Super Secret X-37B Nears One Year In Orbit Doing ???

After nearly a year in orbit, speculation still abounds as to the X-37B spacecraft's true purpose, and what its been doing up there all this time
Continue reading
Is Earth's Magnetic Field Ready to Flip?

Recent data from the ESO's trio of Swarm satellites point to a weakening of the Earth's magnetic field as well as variations in field strength across the planet in recent years.
Continue reading
Weekly Space Hangout - May 13, 2016: Christer Fuglesang

Astronomy Cast Ep. 413: Navigating Near
Amazing Time-lapse Shows Recovered SpaceX Falcon 9 Moving To Land After Port Canaveral Arrival

The recovered SpaceX first stage booster that nailed a spectacular middle-of-the-night touchdown at sea last week sailed back to Port Canaveral, Florida, late Monday and was transferred by crane on Tuesday from the drone ship to land - as seen in an amazing time-lapse video and photos, shown above and below and obtained by Universe Today.
Continue reading
When Can I Die on Mars?

Elon Musk recently announced SpaceX's plans to send a spacecraft to the surface of Mars by 2018. It's never been easier to die on Mars.
Continue reading
What is the Biggest Star in the Universe?

If our Universe could be likened to a playground, our Sun would be one of the little kids playing in it. And the big kids, it turns out, are really big!
Continue reading
2007 OR10 Needs A Name. We Suggest Dwarfplanet McDwarfplanetyface

Astronomers using the Kepler spacecraft and data from the Herschel Space Observatory have given us a revealing glimpse of dwarf planet 2007 OR10.
Continue reading
First Hyperloop Technology Demo A Success

At a facility the Nevada Desert, the startup company known as Hyperloop One recently conducted a successful test of the technology that could revolutionize transport
Continue reading
Watch Mercury Race Across the Sun, Courtesy of the Big Bear Solar Observatory

The Big Bear Solar Observatory Captures a high-res image of this week's transit of Mercury across the face of the Sun.
Continue reading
SpaceX Dragon Returns to Earth After Splashdown with Critical NASA Science

A SpaceX cargo Dragon spacecraft loaded with nearly two tons of critical NASA science and technology experiments and equipment returned to Earth this afternoon, Wednesday, May 11, safely splashing down in the Pacific Ocean - and bringing about a successful conclusion to its mission to the International Space Station (ISS) that also brought aloft a new room for the resident crew.
Continue reading
Thanks, Comet Pluto. Solar System Nomenclature Needs A Major Rethink

Thanks to new data from the New Horizons mission that shows how Pluto behaves as both a planet and a comet, it may be necessary to reclassify this world again!
Continue reading
New Composite Image Of Saturn's Polar Vortex Mesmerizes

A new image from Cassini shows Saturn's southern polar vortex in striking detail.
Continue reading
What Are The Colors of the Planets?

When you remove all the touch-ups and filters, the planets of the Solar System look slightly different than you might imagine, especially in terms of color
Continue reading
Watch Mercury Transit the Sun in Multiple Wavelengths

No one had a better view of the transit of Mercury across the Sun than the space-based Solar Dynamics Observatory, as it had a completely unobstructed view of the entire seven-and-a-half-hour event.
Continue reading
Winged Telescope Detects Martian Atomic Oxygen
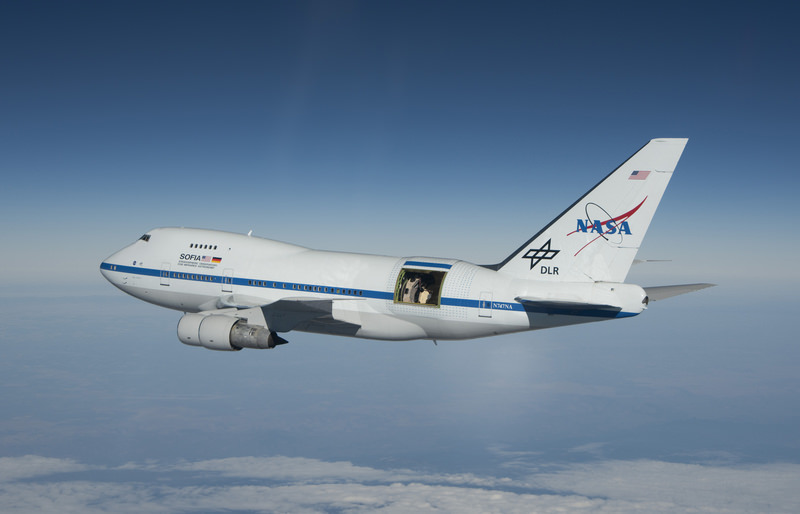

The airborne observatory SOFIA has detected atomic oxygen in Mars' upper atmosphere. It's been 40 years since oxygen has been detected there.
Continue reading
Carnival of Space #456

Recovered SpaceX Falcon 9 Booster Headed Back to Port: Launch/Landing - Photos/Videos

The SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster that successfully launched a Japanese satellite to a Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) just 3 days ago and then nailed a safe middle of the night touchdown on a drone ship at sea minutes minutes later, is headed back to port and may arrive overnight or soon thereafter.
Continue reading
Can We Really Get to Alpha Centauri?

