
NASA's Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover successfully bored a brand new hole in Mars at a tantalizing sandstone outcrop in the 'Lubango' fracture zone this past weekend on Sol 1320, Apr. 23, and is now carefully analyzing the shaken and sieved drill tailings for clues to Mars watery past atop the Naukluft Plateau.
Continue reading

Among Sir Isaac Newton's many contributions to science was the discovery of gravity. one of the fundamental forces of the Universe
Continue reading

Continue reading

How astronomers found an potentially new and exciting exoplanetary system lurking on a glass plate stored away for nearly a century.
Continue reading

SpaceX announced plans today, April 27, for the first ever private mission to Mars which involves sending an uncrewed version of the firms Dragon spacecraft to accomplish a propulsive soft landing - and to launch it as soon as 2018 including certain technical assistance from NASA.
Continue reading

Within the Saturn system, there are many moons which could present the opportunity terraforming. But to do so presents many challenges.
Continue reading

Images from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have identified the lost Beagle 2 lander on the Martian surface, and might explain why the Beagle 2 failed to deploy.
Continue reading

Earlier this morning, SpaceX founder Elon Musk announced via twitter that his company plans to mount its first mission to Mars by 2018
Continue reading

Continue reading
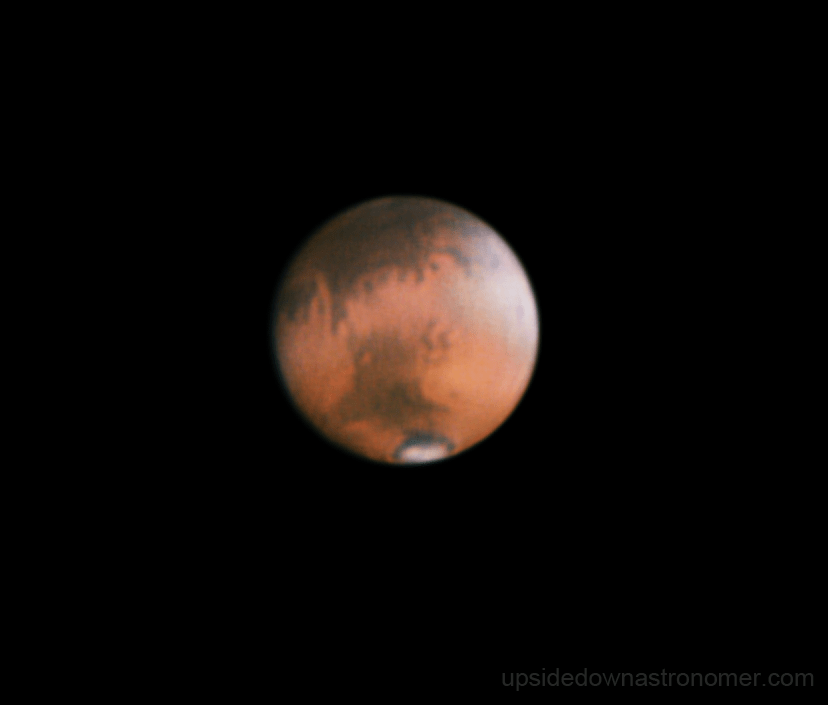

The time to observe Mars is now, as the Red Planet heads towards a favorable opposition in May 2016. Here's our complete guide to all things Martian, including observing, imaging and more.
Continue reading

Planetary scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope have spotted a dark mini-moon orbiting the distant dwarf planet Makemake. The moon, nicknamed MK 2, is roughly 160 km (100 miles) wide and orbits about 20,000 km (13,000 miles) from Makemake.
Continue reading

It's tempting to think that life is plentiful in the Universe, if only we could locate it. But a pair of researchers using Bayesian analysis have poured cold water on that idea.
Continue reading

NASA has selected Aerojet Rocketdyne to design and develop an advanced solar electric propulsion (SEP) system that will serve as a critical enabling technology for sending humans and robots on deep space exploration missions to cislunar space, asteroids and the Red Planet.
Continue reading

