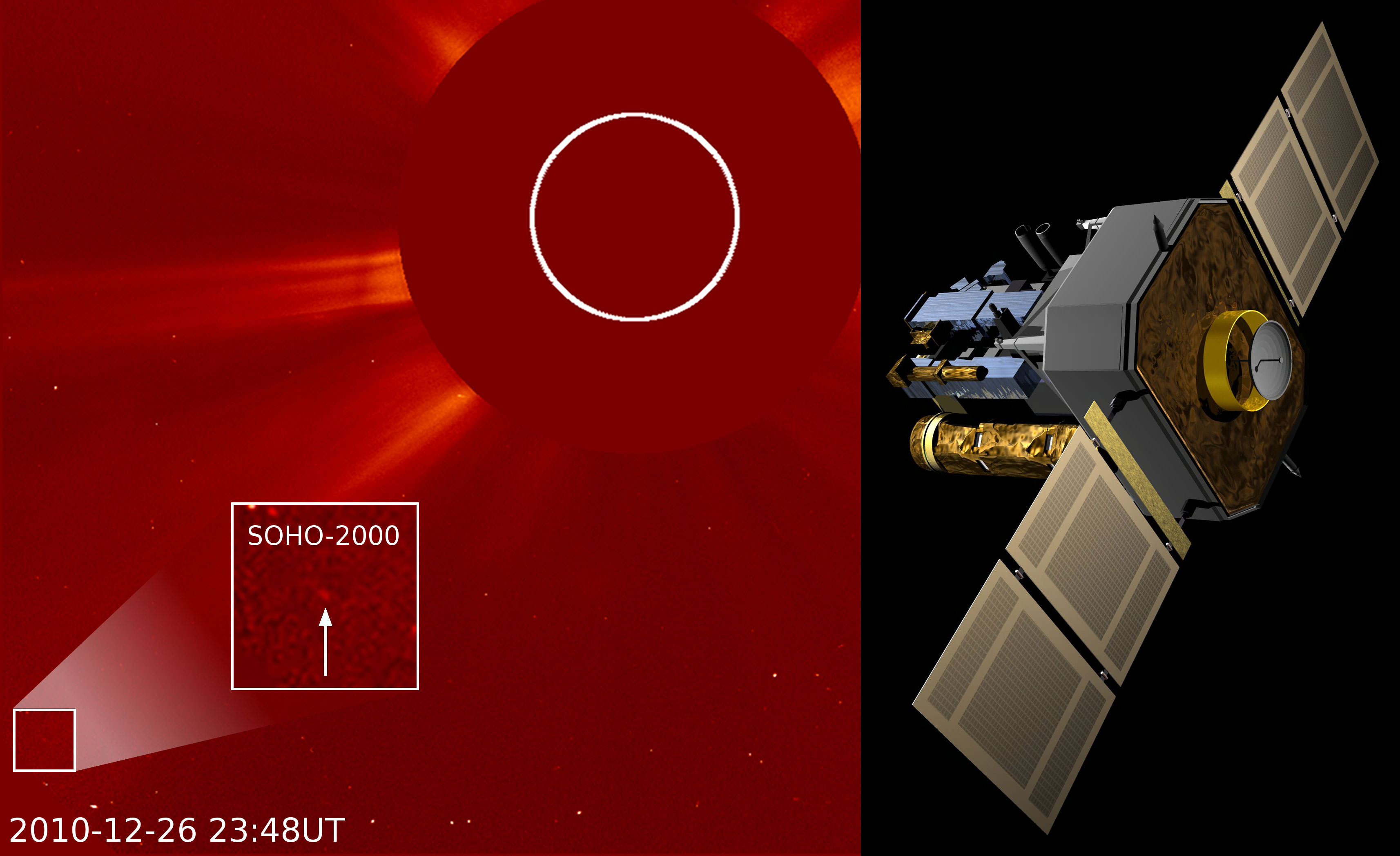
[/caption]
As people on Earth celebrate the holidays and prepare to ring in the New Year, an ESA/NASA spacecraft has quietly reached its own milestone: on December 26, the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) discovered its 2000th comet.
Drawing on help from citizen scientists around the world, SOHO has become the single greatest comet finder of all time. This is all the more impressive since SOHO was not specifically designed to find comets, but to monitor the sun.
