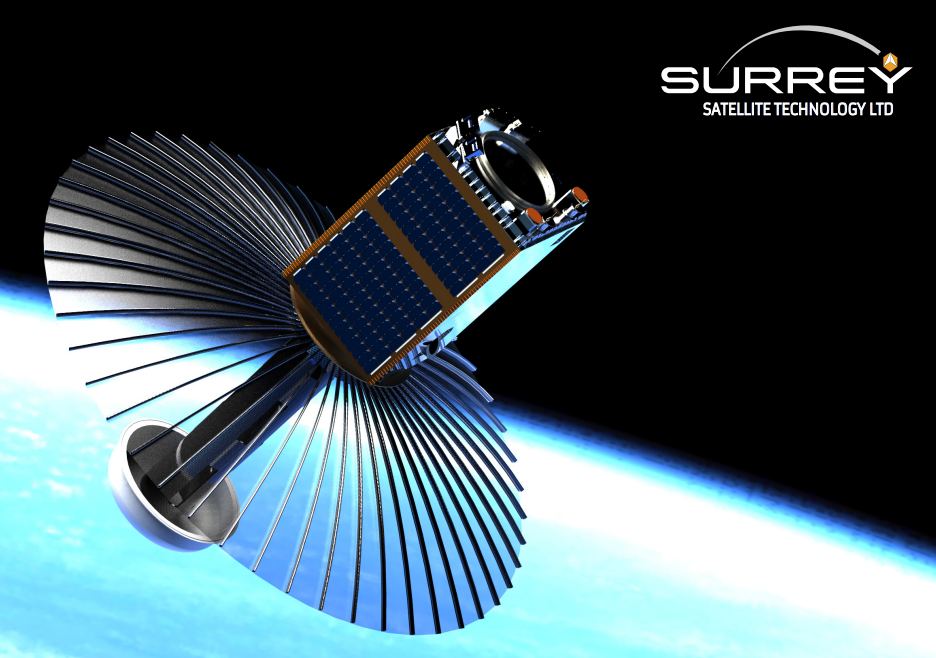
Technology Readiness Levels (or TRLs) are commonly used in the space industry to determine what level of development a technology has undergone. For space technologies, eventually, they get to a TRL where they have to be used in space. In some cases, that can be difficult, as getting a ride on a launch is both risky and expensive. So it’s good news for Oxford Space Systems (OSS) that they penned an agreement with Surrey Satellites Technology Ltd (SSTL) to prove one of their new technologies on an actual flight.
