Nearly two million years ago a species of upright apes known as homo erectus began to utilize fire. It was a gradual process, from opportunistic users of natural fires to masters able to craft flames from flint and tender. We are their descendants. We are creatures of forge and kiln, hearth and home. Fire has become so central to us that instead of homo sapiens, we could call ourselves homo ignus, the fire-wielding ape. Fire is central to the rise of our civilization. It cooks our food, keeps us warm, and illuminates our night. This raises an interesting question. Could we have built a civilization without fire?
Continue reading “Do Technological Civilizations Depend on Atmospheric Oxygen?”NASA Plans to Unleash a Wolf Pack of Rovers Onto the Lunar Surface in 2024
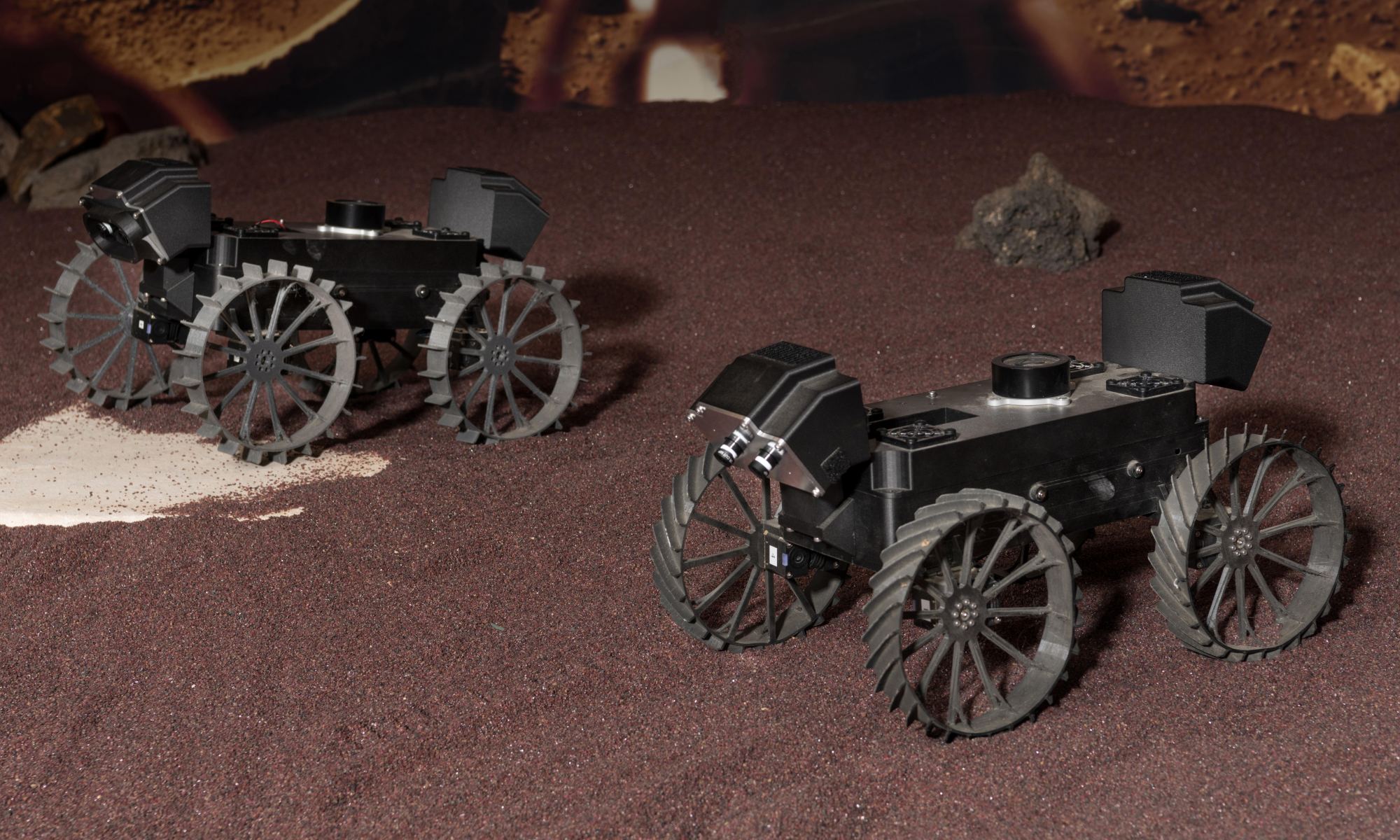

What’s better than one lunar rover? Three lunar rovers! In 2024, NASA plans to send a team of suitcase-sized wheeled robots to the Moon as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program. Collectively called CADRE – Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration – the rovers will spend one full lunar day (14 Earth days) exploring the Moon and showing off their unique capabilities.