It's going to be almost impossible to travel to another star, but a new idea was announced that might get us to a nearby star within our lifetime. How will it work?
Continue reading
Will Earth Survive When the Sun Becomes a Red Giant?
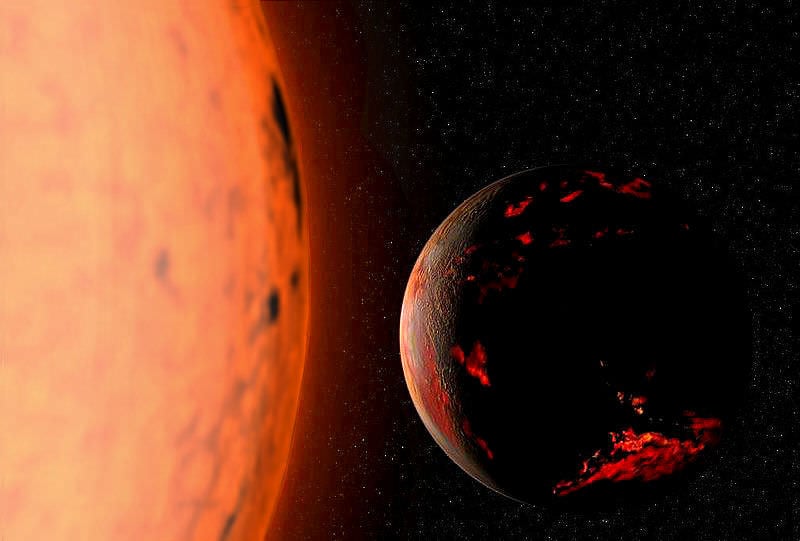

In billions of years, the Sun will enter its "Red Giant" phase and expand considerably. So naturally, we have to ask, will the Earth survive?
Continue reading
SpaceX Maiden Falcon Heavy Launch May Carry Satellite In November

The long-awaited Falcon Heavy from SpaceX may make its inaugural launch in November, 2016. But what will its payload be?
Continue reading
Messier 13 (M13) - The Great Hercules Cluster

Located in the Hercules constellation is M13, a globular cluster so large and bright that its nicknamed the "Great Hercules Cluster"
Continue reading
Images of Today's Transit of Mercury From Around the World

Amazing reader images of today's transit of Mercury across the face of the Sun from around the world.
Continue reading
Give Mom the Aurora Tonight / Mercury Transit Update

A review of last night's spectacular aurora along with a look at tonight's space weather forecast plus a recap of tomorrow's big event - the transit of Mercury.
Continue reading
Enceladus' Jets Selectively Power-Up Farther From Saturn

Unveiled Webb Telescope Mirrors Mesmerize in 'Golden' Glory

NASA GODDARD SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, MD - It's Mesmerizing ! That's the overwhelming feeling expressed among the fortunate few setting their own eyeballs on the newly exposed golden primary mirror at the heart of NASA's mammoth James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) - a sentiment shared by the team building the one-of-its-kind observatory and myself during a visit this week by Universe Today.
Continue reading
The Constellation Auriga

In the northern skies lies the constellation Auriga, one of the 44 described by Ptolemy and one of the 88 constellations recognized today by the IAU
Continue reading
Weekly Space Hangout - May 6, 2016: Paul Reichert - Photography in Space!

How Long Does it Take Mars to Orbit the Sun?

The planet Mars has a highly eccentric orbit around the Sun, and takes a little under two years for it to complete a single orbit
Continue reading
SpaceX Taps Superhero Designer For Its Spacesuits

SpaceX has hired super-hero movie costume designer Jose Fernandez to design space suits for its astronauts.
Continue reading
SpaceX Scores Double Whammy with Nighttime Delivery of Japanese Comsat to Orbit and 2nd Successful Ocean Landing

SpaceX scored a double whammy of successes this morning, May 6, following the stunning nighttime launch of a Japanese comsat to orbit on the firm's Falcon 9 rocket and nailing the breathtaking touchdown of the spent first stage just minutes later - furthering the goal of rocket reusability
Continue reading
SpaceX Set for Night Launch of Japanese Satellite and Drone Ship Landing Friday, May 6 - Watch Live