Continue reading “Two English Companies are Cooperating to Bring a Novel Antenna Architecture To Space”These are the Fastest Stars in the Galaxy
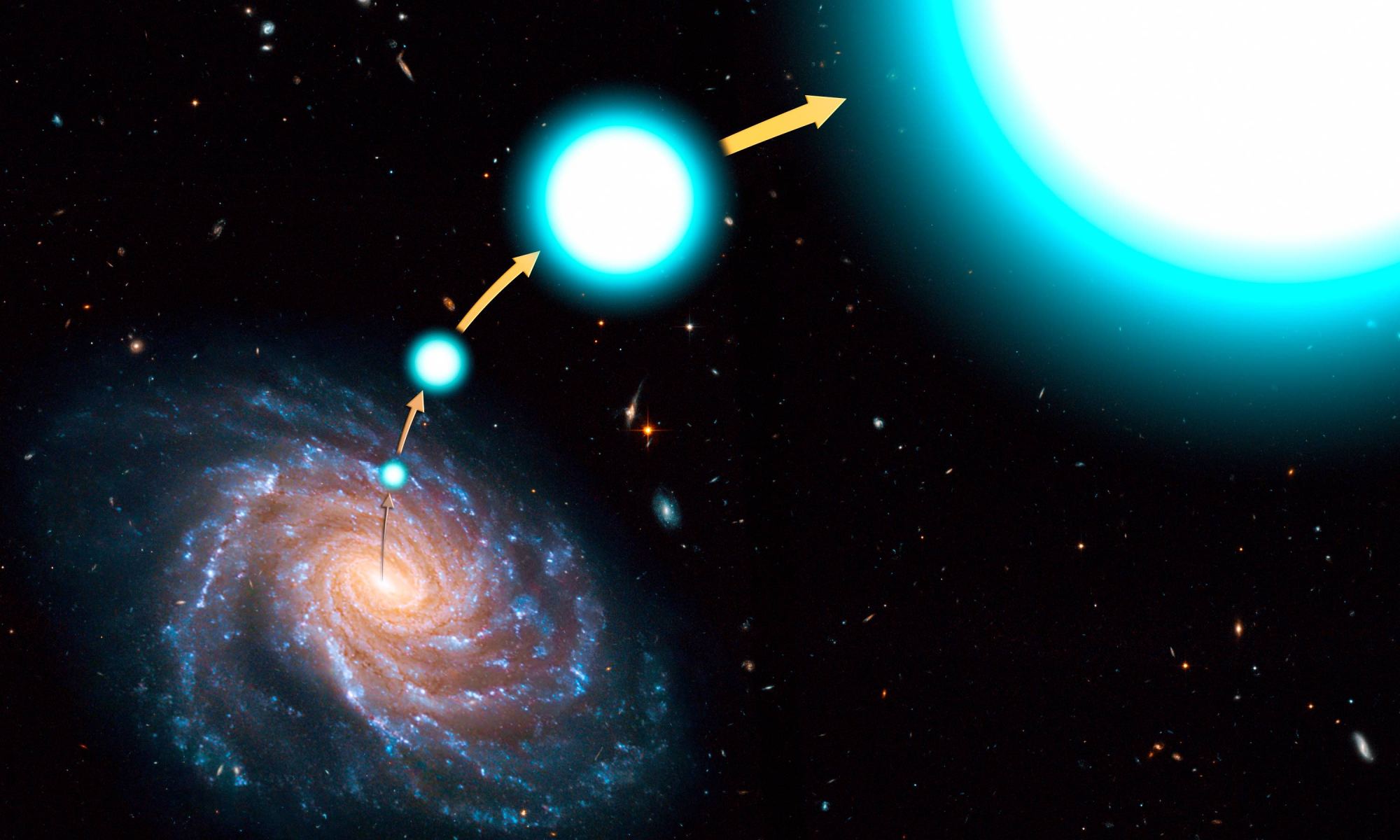
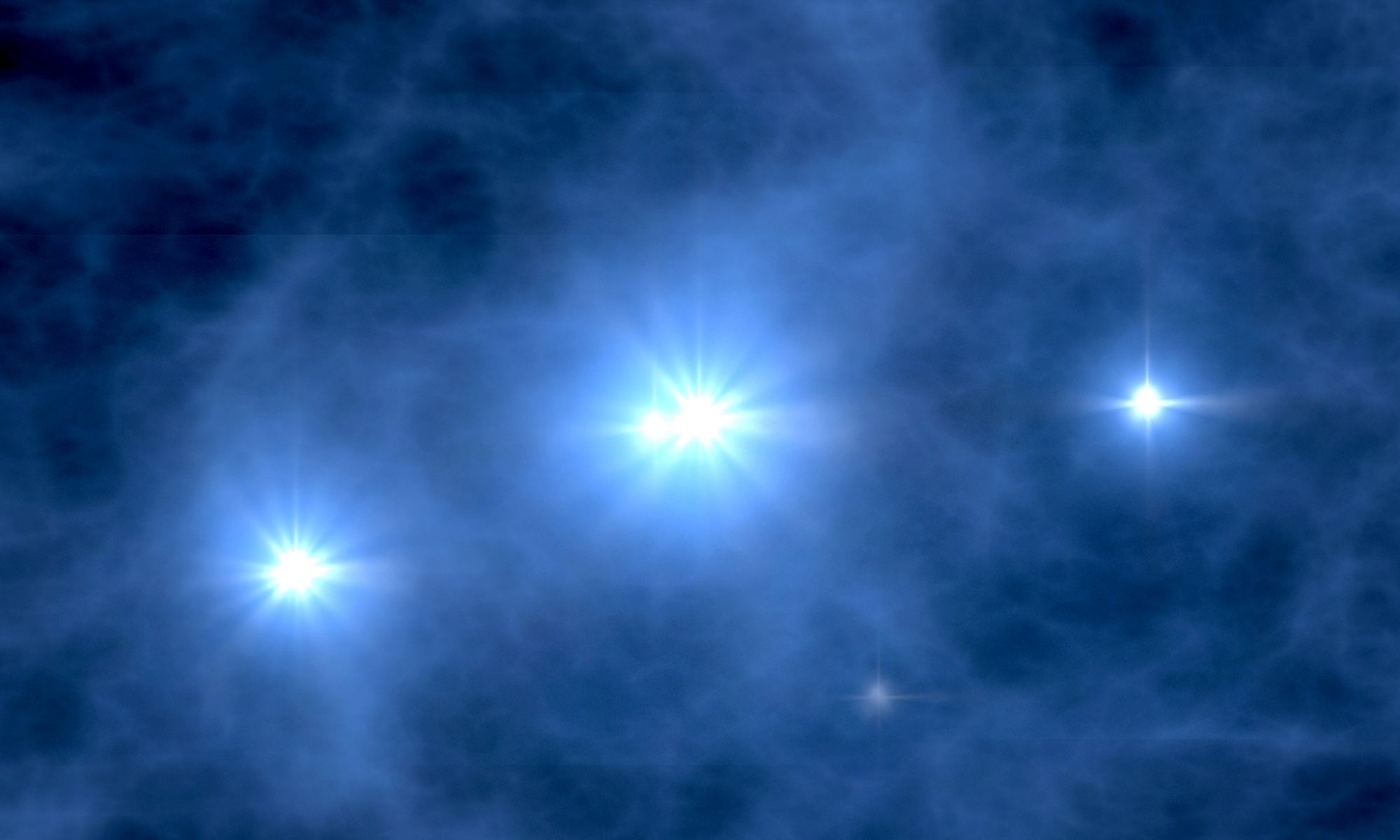
Until recently, there were only ten known stars on trajectories that will allow them to escape the Milky Way Galaxy, thrown astray by powerful supernova explosions. A new study using data from ESA’s Gaia survey this June has revealed an additional six runaways, two of which