Continue reading “NASA Plans to Unleash a Wolf Pack of Rovers Onto the Lunar Surface in 2024”JWST Sees Multiple Gravitational Lenses in a Massive Cluster: “The Fishhook” and “The Thin One”
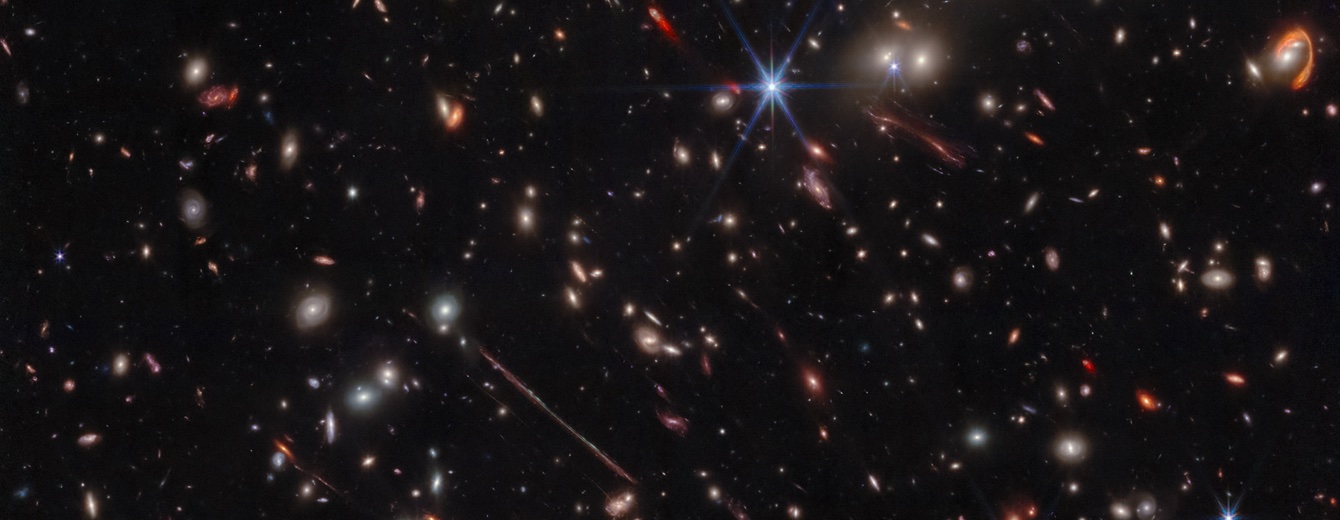
We’ve been getting plenty of spectacular images from the James Webb Space Telescope since it began operations last year. Fraser even covered everything we learned from it in a video a few weeks ago. But the news keeps coming, and recently a science team known as the Prime Extra-Galactic Areas for Reionization and Lensing Science (PEARLS) team released a series of four papers describing Webb’s observations of a galaxy cluster known as El Gordo (“the fat one” in Spanish). But what’s more – they also released another absolutely stunning picture.