Less than 4 weeks after launching a Dragon cargo ship for NASA to the International Space Station (ISS), SpaceX is poised for their next nearly simultaneous Falcon 9 rocket launch and first stage landing attempt for what promises to be a spectacular skyshow shortly after midnight on Friday, May 6.
Continue reading
How Do We Terraform Ceres?
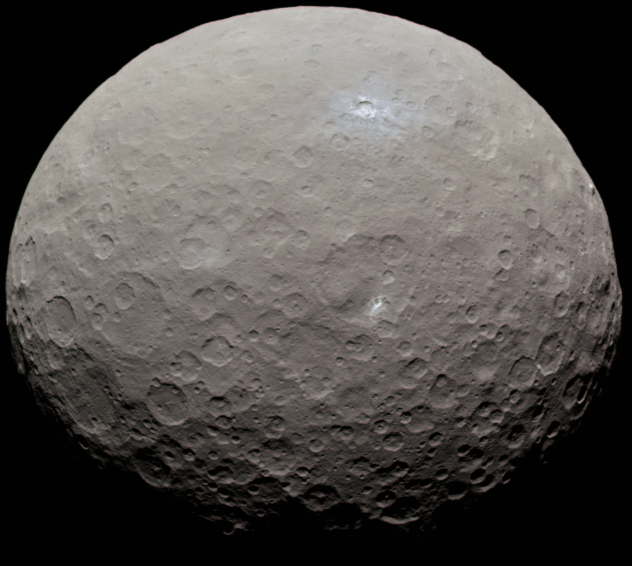

It is possible that we could someday transform Ceres, the largest object in the Asteroid Belt, to make it friendly for human habitation?
Continue reading
2016 Eta Aquarid Meteor Shower Peaks May 5-6

If you notice a rise in meteors before dawn now through the weekend, you're not imagining things. It's the annual peak of the Eta Aquarid meteor shower, when pieces of Halley's Comet strike our atmosphere.
Continue reading
Is A New Particle About To Be Announced?

The unexplained results from two separate experiments at the Large Hadron Collider point to the possible discovery of a new type of particle.
Continue reading
Starshade Prepares To Image New Earths

In the coming years, NASA will be launching its Starshade, a large spacecraft that will block the bright light of distant stars to make spotting expolanets easier
Continue reading
Boiling Water Is Carving Martian Slopes

Surface features on Mars may have been caused by boiling water.
Continue reading
A Summer Comet: Our Guide to Observing X1 PanSTARRS

Get set to observe binocular Comet C/2013 X1 PanSTARRS this summer, as it moves from the dawn to the dusk sky. Here's our handy guide, with key dates, predictions and more.
Continue reading
ExoMars 2018 Rover Postponed to 2020 Launch
Messier 12 (M12) - The NGC 6118 Globular Cluster

Messier 12, a globular cluster located some 15,700 light-years from Earth, is one of the brightest objects in the Ophiuchus constellation
Continue reading
Three New Earth-sized Planets Found Just 40 Light-Years Away

Scientists Assemble Fresh Global Map of Pluto Comprising Sharpest Flyby Images

The science team leading NASA's New Horizons mission that unveiled the true nature of Pluto's long hidden looks during the history making maiden close encounter last July, have published a fresh global map that offers the sharpest and most spectacular glimpse yet of the mysterious, icy world.
Continue reading
Fuel Control Valve Faulted for Atlas Launch Anomaly, Flights Resume Soon

A critical fuel control valve has been faulted for the Atlas V launch anomaly that forced a premature shutdown of the rockets first stage engines during its most recent launch of a Cygnus cargo freighter to the International Space Station (ISS) last month - that nevertheless was successful in delivering the payload to its intended orbit.
Continue reading
Fermi Links Neutrino Blast To Known Extragalactic Blazar

The Fermi Space Telescope has found the source of 'Big Bird', one of the most energetic neutrinos ever detected.
Continue reading
The Constellation Aries

On the ecliptic plane, bordered by constellations of Perseus, Pisces, and Taurus, is the ancient constellation known as Aries
Continue reading
Astronomy Cast Ep. 412: The Color of the Universe
The New Vostochny Cosmodrome Brings Launches Back To Russian Soil
Russia's new spaceport, the Vostochny Cosmodrome, will allow Roscosmos, the Russian Space Agency, to conduct the bulk of its launches on home soil.
Continue reading
Weekly Space Hangout - Apr. 29, 2016: Dr. Michael Richmond

How Do We Terraform Mercury?

Mercury is a hot and hostile planet, but it has many things going for it that make it an attractive option for colonizing and even partial terraforming
Continue reading
 Universe Today
Universe Today