“Since it launched on December 2, 1995 to observe the sun, SOHO has more than doubled the number of comets for which orbits have been determined over the last three hundred years,” says Joe Gurman, the U.S. project scientist for SOHO at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
Of course, it is not SOHO itself that discovers the comets — that is the province of the dozens of amateur astronomer volunteers who daily pore over the fuzzy lights dancing across the pictures produced by SOHO’s LASCO (or Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph) cameras. Over 70 people representing 18 different countries have helped spot comets over the last 15 years by searching through the publicly available SOHO images online.
The 1999th and 2000th comet were both discovered on December 26 by Michal Kusiak, an astronomy student at Jagiellonian University in Krakow, Poland. Kusiak found his first SOHO comet in November 2007 and has since found more than 100.
“There are a lot of people who do it,” says Karl Battams who has been in charge of running the SOHO comet-sighting website since 2003 for the Naval Research Lab in Washington, where he also does computer processing for LASCO. “They do it for free, they’re extremely thorough, and if it wasn’t for these people, most of this stuff would never see the light of day.”
Battams receives reports from people who think that one of the spots in SOHO’s LASCO images looks to be the correct size and brightness and headed for the sun – characteristics typical of the comets SOHO finds. He confirms the finding, gives each comet an unofficial number, and then sends the information off to the Minor Planet Center in Cambridge, Mass, which categorizes small astronomical bodies and their orbits.
It took SOHO ten years to spot its first thousand comets, but only five more to find the next thousand. That’s due partly to increased participation from comet hunters and work done to optimize the images for comet-sighting, but also due to an unexplained systematic increase in the number of comets around the sun. Indeed, December alone has seen an unprecedented 37 new comets spotted so far, a number high enough to qualify as a “comet storm.”
LASCO was not designed primarily to spot comets. The LASCO camera blocks out the brightest part of the sun in order to better watch emissions in the sun’s much fainter outer atmosphere, or corona. LASCO’s comet finding skills are a natural side effect — with the sun blocked, it’s also much easier to see dimmer objects such as comets.
“But there is definitely a lot of science that comes with these comets,” says Battams. “First, now we know there are far more comets in the inner solar system than we were previously aware of, and that can tell us a lot about where such things come from and how they’re formed originally and break up. We can tell that a lot of these comets all have a common origin.” Indeed, says Battams, a full 85% of the comets discovered with LASCO are thought to come from a single group known as the Kreutz family, believed to be the remnants of a single large comet that broke up several hundred years ago.
The Kreutz family comets are “sungrazers” – bodies whose orbits approach so near the Sun that most are vaporized within hours of discovery – but many of the other LASCO comets boomerang around the sun and return periodically. One frequent visitor is comet 96P Machholz. Orbiting the sun approximately every six years, this comet has now been seen by SOHO three times.
SOHO is a cooperative project between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA. The spacecraft was built in Europe for ESA and equipped with instruments by teams of scientists in Europe and the USA.
Zombie Satellite Now Under Control
[/caption]
A geostationary satellite that become a “zombie” earlier this year and stopped communicating with ground controllers has now finally been reset and is under control. The Galaxy 15 communications satellite had its “brains fried” by a solar flare and went rogue in early May. Although it was still functional, its navigation and communications systems would not accept commands, and the satellite drifted out of its orbit. On December 23, 2010, engineers at the company Intelsat were finally able to command the unit to reset after a battery drained. Shortly thereafter Galaxy 15 began accepting commands, and then was put into safe mode. “We are pleased to report it no longer poses any threat of satellite interference to either neighboring satellites or customer services,” IntelSat said on their website.
While there was little chance that Galaxy 15 would crash into another satellite, it caused some problems when it entered an orbital space occupied by other satellites and “stole” their signal, thereby interrupting other vendor’s services to customers on Earth.
Engineers will now do some diagnostic tests and load updated commanding software to the satellite.
“We expect to relocate the satellite to an Intelsat orbital location where engineers at our Satellite Operations Control Center will initiate extensive in-orbit testing to determine the functionality of every aspect of the spacecraft,” Intelsat said.
The satellite is currently pointed towards the Sun, allowing the spacecraft’s batteries to become fully charged and the satellite thermally balanced.
Once initial diagnostic testing has been completed, IntelSat will attempt to stop the drift of the satellite. This phase could take as long as two weeks to complete.