Continue reading “JWST Sees Multiple Gravitational Lenses in a Massive Cluster: “The Fishhook” and “The Thin One””Follow a Simulated Journey of the Destruction of ESA’s Aeolus Mission
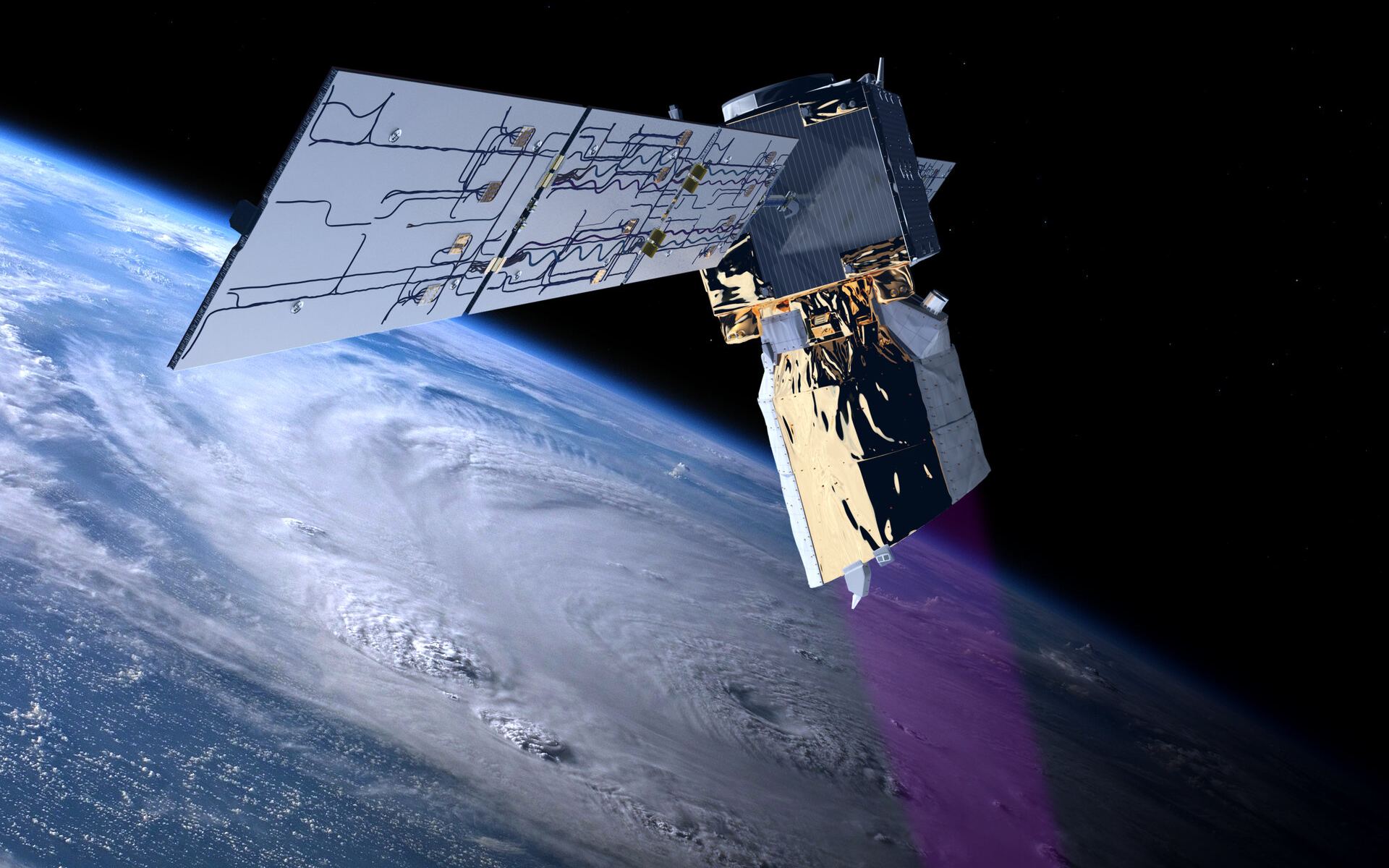

On July 28th, the European Space Agency commanded its long-working Aeolus wind profile mission to re-enter Earth’s atmosphere. It did that and disintegrated into pieces over Antarctica. Of course, satellites do this often. But, Aeolus was different. It maneuvered its way into a safe re-entry profile, a first-of-its kind activity designed to avoid populated regions on Earth.
