Astronomers from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics announced today that they have discovered a Jupiter-class planet orbiting a star 5,000 light years away – the most distant ever found. The planet, called Ogle-TR-56b is important because it’s only the second planet ever discovered that passes directly in front of its star, dimming it slightly. More than 100 extrasolar planets have now been discovered. (BBC Article)
Starving Black Hole at the Centre of our Galaxy

Image credit: Chandra
Using the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, astronomers have created one of the most vivid images of Sagittarius A, an area at the centre of our Milky Way galaxy thought to contain a supermassive black hole. The exposure was made over a period of two weeks, and during that time, the region flared up several times; presumably when additional material reached the black hole’s event horizon.
This Chandra image of the supermassive black hole at our Galaxy’s center, a.k.a. Sagittarius A* or Sgr A*, was made from the longest X-ray exposure of that region to date. In addition to Sgr A* more than two thousand other X-ray sources were detected in the region, making this one of the richest fields ever observed.
During the two-week observation period, Sgr A* flared up in X-ray intensity half a dozen or more times. The cause of these outbursts is not understood, but the rapidity with which they rise and fall indicates that they are occurring near the event horizon, or point of no return, around the black hole. Even during the flares the intensity of the X-ray emission from the vicinity of the black hole is relatively weak. This suggests that Sgr A*, weighing in at 3 million times the mass of the Sun, is a starved black hole, possibly because explosive events in the past have cleared much of the gas from around it.
Evidence for such explosions was revealed in the image – huge lobes of 20 million-degree Centigrade gas (the red loops in the image at approximately the 2 o’clock and 7 o’clock positions) that extend over dozens of light years on either side of the black hole. They indicate that enormous explosions occurred several times over the last ten thousand years.
Further analysis of the Sgr A* image is expected to give astronomers a much better understanding of how the supermassive black hole in the center of our galaxy grows and how it interacts with its environment. This knowledge will also help to understand the origin and evolution of even larger supermassive black holes found in the centers of other galaxies.
Original Source: Chandra News Release
Distant and Fast Moving Object Discovered

Image credit: NASA
A team of astronomers from the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena presented images today of a rare Hyper Extremely Red Object (Hero). This dim object, located near a galaxy 10 billion light years away is traveling away from us at almost the speed of light. In fact, it’s so far, and moving so fast, it has gone way past being red-shifted – it’s only visible in infrared light.
Heroes are usually confined to comic books and movies, but as the saying goes, we all need one. So astronomers have turned to the deep, dark cosmos to find their heroic figure — the “Hyper Extremely Red Object,” or “Hero.”
At the American Astronomical Society winter meeting in Seattle today, an astronomer from the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena reports the discovery of a Hero near the radio galaxy 53W002, more than 10 billion light years away. This marks the first time a Hero has been found near a radio galaxy, suggesting that radio galaxies — which are optically dim but have strong radio emissions — may provide a guidepost for scouting out other Hero objects.
“Hero objects are intriguing. Like comic book heroes, they travel really fast — almost at the speed of light. They are virtually invisible to our eyes and they are very mysterious. Most importantly, this type of Hero may hold a key for understanding how the first galaxies formed and evolved in the universe,” said Dr. Myungshin Im, a staff research scientist at the Space Infrared Telescope Facility Science Center, located at Caltech.
So far, the astronomical version of a hero has taken on the unassuming guise of a small, glowing, red patch in deep space. More advanced infrared telescopes like NASA’s Space Infrared Telescope Facility, managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., and launching in spring 2003, may, among other things, lift this red veil and reveal these remote objects for what they really are — quite possibly the universe’s earliest stars and galaxies.
Due to expansion of the universe after the Big Bang, a distant object in the universe races away from us so fast that any visible light from it “redshifts” — in other words, a light source becomes redder when it recedes from observers on Earth, and, conversely, bluer when it approaches. So when a visible light source moves away from us at nearly the speed of light, it often appears in infrared wavelengths. Big Bang theory also implies that the farther away an object is, the faster it moves away from us.
53W002_HERO1, the designation for the newly found Hero, is so far away and moves so fast it appears as a faint infrared source. In fact, it took two powerful telescopes equipped with infrared cameras to spot it in the deep sky. Im discovered 53W002_HERO1 from images taken by the near-infrared camera and multi-object spectrometer on NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the cooled infrared spectrograph and camera attached to the Subaru 8-meter (26-feet) telescope atop Mauna Kea in Hawaii. Dr. Toru Yamada and collaborators at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan provided Im with the Subaru data.
