[/caption]
Well, not only may up to 25% of Sun-like stars have Earth-like planets – but if they are in the right temperature zone, apparently they are almost certain to have oceans. Current thinking is that Earth’s oceans formed from the accreted material that built the planet, rather than being delivered by comets at a later time. From this understanding, we can start to model the likelihood of a similar outcome occurring on rocky exoplanets around other stars.
Assuming terrestrial-like planets are indeed common – with a silicate mantle surrounding a metallic core – then we can expect that water may be exuded onto their surface during the final stages of magma cooling – or otherwise out-gassed as steam which then cools to fall back to the surface as rain. From there, if the planet is big enough to gravitationally retain a thick atmosphere and is in the temperature zone where water can remain fluid, then you’ve got yourself an exo-ocean.
We can assume that the dust cloud that became the Solar System had lots of water in it, given how much persists in the left-over ingredients of comets, asteroids and the like. When the Sun ignited some of this water may have been photodissociated – or otherwise blown out of the inner solar system. However, cool rocky materials seem to have a strong propensity to hold water – and in this manner, could have kept water available for planet formation.
Meteorites from differentiated objects (i.e. planets or smaller bodies that have differentiated such that, while in a molten state, their heavy elements have sunk to a core displacing lighter elements upwards) have around 3% water content – while some undifferentiated objects (like carbonaceous asteroids) may have more than 20% water content.
Mush these materials together in a planet formation scenario and materials compressed at the centre become hot, causing outgassing of volatiles like carbon dioxide and water. In the early stages of planet formation much of this outgassing may have been lost to space – but as the object approaches planet size, its gravity can hold the outgassed material in place as an atmosphere. And despite the outgassing, hot magma can still retain water content – only exuding it in the final stages of cooling and solidification to form a planet’s crust.
Mathematical modelling suggests that if planets accrete from materials with 1 to 3% water content, liquid water probably exudes onto their surface in the final stages of planet formation – having progressively moved upwards as the planet’s crust solidified from the bottom up.
Otherwise, and even starting with a water content as low as 0.01%, Earth-like planets would still generate an outgassed steam atmosphere that would later rain down as fluid water upon cooling.
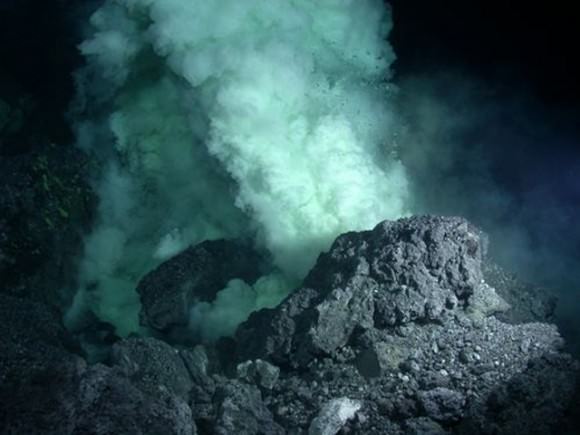

If this ocean formation model is correct, it can be expected that rocky exoplanets from 0.5 to 5 Earth masses, which form from a roughly equivalent set of ingredients, would be likely to form oceans within 100 millions years of primary accretion.
This model fits well with the finding of zircon crystals in Western Australia – which are dated at 4.4 billion years and are suggestive that liquid water was present that long ago – although this preceded the Late Heavy Bombardment (4.1 to 3.8 billion years ago) which may have sent all that water back into a steam atmosphere again.
Currently it’s not thought that ices from the outer solar system – that might have been transported to Earth as comets – could have contributed more than around 10% of Earth’s current water content – as measurements to date suggest that ices in the outer solar system have significantly higher levels of deuterium (i.e. heavy water) than we see on Earth.
Further reading: Elkins-Tanton, L. Formation of Early Water Oceans on Rocky Planets.