break the record for the fastest radial velocity of any runaway star ever seen: 1694 km/s and 2285 km/s.
Continue reading “These are the Fastest Stars in the Galaxy”Thierry Legault’s Stunning Views of the Space Station (with spacewalking astronauts) Crossing in Front of Sunspots
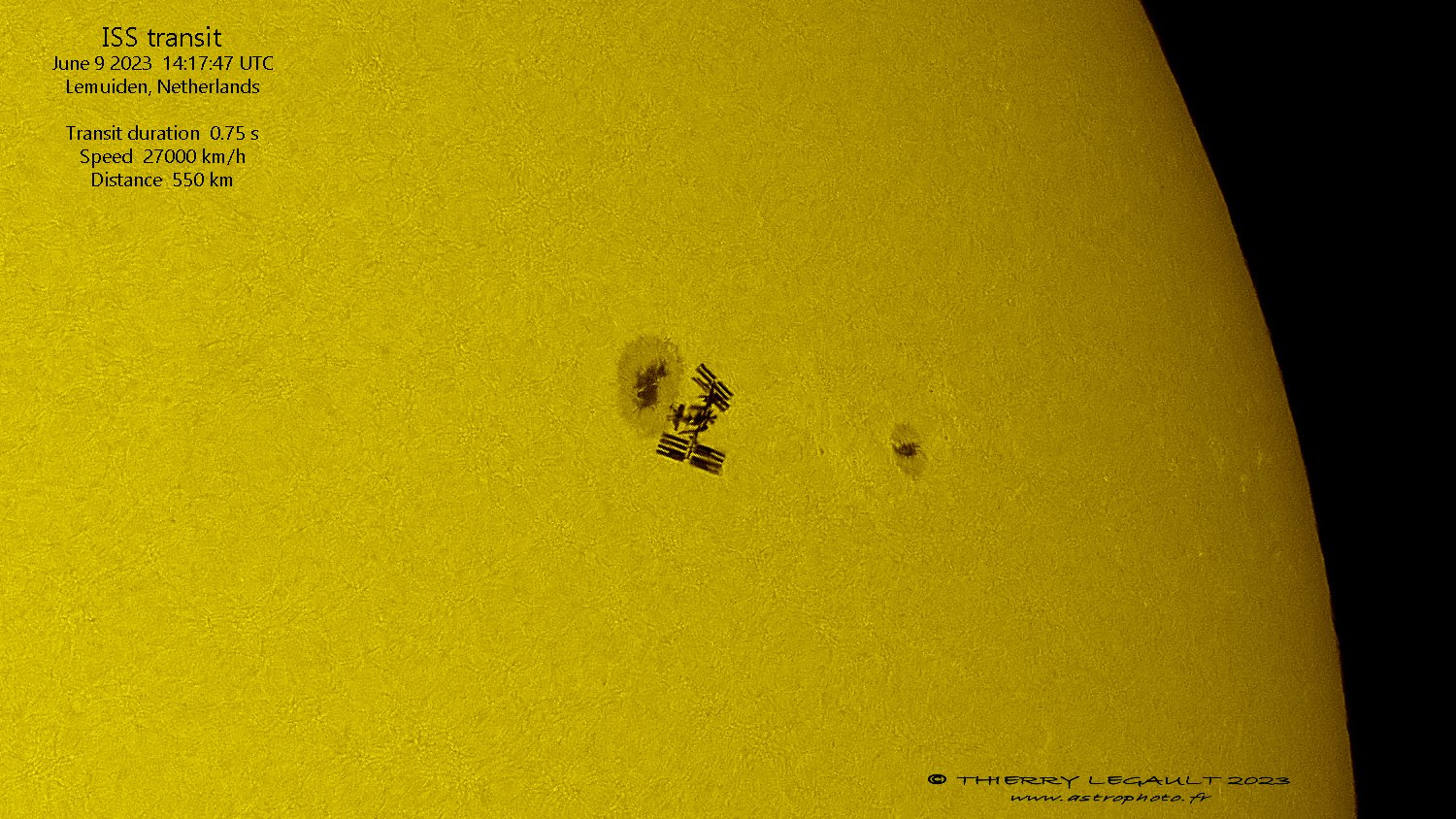

He’s done it again, outdoing even his own incredible work.
Over the years, we’ve written many articles to share the beautiful and mind-bending astrophotography of Thierry Legault. Each year he seems to come up with ideas to try to surpass even his own craziest attempts of astrophotography feats – such as capturing spy satellites in orbit, or snapping pictures of the International Space Station (ISS) transiting the Sun during a solar eclipse.
Now, he was able to take pictures of the ISS transiting the Sun while two astronauts were doing a spacewalk. As an added challenge, Legault made sure he was in the right place at the right time so he could capture the ISS (and astronauts) while they were passing by three enormous sunspots.
WHAT??