The more distant a cosmic object is, the further in the past we see it. But for Im and colleagues to glean information about the early universe from 53W002_HERO1, they first need to determine its intrinsic color — that is, how would this astronomical hero appear to a human observer nearby?
It could be red, indicating either dust-obscured galaxies cocooning intense star formation, or older galaxies filled with an overabundance of elderly, reddish stars, both of which would lie about 10 billion light-years away. If the former condition exists, astronomers will appreciate the degree to which dust hid star formation during that epoch. However, if the latter holds then scientists can trace back to a time when a significant population of stars were born.
Another possibility is that a Hero might really be blue — a very young galaxy populated with fresh, super-hot blue stars at a distant 13 to 14 billion light years. In this instance, we may be witnessing the formation of the universe’s very first galaxies.
To determine whether 53W002_HERO1 is intrinsically red or blue, Im and his colleagues will peer at these mysterious objects in the redder part of infrared, a feat that requires a view from above Earth’s infrared-absorbing atmosphere. This will be accomplished with the Space Infrared Telescope Facility.
Original Source: NASA/JPL News Release
Ring of Stars Found Around our Milky Way

Image credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Astronomers announced today that they have discovered a giant ring of stars circling the Milky Way. They believe this ring could contain as many as 500 million stars, and was formed when our galaxy collided with a smaller, dwarf galaxy several billion years ago. Other galaxies have been seen with a halo of stars, including Andromeda.
A previously unseen band of stars beyond the edge of the Milky Way galaxy has been discovered by a team of scientists from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). The discovery could help to explain how the galaxy was assembled 10 billion years ago.
This ring around the Milky Way galaxy discovered by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey may be what’s left of a collision between our galaxy and a smaller, dwarf galaxy that occurred billions of years ago. It’s an indication that at least part of our galaxy was formed by many smaller or dwarf galaxies mixing together, explained investigators Heidi Jo Newberg of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and Brian Yanny of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory’s Experimental Astrophysics Group. For illustration purposes, the sun is approximately 30,000 light years from the center of the galaxy. Traveling from Earth at the speed of light, it would take 40,000 light years to reach the newly-discovered ring of stars.
Hidden from view behind stars and gas on the same visual plane as the Milky Way, this ring of stars is approximately 120,000 light years in diameter, says Heidi Newberg, associate professor of physics and astronomy at Rensselaer and a co-lead investigator on the project. Traveling from Earth at the speed of light, it would take 40,000 light years to reach the ring.
“These stars may be what’s left of a collision between our galaxy and a smaller, dwarf galaxy that occurred billions of years ago,” says Newberg. “It’s an indication that at least part of our galaxy was formed by many smaller or dwarf galaxies mixing together.”
The ring of stars is probably the largest of a series of similar structures being found around the galaxy. Investigators believe that as smaller galaxies are pulled apart, the remnants dissolve into streams of stars around larger galaxies. Gravity, primarily from unseen dark matter, holds the ring in a nearly circular orbit around the Milky Way.
“What’s new is the position of the star belt on the outskirts of the Milky Way, an ideal position to study the distribution and amount of dark and light mass within the band,” said Brian Yanny, a scientist at Fermilab’s Experimental Astrophysics Group and a co-lead investigator on the project.
Newberg and Yanny presented their findings today at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Seattle, Washington.
Evidence of this new unexpected band of stars hidden by the Milky Way comes from multi-color photo imagery of hundreds of square degrees of sky and hundreds of spectroscopic exposures from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, the largest international collaborative astronomical survey ever undertaken.
For four years Newberg, Yanny, and a collaboration of SDSS scientists have been examining the distribution of stars in the Milky Way. At the outer edge of the galaxy in the direction of the constellation Monoceros (the Unicorn) they found tens of thousands of unexpected stars that altered then-standard galactic models.
Three-dimensional mapping from the SDSS revealed the excess stars were actually parts of a separate structure outside the Milky Way.
“The large area covered by the Sloan Survey and the accuracy of the multi-colored observations has allowed us to revisit some classic questions, questions from 50 to 100 years ago,” Yanny said. “What does our Milky Way look like as a whole? How did it form? Did it form in one ‘whoosh,’ or was it built up slowly via mergers of collapsing dwarf galaxies? And how does the mysterious dark (invisible) matter affect the distribution of stars?”