Intelsat is hoping full functionality of Galaxy 15 can be regained and they hope to relocate the satellite to an orbital location where we they can assess the viability of the payload, and conduct extensive in-orbit testing to determine the functionality of every aspect of the spacecraft.
Source: Intelsat
Oldest Black Holes are Growing the Fastest
[/caption]
Astronomers have determined that the era of first fast growth of the most massive black holes occurred when the universe was much younger than previously thought. A team of researchers from Tel Aviv University found that the epoch of the first fast growth of black holes occurred when the Universe was only about 1.2 billion years old, and not two to four billion years old, as was previously believed. The team also found that these black holes are continuing to grow at a very fast rate.
The supermassive blackholes that most galaxies are thought to have vary in mass from about one million to about 10 billion times the size of our sun. To find them, astronomers look for the enormous amount of radiation emitted by gas which falls into such objects during the times that the black holes are “active,” or accreting matter. This gas infall into massive black holes is believed to be the means by which black holes grow.

Prof. Hagai Hetzer and his research student Benny Trakhtenbrot used data from two different telescopes, Gemini North on top of Mauna Kea in Hawaii, and the Very Large Telescope Array on Cerro Paranal in Chile.
The data show that the black holes that were active when the universe was 1.2 billion years old are about ten times smaller than the most massive black holes that are seen at later times. However, they are growing much faster. The measured rate of growth allowed the researchers to estimate what happened to these objects at much earlier as well as much later times. The team found that the very first black holes, those that started the entire growth process when the universe was only several hundred million years old, had masses of only 100-1000 times the mass of the sun. Such black holes may be related to the very first stars in the universe. They also found that the subsequent growth period of the observed sources, after the first 1.2 billion years, lasted only 100-200 million years.
The team found that the very first black holes ? those that started growing when the universe was only several hundred million years old ? had masses of only 100-1000 times the mass of the sun. Such black holes may be related to the very first stars in the universe. They also found that the subsequent growth period of these black holes, after the first 1.2 billion years, lasted only 100-200 million years.
The new study is the culmination of a seven year-long project at Tel Aviv University designed to follow the evolution of the most massive black holes and compare them with the evolution of the galaxies in which such objects reside.
The results will be reported in the Astrophysical Journal.
Faulty Valve Caused Akatsuki Failure at Venus
[/caption]
The Japanese space agency has deduced that a faulty engine valve was the reason the Akatsuki spacecraft did not go into orbit around Venus as planned on December 6, 2010. According to the Daily Yomiuri, a malfunctioning valve in the probe’s fuel pressure system caused the engine to function abnormally. The valve is a standard component in many previous space missions, JAXA said, and it was not modified at all for Akatsuki.
Earlier, JAXA reported that Akatsuki’s engine did perform a burn to slow it down, but 152 seconds into the burn the fuel pressure dropped and the probe became unbalanced. Because the retrofiring of the rockets failed to slow down the probe enough for Venus to capture it, it was unable to enter into orbit around the planet, and then went into safe mode.
The JAXA investigation identified five possible causes of the mishap and all stemmed from the valve’s failure to open. JAXA also said they intend “to further investigate why the valve did not open, and how much damage was caused to Akatsuki’s thruster nozzle, by conducting tests that also will indicate whether the probe will be able to go into orbit around Venus when it comes near the planet six years from now.”
After Akatsuki’s launch in May, the functions of its main engine were tested in June. However, the engine was fired for too short a time to detect the problem with the valve, JAXA said.
The findings were presented to the Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Ministry’s Space Activities Commission.