Continue reading “Thierry Legault’s Stunning Views of the Space Station (with spacewalking astronauts) Crossing in Front of Sunspots”The Sun Reaches Solar Maximum in 2032. A new NASA Flagship Mission Could Give Us a Perfect View
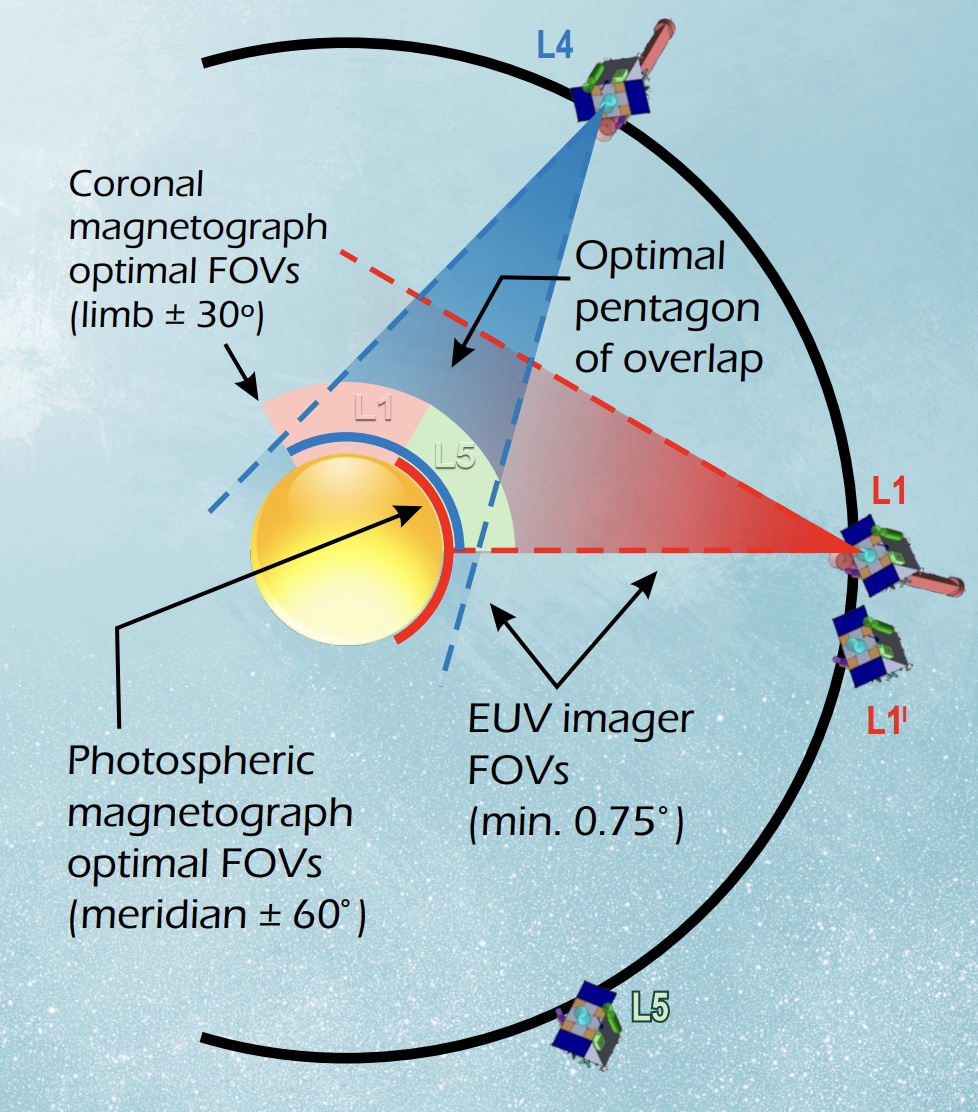
There are always more space missions than there is money to support them. Ultimately, some make the funding cut, and some do not. Various factors go into that decision, though those factors can change over the years and decades that some of these missions are designed to take. But the more ideas, the better, and now a new idea has sprung up from a group of scientists at SWRI, NASA, and the University of Minnesota, among others. It involves four different probes sent to various points in the solar system to observe the Sun as it has never been seen before – and just in time to see its most spectacular display in 2032.