Original Source: SDSS News Release
Titan II Lofts Coriolis Satellite

Image credit: USAF
After five scrubbed launch attempts, a Titan II rocket finally roared up from Vandenberg Air Force Base on Monday, lifting a Coriolis spacecraft into orbit. The $224 million satellite was funded by the US Air Force and Navy to study wind patterns in the Earth’s oceans. The Titan II rocket that launched the satellite used to be tipped with a nuclear warhead, but it was repurposed as part of the strategic arms reductions.
The 30th Space Wing, the 576th Flight Test Squadron here and a task force from the 91st Space Wing, Minot AFB, N.D., launched an unarmed Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile at 4:31 a.m. today from North Vandenberg as part of a flight test for Air Force Space Command’s Force Development Evaluation Program.
Launch activities were directed by Capt. Rob Light, 576th FLTS. Lt. Col. James Cardinal, 91st Maintenance Operations Squadron commander, was the task force commander. Lt. Col. Anthony Blaylock, 576th FLTS commander, was mission director for this launch. Col. Wayne Louis, 30th Space Wing vice commander, was the spacelift commander, or final go/no-go authority for the launch.
Original Source: Air Force News Release
Finding Salt on Io
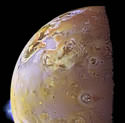
Image credit: NASA
A team of French and American astronomers have discovered the presence of salt (NaCl) in Io’s atmosphere. They think that the salt was ejected into the Jovian moon’s atmosphere by the many volcanos that ceaselessly bubble across its surface. The atmosphere of Io has been studied for several years now, first observed closely by the Voyager spacecraft, but this is the first time it’s been found to contain good old “table salt”.
The atmosphere of Jupiter’s moon Io is one of the most peculiar of the Solar System. In 1979, theVoyager spacecraft revealed active volcanism (Figure 1, left) at the surface of the satellite and discovered a local, tenuous SO2 atmosphere. Since 1990, millimeter-wave observations acquired at IRAM (French-German-Spanish telescope) and UV observations with HST provided a somewhat more detailed description of this atmosphere. The typical surface pressure is about 1 nanobar, and, in a unique fashion in the Solar System, the atmosphere exhibits strong horizontal variations, being apparently concentrated in an equatorial band.The main atmospheric compounds are SO2, SO and S2. The atmosphere is probably produced, on the one hand by direct volcanic output, and on the other hand by the sublimation of SO2 ices that cover Io’s surface.
However, it has been long suspected than Io’s atmosphere must contain other chemical species. As early as 1974, visible imaging and spectroscopy revealed a “cloud” of atomic sodium (Figure 1, right), roughly centered about Io’s orbit. Detailed subsequent studies of this cloud indicated a complex structure, including notably “fast sodium” features, for the production of which the role of molecular ions (NaX+ ) was evidenced. These discoveries naturally raised the question of the origin of sodium in Io’s environment. From the brightness of the optical emissions of Na, one can estimate that about 1026-1027 sodium atoms leave Io each second.
In 1999, chlorine in atomic and ionized form was discovered around Io, with an abundance comparable to that of sodium (while the cosmochemical abundance of Na is about 15 times that of Cl). This suggests a common origin, NaCl being a natural plausible parent of both. At the same time, on the basis of thermochemical equilibrium calculations, NaCl was proposed to be an important compound of Io’s volcanic magmas, with an abudance relative to SO2 as high as several percent.
Based on these discoveries and predictions, an observing campaign was conducted by E. Lellouch, from Paris Observatory, and several French and American colleagues at the IRAM 30-m radiotelescope in January 2002. Two rotational lines of NaCl at 143 and 234 GHz were unambiguously detected (Figure 2.). Because the vapor pressure of this salt is entirely negligible, NaCl cannot be in sublimation equilibrium with Io’s surface and its presence must directly result from continuous volcanic output. It appears to be a minor armospheric species. The most plausible physical model depicts the NaCl atmosphere as more localized than SO2, due to its very short lifetime (a few hours at most), and probably restricted to the volcanic centers. The local NaCl abundance in this model is 0.3-1.3 % of SO2, significantly lower than predicted. From the line strengths, volcanic emission rates of (2-8)x1028 NaCl molecules per second can be derived. According to photochemical and escape models, only a small fraction of these molecules escape from Io (about 0.1 %). A somewhat larger amount (1-2 %) leaves Io in atomic form after being photolyzed to Na and Cl. The vast majority of the volcanically-emitted NaCl molecules fall back to the surface where they condense out, potentially contributing to the white color of some of Io’s terrains. In conclusion, it appears that NaCl provides an importante source of sodium and chlorine in Io’s environment; however the precise chemical nature of the NaX+ molecular ions remains to be elucidated.