Source: Daily Yomiuri
Video: Satellite Views of the “Christmas Blizzard”
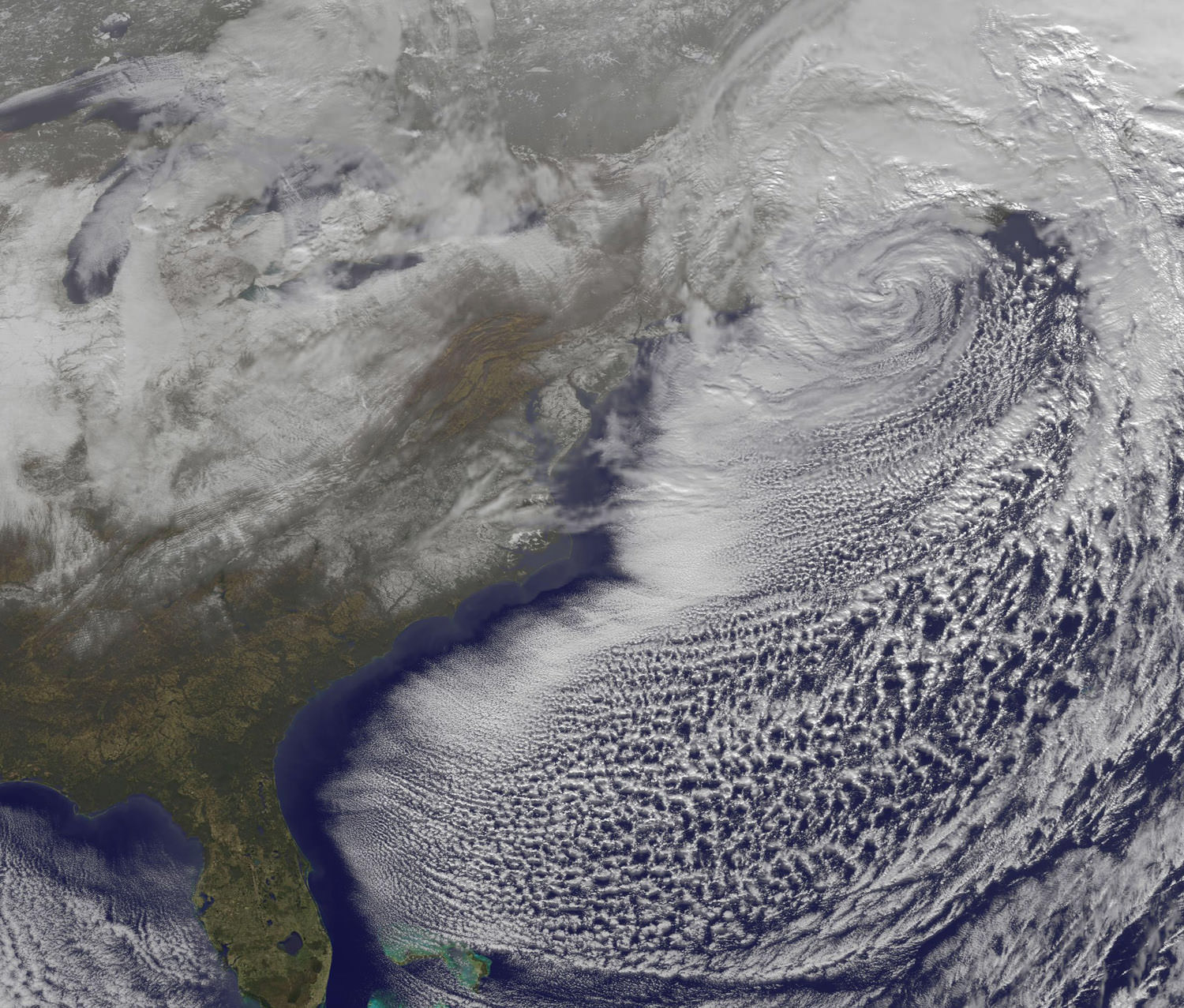

The Christmas Blizzard of 2010 dumped up to 30 inches of snow in the northeast United States, with winds gusts up to 60 mph. An Earth-orbiting satellite, GOES-13 captured a series of visible images of the storm, showing its progression. News reports from New York City say this is the sixth largest snowstorm in the city’s history and it buried the streets in four-foot drifts, bringing transit to a halt with cars and buses stranded in the streets.
Snowfall ranged from 1.5 inches in Atlanta, Georgia to more than two feet in various areas of New Jersey, New York and the New England states.
[/caption]
Some of those snows are visible in the above GOES-13 satellite image. Snowfall on the ground can be seen in the image over South and North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, Delaware, eastern Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and southeastern New York. The clouds of the low obscure New England in the image.
Photographer Michael Black took an amazing timelapse of the blizzard, with a Canon DLSR on tripod with remote timer taking a photo once every five minutes (approximately 20 hours in 40 seconds.) — and obviously having to go outside and readjust the clock and markers.