Continue reading “The Sun Reaches Solar Maximum in 2032. A new NASA Flagship Mission Could Give Us a Perfect View”We Might Soon Detect the Gravitational Waves from Dying Stars
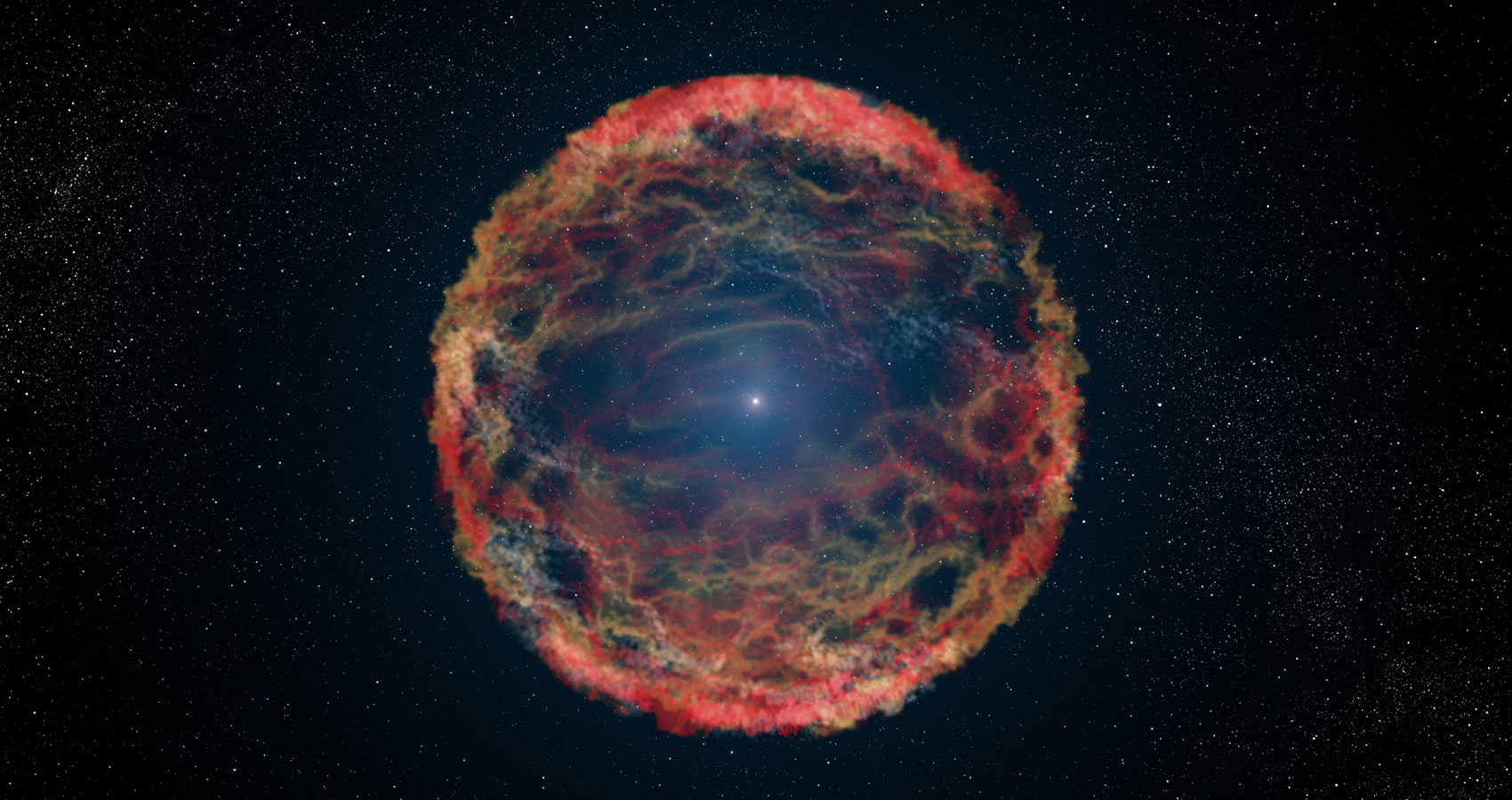
Researchers have discovered an exciting new source of gravitational waves. They are the remnants left over from a supernova explosion, and they may just reveal the secrets to how those explosions work.
Continue reading “We Might Soon Detect the Gravitational Waves from Dying Stars”Why Didn’t the Big Bang Collapse in a Giant Black Hole?

Despite the enormous densities, the early universe didn’t collapse into a black hole because, simply put, there was nothing to collapse into.
