Image credit: NASA
NASA announced today that the Spitzer Space Telescope will be their new name for the Space Infrared Telescope Facility, which was launched a few months ago. The space observatory was named after the late Dr. Lyman Spitzer Jr., who was an influential scientist and one of the first to propose building space-based telescopes. As part of the announcement, NASA also released a series of new images taken by the observatory, including a glowing stellar nursery, a dusty galaxy, and a disc of planet-forming debris.
A new window to the universe has opened with today’s release of the first dazzling images from NASA’s newly named Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly known as the Space Infrared Telescope Facility.
The first observations, of a glowing stellar nursery; a swirling, dusty galaxy; a disc of planet-forming debris; and organic material in the distant universe, demonstrate the power of the telescope’s infrared detectors to capture cosmic features never before seen.
The Spitzer Space Telescope was also officially named today after the late Dr. Lyman Spitzer, Jr. He was one of the 20th century’s most influential scientists, and in the mid-1940s, he first proposed placing telescopes in space.
“NASA’s newest Great Observatory is open for business, and it is beginning to take its place at the forefront of science,” said NASA’s Associate Administrator for Space Science, Dr. Ed Weiler. “Like Hubble, Compton and Chandra, the new Spitzer Space Telescope will soon be making major discoveries, and, as these first images show, should excite the public with views of the cosmos like we’ve never had before.”
“The Spitzer Space Telescope is working extremely well. The scientists who are starting to use it deeply appreciate the ingenuity and dedication of the thousands of people devoted to development and operations of the mission,” said Dr. Michael Werner, project scientist for the Spitzer Space Telescope at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
Launched Aug. 25 from Cape Canaveral, Fla., the Spitzer Space Telescope is the fourth of NASA’s Great Observatories, a program designed to paint a more comprehensive picture of the cosmos using different wavelengths of light.
While the other Great Observatories have probed the universe with visible light (Hubble Space Telescope), gamma rays (Compton Gamma Ray Observatory) and X-rays (Chandra X-ray Observatory), the Spitzer Space Telescope observes the cosmos in the infrared. Spitzer’s unprecedented sensitivity allows it to sense infrared radiation, or heat, from the most distant, cold and dust-obscured celestial objects. Today’s initial images revealed the versatility of the telescope and its three science instruments. The images:
— Resembling a creature on the run with flames streaming behind it, the Spitzer image of a dark globule in the emission nebula IC 1396 is in spectacular contrast to the view seen in visible light. Spitzer’s infrared detectors unveiled the brilliant hidden interior of this opaque cloud of gas and dust for the first time, exposing never-before-seen young stars.
— The dusty, star-studded arms of a nearby spiral galaxy, Messier 81, are illuminated in a Spitzer image. Red regions in the spiral arms represent infrared emissions from dustier parts of the galaxy where new stars are forming. The image shows the power of Spitzer to explore regions invisible in optical light, and to study star formation on a galactic scale.
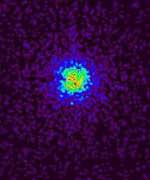
— Spitzer revealed, in its entirety, a massive disc of dusty debris encircling the nearby star Fomalhaut. Such debris discs are the leftover material from the building of a planetary system. While other telescopes have imaged the outer Fomalhaut disc, none was able to provide a full picture of the inner region. Spitzer’s ability to detect dust at various temperatures allows it to fill in this missing gap, providing astronomers with insight into the evolution of planetary systems.
— Data from Spitzer of the young star HH 46-IR, and from a distant galaxy 3.25 billion light-years away, show the presence of water and small organic molecules not only in the here and now, but, for the first time, far back in time when life on Earth first emerged.
JPL manages the Spitzer Space Telescope mission for NASA’s Office of Space Science, Washington. Science operations are conducted at the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. Major partners are Lockheed Martin Corporation, Sunnyvale, Calif.; Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corporation, Boulder, Colo.; NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.; Boeing North America (now DRS Technologies, Inc.) Anaheim, Calif.; the University of Arizona, Tucson; and Raytheon Vision Systems, Goleta, Calif. The instrument principal investigators are Dr. Giovanni Fazio, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, Mass.; Dr. James Houck, Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y.; and Dr. George Rieke, University of Arizona, Tucson.
The images are available at http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu and http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov . Additional information about the Spitzer Space Telescope is available at http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu .
Original Source: NASA/JPL News Release