December 2010 Blizzard Timelapse from Michael Black on Vimeo.
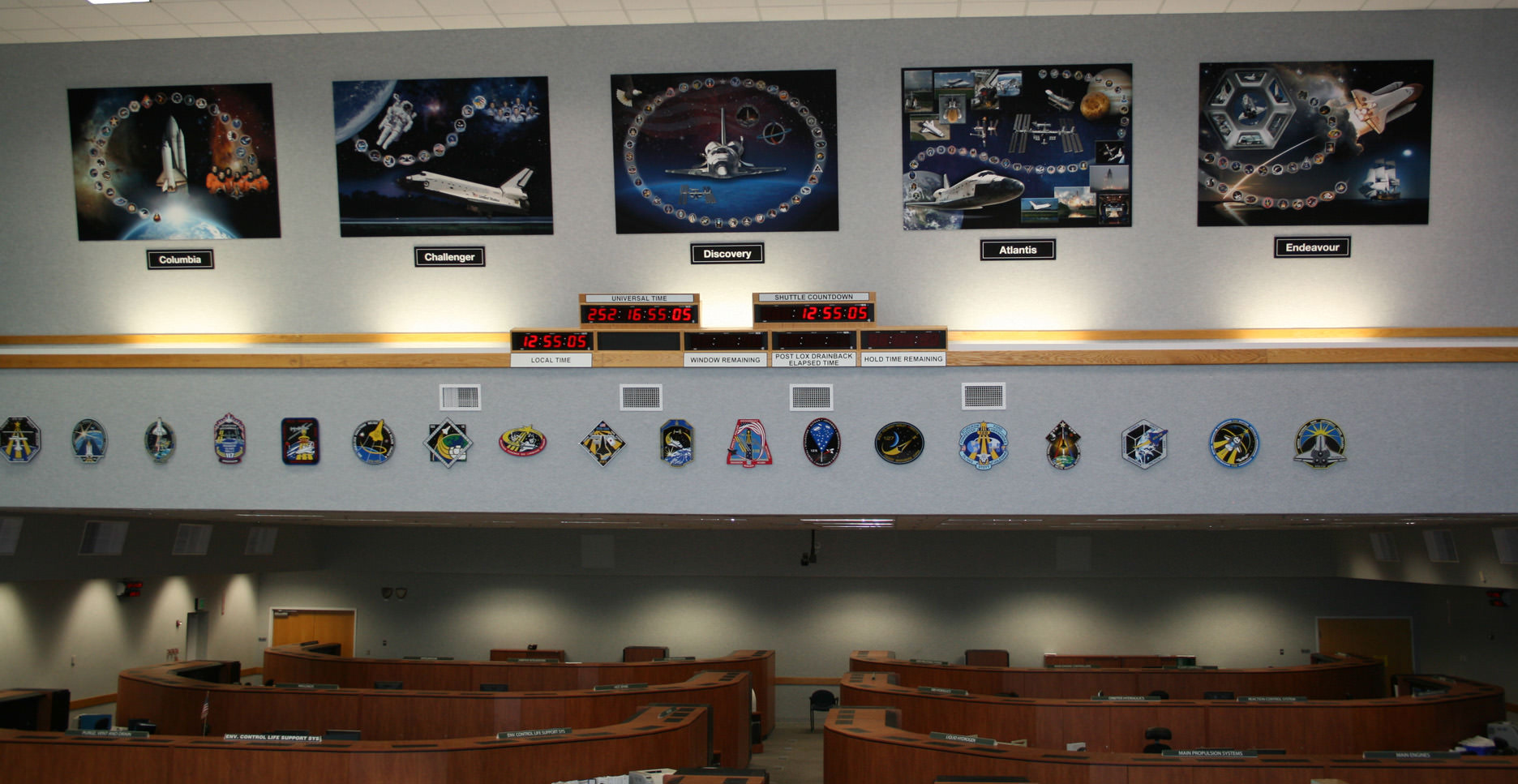
Twas the Shuttles last Christmas

[/caption]
To mark the occasion of the Shuttle’s last Christmas, space shuttle worker Terry Sibile drafted a touching poem titled; “T’was the Shuttle’s Last Christmas”.
For your enjoyment Terry’s poem is reprinted below; as it appeared at Florida Today. The poem initially was circulated via email at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and other NASA sites across the US.