Continue reading “Why Didn’t the Big Bang Collapse in a Giant Black Hole?”What Role Will NASA Play In Developing ISRU On The Moon?

Space agencies will play a vital role in the developing space economy, especially in the beginning. But what will the part of the biggest of all space agencies be when considering how space resources, especially those on the Moon, are accessed? NASA has a plan for that as it does for so many other things – and this article will dig into a slideshow that describes that plan in detail.
Continue reading “What Role Will NASA Play In Developing ISRU On The Moon?”Parker Solar Probe Flies Close Enough to the Sun to See the Source of the Fast Solar Wind
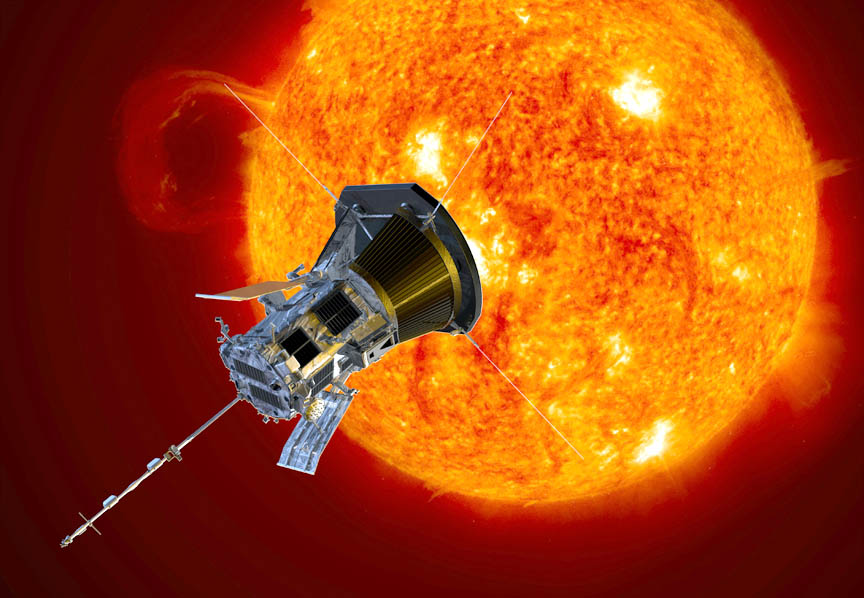
Where does the solar wind come from? That’s a question solar physicists have wanted an answer to for decades. Now, the Parker Solar Probe is showing them exactly where this stream of particles exits our star on a journey out through interplanetary space.
Continue reading “Parker Solar Probe Flies Close Enough to the Sun to See the Source of the Fast Solar Wind”Has JWST Finally Found the First Stars in the Universe?
In astronomy, elements other than hydrogen and helium are called metals. While that might make your high-school chemistry teacher cringe, it makes sense for astronomers. The two lightest elements were the first to appear in the universe. They are the atomic remnants of the big bang and make up more than 99% of atoms in the universe. All the other elements, from carbon to iron to gold, were created through astrophysical processes. Things like nuclear fusion in stellar cores, supernova explosions, and collisions of white dwarfs and neutron stars.