Continue reading “Follow a Simulated Journey of the Destruction of ESA’s Aeolus Mission”A Massive Solar Storm was Detected on Earth, Mars, and the Moon
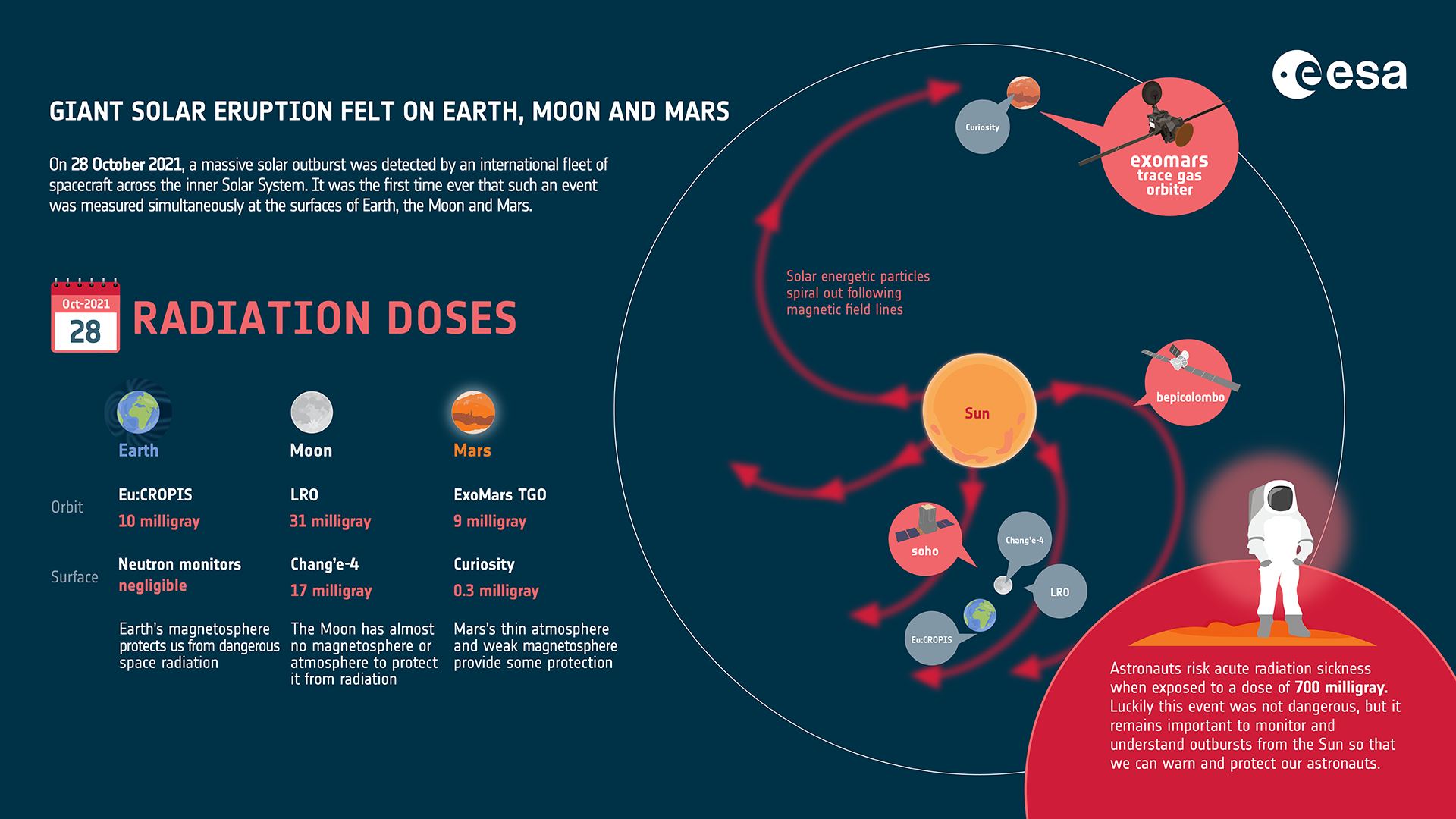
A coronal mass ejection erupted from the Sun on October 28th, 2021, spreading solar energetic particles (SEPs) across a volume of space measuring more than 250 million km (155.34 million mi) wide. This means that the event was felt on Earth, Mars, and the Moon, which was on the opposite side of the Sun at the time. It was also the first time that a solar event was measured simultaneously by robotic probes on Earth, Mars, and the Moon, which included ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and Eu:CROPIS orbiter, NASA’s Curiosity rover and Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), and China’s Chang’e-4 lander.