According to this article at Florida Today, Terry is a member of the engineering team dealing with cranes, platforms and doors which abound at the space center.
Only 2 or 3 flights remain before the shuttle is retired – at the peak of its performance – probably around mid-2011. NASA is still evaluating whether the budget will support flying the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station.
So it’s unlikely the shuttles will see another Christmas. Sibile’s poem thus marks another installment in the string of sad and bittersweet “lasts” for the shuttle program – “Our spirits were low … and soon we’d all go.”
The Space Shuttle Launch team at KSC recently created tribute displays to honor the achievements of all 5 Space Shuttle Orbiters and all the NASA and contractor workers involved. See photo above. Sibile’s poetry poignantly puts these displays into words.
‘Twas the Shuttle’s last Christmas by Terry Sibile
‘Twas the Shuttle’s last Christmas
and our spirits were low,
For the program was ending
and soon we’d all go.
We’d processed the Shuttles
with infinite care
And followed each mission
as if we were there.
We made every effort
to achieve all our goals;
We offered our talents,
our hearts and our souls.
Our work was much more
than a meager career;
‘Twas an honor and privilege
beyond all compare.
As this marvel of science
was applauded worldwide,
We looked on each Shuttle
with unfettered pride:
Columbia, Challenger,
Discovery, and then
Atlantis, Endeavour
all ferried brave men
And women to realms
past the confines of Earth,
Uncovering knowledge
of infinite worth.
We rejoiced with each mission’s
success, and we grieved
For the losses too painful
for us to conceive.
And over the years,
something wondrous took place:
We became kindred spirits,
united by Space.
And so, as we part,
I will bear a great loss.
And hope in the future
our paths again cross.
But until then, my friend,
this wish I confide:
Happy Christmas to all
— we had a great ride!
————————————-
Check out this 360 degree panoramic view from inside Firing Room 4 showing all five Shuttle tribute displays; recorded during my visit with Space Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach. Leinbach led the effort to create the tribute displays. Courtesy of Nasatech.net
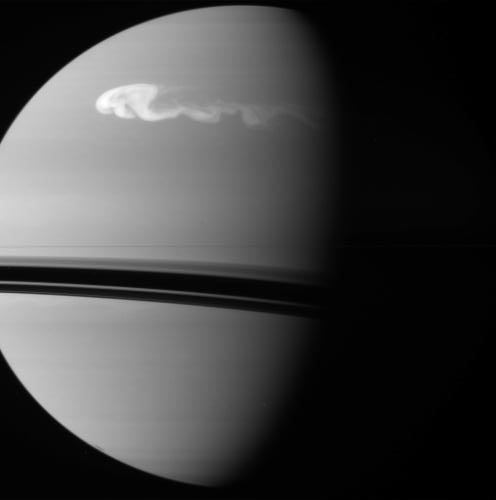
Cassini Takes Images of Growing Storm on Saturn
[/caption]
The white storm on Saturn’s northern hemisphere is growing and expanding. This raw image from the Cassini collection was taken on Dec. 24, 2010, showing the storm getting bigger. You can compare the storm from earlier images taken by amateur astronomer Anthony Wesley.
Below is a color version, as well as other recent raw images showing the “real” moon Pandora is on the line.
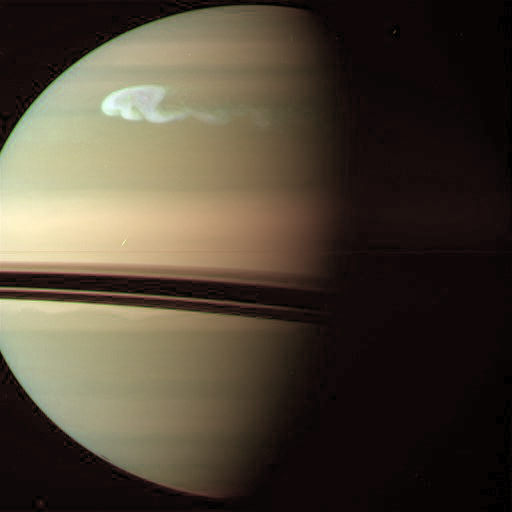

Here’s a color version sent in by Stu Atkinson, who said he did a “quick” go at adding color to the image. Looks great, Stu!