Continue reading “Has JWST Finally Found the First Stars in the Universe?”If We Can Master Artificial Photosynthesis, We Can Thrive in Space
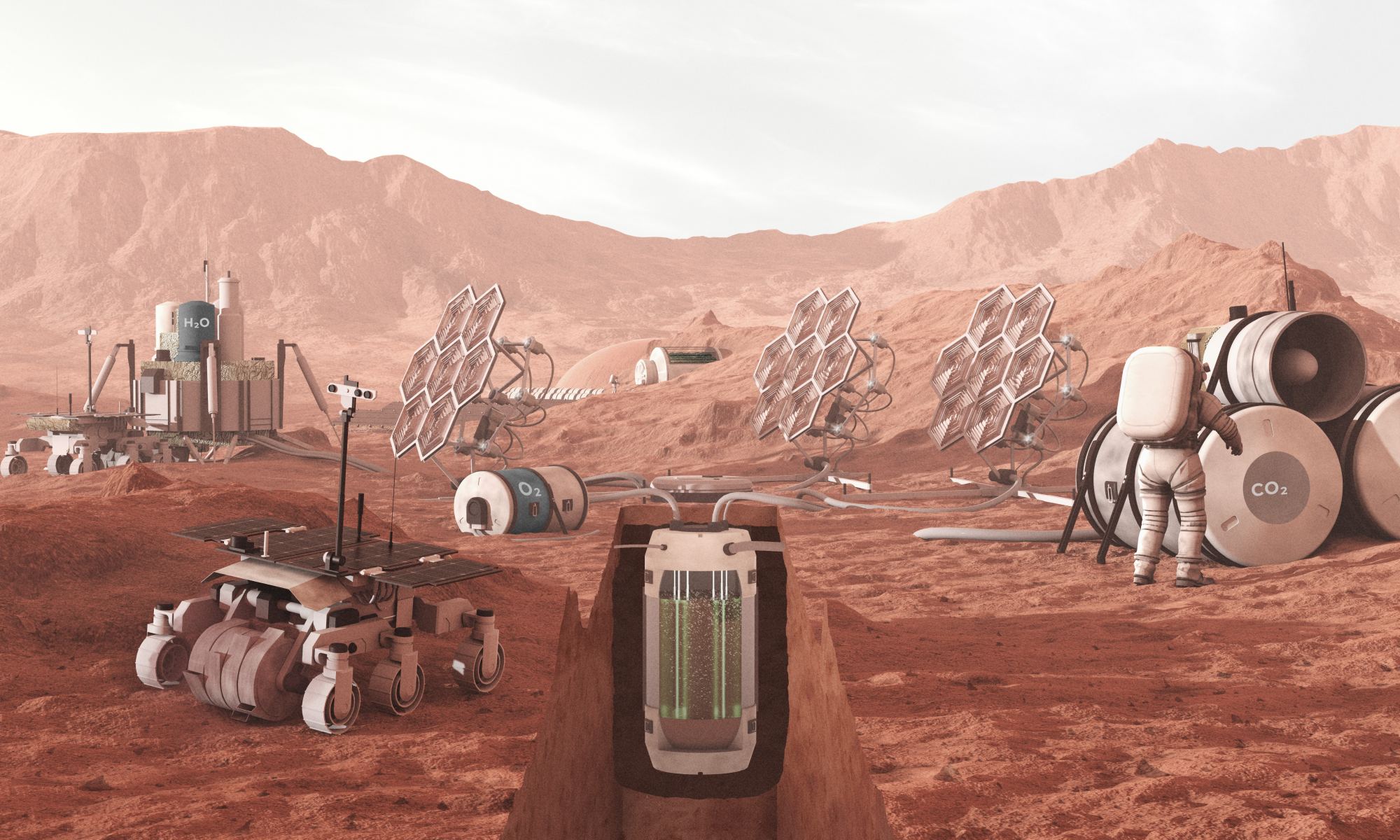

By 2030, multiple space agencies will have sent astronauts to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Program ended over 50 years ago. These programs will create lasting infrastructure, like the Lunar Gateway, Artemis Base Camp, Moon Village, and the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS). In the ensuing decade, the first crewed missions to Mars are expected to occur, culminating with the creation of the first human outposts on another planet. Commercial ventures also want to establish habitats in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), enabling everything from asteroid mining to space tourism.
One of the biggest challenges for this renewed era of space exploration (Space Age 2.0) is ensuring that humans can remain healthy while spending extended periods in space. Foremost among them is ensuring that crews have functioning life support systems that can provide a steady supply of breathable air, which poses its own technical challenges. In a recent study, a team of researchers led by Katharina Brinkert of the University of Warwick described how artificial photosynthesis could lead to a new type of life support system that is smaller, lighter, easier, and more cost-effective to send to space.
Continue reading “If We Can Master Artificial Photosynthesis, We Can Thrive in Space”