A recent study released by CU Anschutz indicates that prolonged time in space can cause liver damage, adding to overall health concerns
Continue reading

Stunning high definition views of Earth's auroras and dancing lights as seen from space like never before have just been released by NASA in the form of ultra-high definition videos (4K) captured from the International Space Station (ISS).
Continue reading

Jupiter's four largest moons - the Galileans - have long been considered as possible sites for human habitation, and even terraforming
Continue reading

China claims success in an experiment designed to test mammalian reproductive cell development in low-gravity.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Are you having trouble keeping track of all the planets in the Solar System? Good news! Astronomers have found evidence that there's another huge planet far out in the Solar System. Textbooks will need to be rewritten again. You're welcome.
Continue reading

The team in charge of NASA's Dawn mission have asked to extend the spacecraft's journey to a third destination.
Continue reading

Now in orbit for just over a year at dwarf planet Ceres, NASA's Dawn spacecraft continues to astound us with new discoveries gleaned from spectral and imagery data captured at ever decreasing orbits as well as since the probe arrived last December at the lowest altitude it will ever reach during the mission.
Continue reading

The recovered SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster that successfully carried out history's first upright touchdown from a just flown rocket onto a droneship at sea, has just been moved back to the firms processing hanger at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) for testing and eventual reflight.
Continue reading

A new paper concludes that a super-Earth size planet may reside in the habitable zone of a star only 16 light years away.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Recent findings from a team of researchers in South Africa have shown that supermassive black holes in distance are all spinning in the same direction
Continue reading

A Super-Earth may have formed in our Solar System's earlier days, and then been destroyed by the Sun.
Continue reading

As a gas giant, Neptune has no surface, in the traditional sense. But atop its cloud layers, some pretty amazing things are happening
Continue reading

I've said in the past that the Universe isn't expanding into anything. But what if we're living in a vast multiverse, and our Universe is bumping up against other universes?
Continue reading

One weld at a time, the flight hardware for NASA's mammoth new Space Launch System (SLS) booster has at last started taking shape, promising to turn years of planning and engineering discussions into reality and a rocket that will one day propel our astronauts on a 'Journey to Mars.'
Continue reading

The changing brightness of the haze layers in Pluto's nitrogen atmosphere are caused by atmospheric gravity waves, according to data from New Horizons.
Continue reading

Why this week's Full Moon is the smallest of 2016. It's Mini-Moon season!
Continue reading

Antarctica is a rich source of Martian meteorites, which are studied for clues to the formation and evolution of the Solar System.
Continue reading

The discovery of a Dwarf Dark Galaxy addresses the Missing Satellite Problem, and tells us we're on the right track in our understanding of the Universe, and Dark Matter's role in it.
Continue reading

Nearly 40 years after it was first detected, a Florida astronomer proposes that comets may be to blame for the famed extraterrestrial "Wow! signal".
Continue reading

The International Space Station (ISS) grew in size today, April 16, following the successful installation of an experimental new room - the BEAM expandable habitat module.
Continue reading
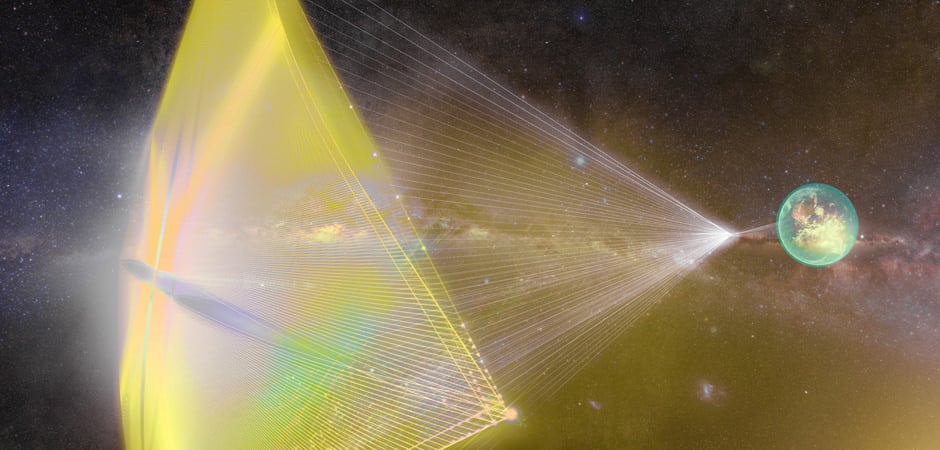
With all the attention Breakthrough Starshot has been getting some are wondering if Alpha Cantauri is the best place to mount an interstellar mission
Continue reading

