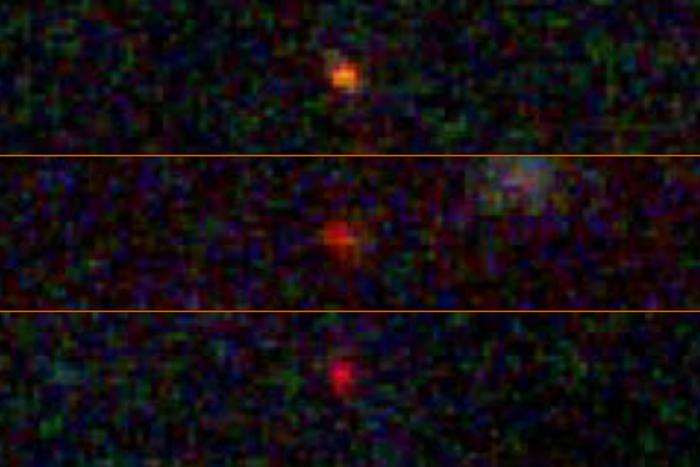
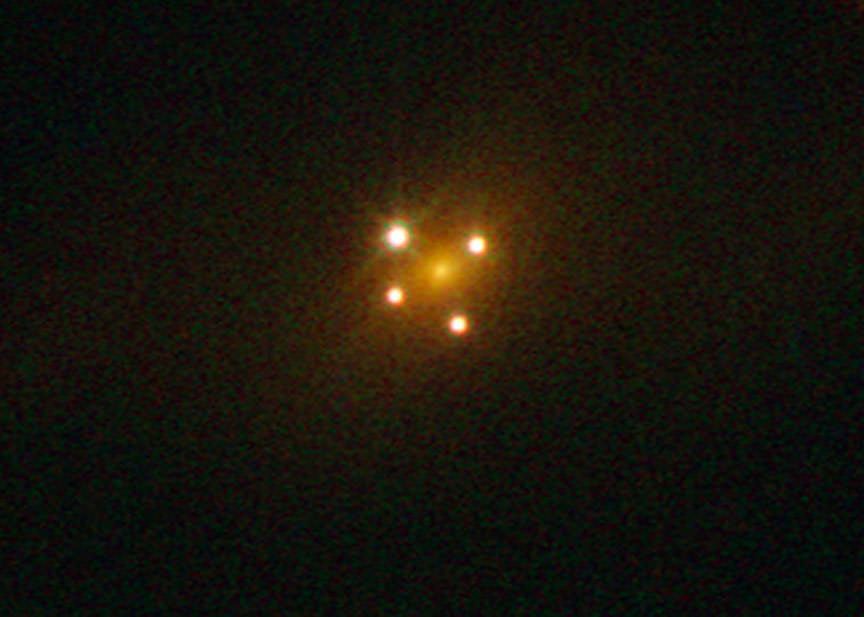
A recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) examines what are known as dark stars, which are estimated to be much larger than our Sun, are hypothesized to have existed in the early universe, and are allegedly powered by the demolition of dark matter particles. This study was conducted using spectroscopic analysis from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), and more specifically, the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES), and holds the potential to help astronomers better understand dark stars and the purpose of dark matter, the latter of which continues to be an enigma for the scientific community, as well as how it could have contributed to the early universe.
Continue reading “Have We Seen the First Glimpse of Supermassive Dark Stars?”Have We Seen the First Glimpse of Supermassive Dark Stars?