The ESA’s Solar Orbiter, Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), and BepiColombo missions were also caught by the outburst and provided additional measurements of this solar event. The study of Solar Particle Events (SPE) – aka. solar flares – and “space weather” phenomena are vital to missions operating in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) – for example, crews living and working on the International Space Station (ISS). But it is especially vital for missions destined for locations beyond LEO and cislunar space, including Project Artemis and the many proposals for sending astronauts to the Moon and Mars in the coming years.
Continue reading “A Massive Solar Storm was Detected on Earth, Mars, and the Moon”Yes! A JWST Image of the Ring Nebula
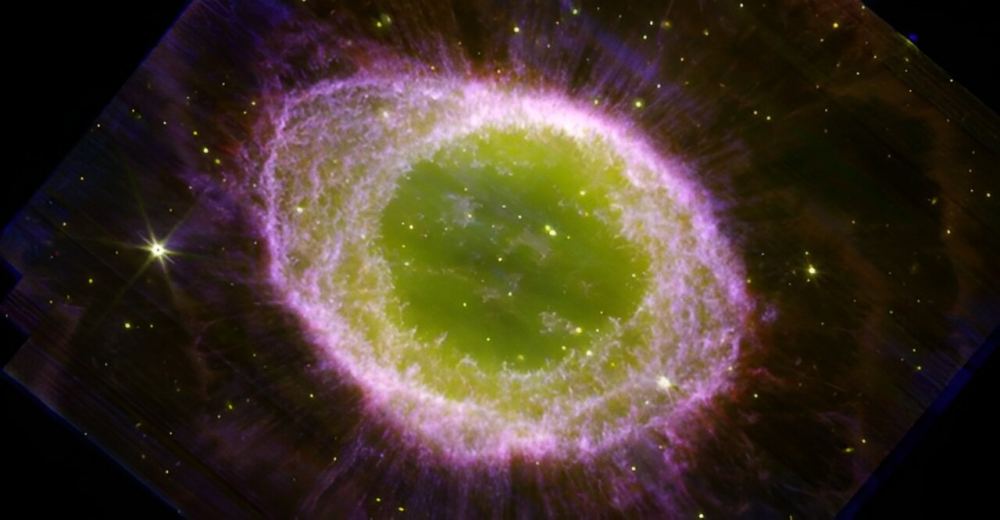

Brace yourselves for great JWST views of the iconic Ring Nebula (M57). An international team of astronomers just released a fantastic near-infrared image of the nebula, showing incredible details.
Continue reading “Yes! A JWST Image of the Ring Nebula”Light Pollution from Skyglow Changes Bird Behavior
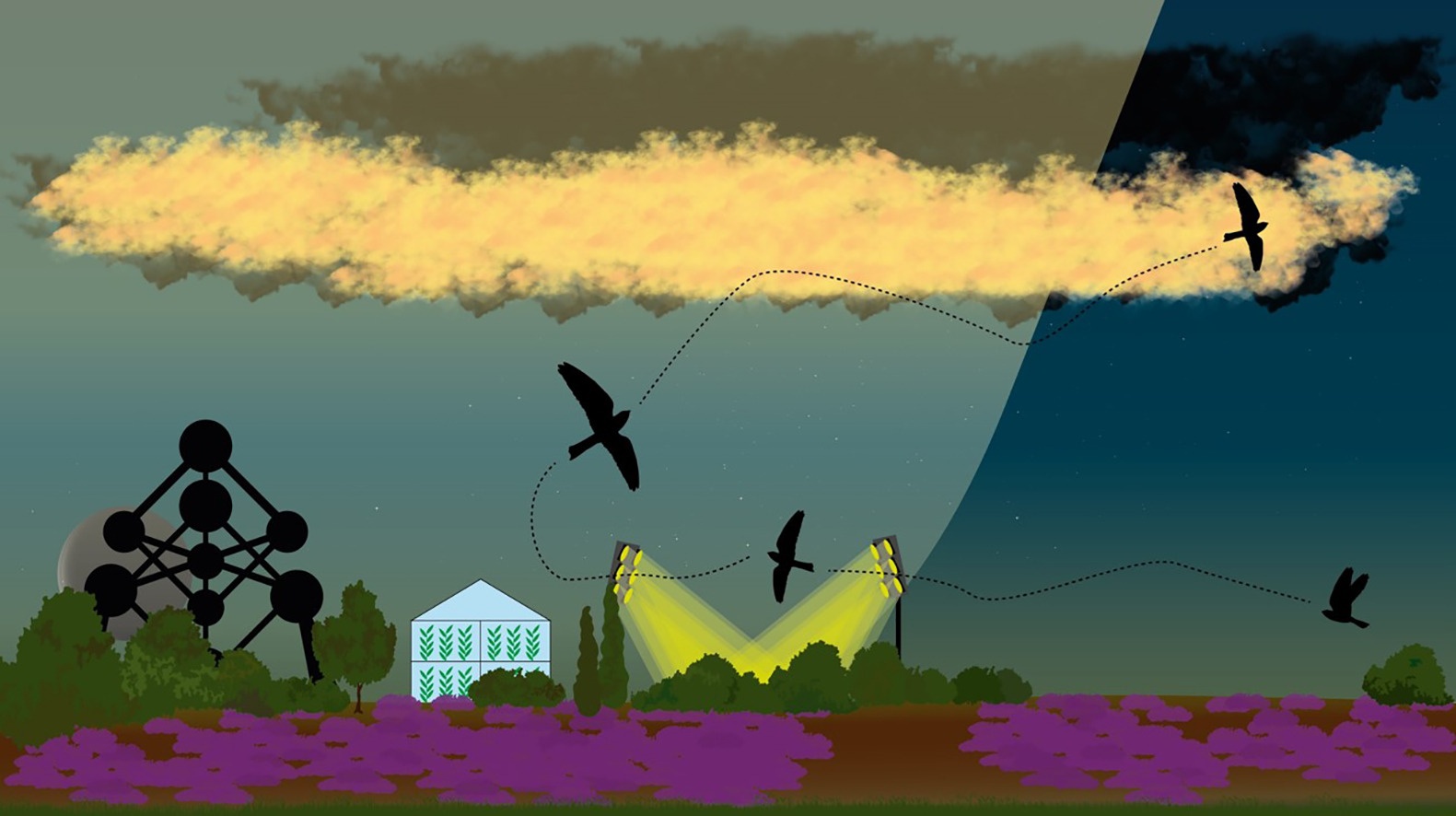
In the astronomy community, we typically this of light pollution as an overall negative. Much research points out its negative effect on our sleep and even our observational equipment. It also significantly impacts wildlife; however, according to a new paper from some Belgian, Swiss, and German researchers, not all of that impact is negative.
Continue reading “Light Pollution from Skyglow Changes Bird Behavior”JWST is the Perfect Machine to Resolve the Hubble Tension
You’ve just found the perfect work desk at a garage sale, and you measure it to see if it will fit in your apartment. You brought a tape measure to size it up and find it’s 180 cm. Perfect. But your friend also brought a tape measure, and they find it’s 182 cm, which would be a smidge too long. You don’t know which tape measure is right, so you have a conundrum. Astronomers also have a conundrum, and it’s known as the Hubble tension.
Continue reading “JWST is the Perfect Machine to Resolve the Hubble Tension”China’s Chang’e-7 Will Deploy a Hopper that Jumps into a Crater in Search of Water Ice
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese National Space Administration recently published a study in the journal Space: Science & Technology outlining how the upcoming Chang’e-7 mission, due to launch in 2026, will use a combination of orbital observations and in-situ analyses to help identify the location, amount, and dispersion of water-ice in the permanently-shadowed regions (PSRs) of the Moon, specifically at the lunar south pole.
Continue reading “China’s Chang’e-7 Will Deploy a Hopper that Jumps into a Crater in Search of Water Ice”Does the Milky Way's Supermassive Black Hole Have a Companion?