SpaceX has released a slew of up close photos showing the sensational "super smooth" touchdown last week of a Falcon 9 booster on a tiny droneship at sea located several hundred miles (km) off the East coast of Florida. "This time it really went super smooth," Hans Koenigsmann, SpaceX VP of Flight Reliability, told Universe Today
Continue reading
Continue reading

Continue reading

ExoMars returns its first image, proof that the camera system is functioning as intended.
Continue reading

Researchers have discovered the first Hyper-Velocity binary star, and its location, and possible relationship with Dark Matter, is a puzzle.
Continue reading

Continue reading

On Monday, May 9 Mercury will make one of its relatively rare transits of the Sun. Get ready for the event by making sure you have access to a telescope and solar filter.
Continue reading

We're always concerned about the weather here on Earth, but what about the Moon? Is there any weather up there that astronauts will have to worry about?
Continue reading
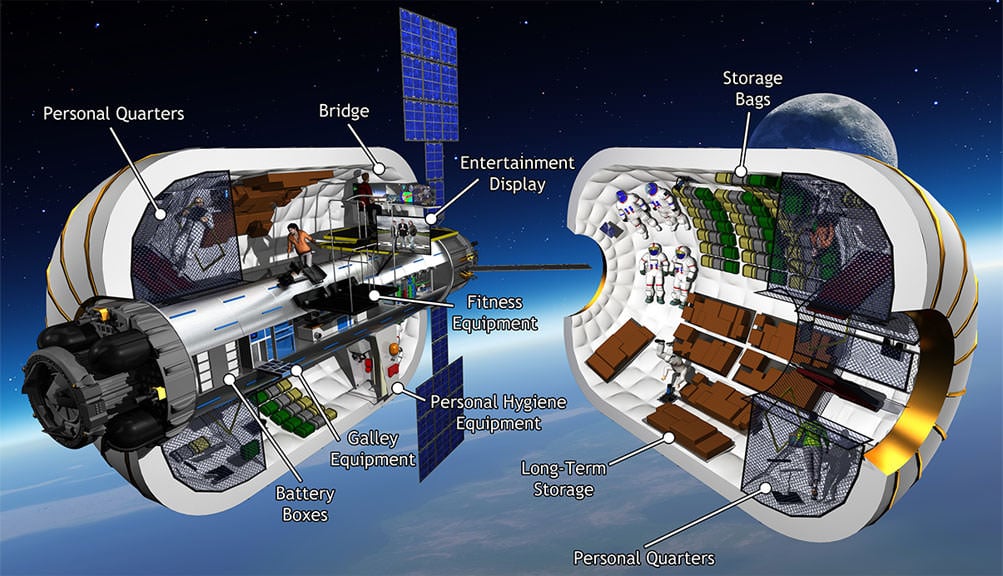
Bigelow Aerospace and United Launch Alliance (ULA) announced they are joining forces to develop and launch the world's first commercial space habitat to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) by 2020 - potentially as a huge and revolutionary new addition to the International Space Station (ISS).
Continue reading

Since 2013, the NEOWISE mission has surveyed more than 19,000 asteroids and comets and discovered 72 new Near Earth Objects (NEOs)
Continue reading

Stephen Hawking supports a plan to send tiny nano-spacecraft to the Centauri system within a generation.
Continue reading

Air pollution is a major issue facing us Earthlings, and knowing its causes (both natural and man-made) is a key part in addressing it
Continue reading

On April 12, 1961, Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first person in space.
Continue reading

A more accurate measurement of standard candles has thrown a wrench into our standard model of cosmology.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today














