Original Source: Paris Observatory News Release
Shenzhou 4 Lands
China’s fourth unmanned space capsule, Shenzhou IV, returned to Earth on Sunday landing on the central grasslands of Inner Mongolia. According to several Chinese news sources, the capsule functioned properly, and several experiments were carried out successfully. The spacecraft was built to match the actual operations of a manned capsule, so it’s expected this will be China’s final test before actually putting humans in space – some time in 2003.
Want Me to Start an International Space Agency?
In my previous newsletter, I griped about the fact that we Canadians, and in fact the rest of the world aren’t able to participate in naming NASA’s next set of Mars rovers. Okay, I can understand why; it’s a US mission, so only Americans should get to name the little critters. Fine, I’m cool with that. Then I joked that someone should start an International Space Agency.
Mixed in with the “welcome back” email I received on Friday, I received a clever idea from one reader that suggested I start an International Space Agency. Accept people’s donations through Paypal or something, and then portion it out to various deserving research institutions, space associations, etc. – anyone who’s actually working on space exploration.
Obviously, the first instinct was to reject the idea instantly. Where are the engineers? The astronauts? The paperwork? Isn’t what makes a space agency? But then I thought, why not? Isn’t that just what NASA does, but on a vastly larger level?
Of course there are a few details (finding worthy recipients, doing the accounting, etc), but it actually sounds like quite a simple thing to put together initially. So let me know what you think? Are you looking for a way to contribute to the exploration of space? Send me your feedback? maybe I’ll figure out a way to organize all of us armchair space patrons.
Fraser Cain, Publisher
[email protected]
Fourth Shenzhou Spaceflight Proceeding Normally
The Chinese space program reached its next objective on Monday with the launch of its fourth unmanned Shenzhou spacecraft. Officials from the country’s space agency say that everything has gone according to plan, and the spacecraft is functioning normally. The spacecraft is designed to be identical with a future, manned version – which China hopes to launch some time in 2005.
Dark Energy Dominated Universe

Image credit: Hubble
A new paper published by Dartmouth university researcher Brian Chaboyer reports that our universe might be dominated by “dark energy”; a mysterious force that seems to be causing objects in the universe to accelerate away from each other. The researchers came to this conclusion by calculating the age of distant globular clusters, and matching it to the expansion age of the universe. The numbers only match if the universe has been accelerating up until now.
A Dartmouth researcher is building a case for a “dark energy”-dominated universe. Dark energy, the mysterious energy with unusual anti-gravitational properties, has been the subject of great debate among cosmologists.
Brian Chaboyer, Assistant Professor of Physics and Astronomy at Dartmouth, with his collaborator Lawrence Krauss, Professor of Physics and Astronomy at Case Western Reserve University, have reported their finding in the January 3, 2003, issue of Science. Combining their calculations of the ages of the oldest stars with measurements of the expansion rate and geometry of the universe lead them to conclude that dark energy dominates the energy density of the universe.
?This finding provides strong support for a universe which is dominated by a kind of energy we?ve never directly observed,? says Chaboyer. ?Observations of distant supernova have suggested for a few years that dark energy dominates the universe, and our finding provides independent evidence that the universe is dominated by this type of energy we do not understand.?
The researchers came to this conclusion as they were refining their calculations for the age of globular clusters, which are groups of about 100,000 or more stars found in the outskirts of the Milky Way, our galaxy. Because this age (about 12 billion years old) is inconsistent with the expansion age for a flat universe (only about 9 billion years old), Krauss and Chaboyer came to the conclusion that the universe is expanding more quickly now than it did in the past.
The only explanation, according to Chaboyer and Krauss, for an accelerating universe is that the energy content of a vacuum is non-zero with a negative pressure, in other words, dark energy. This negative pressure of the vacuum grows in importance as the universe expands and causes the expansion to accelerate.
Original Source: Dartmouth College News Release