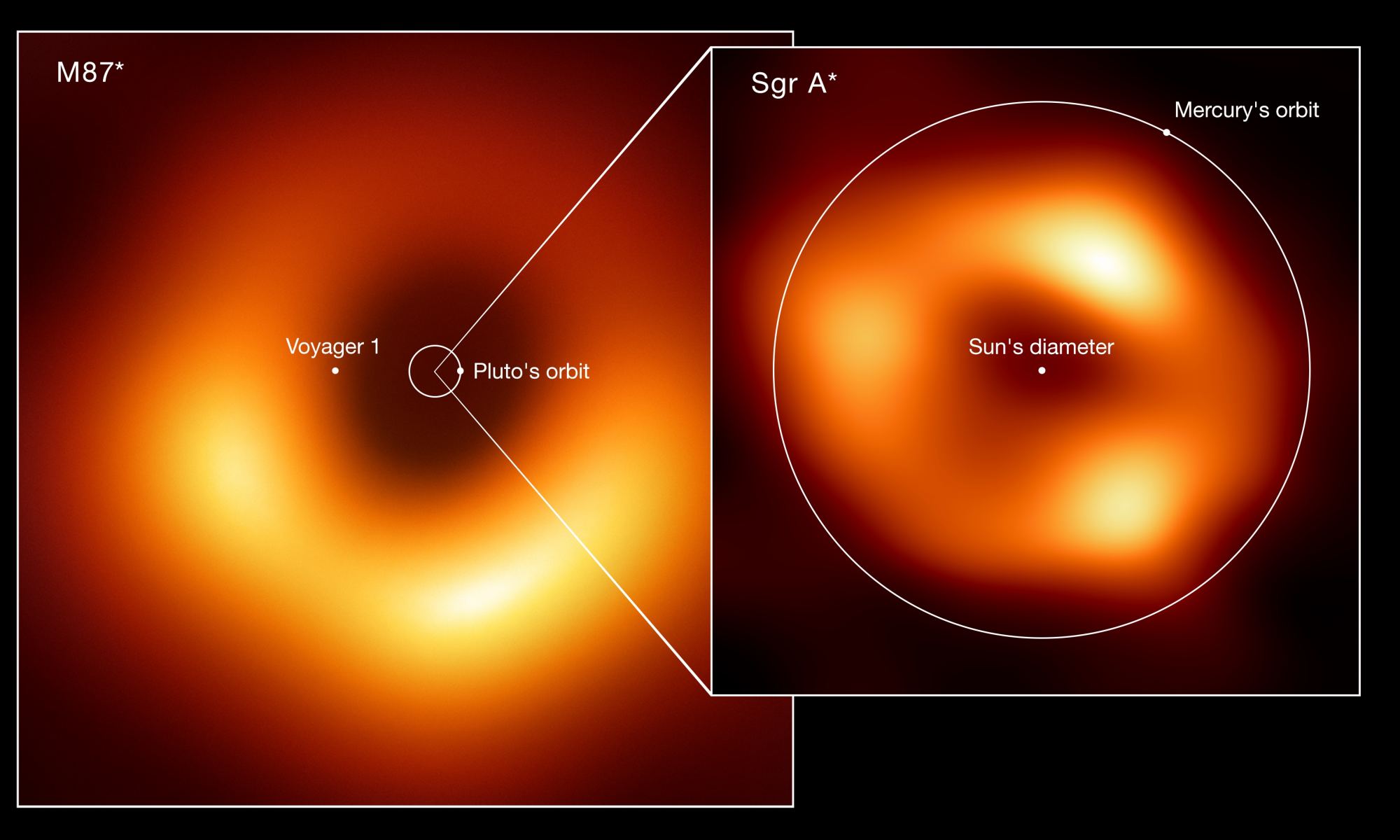
At the heart of our galaxy, there is a monster black hole. Known as Sagittarius A*, it has a mass of 4.2 million Suns, and it’s only about 27,000 light-years from Earth. Sag A* is the closest supermassive black hole, and one of only two that we’ve observed directly. It is so close that we can even see stars closely orbiting it. Some of those stars we’ve been observing for more than 20 years, which means we have a very good handle on their orbits. We’ve used those orbits to determine the mass of Sag A*, but a new study looks at a different question: does our galaxy’s black hole have a companion?
Continue reading “Does the Milky Way's Supermassive Black Hole Have a Companion?”