Image credit: Hubble
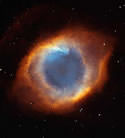
One of the most detailed images ever taken of the Helix Nebula was unveiled in celebration of Astronomy Day on May 10th. The composite picture was made by blending photos taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and a telescope at Kitt Peak Observatory. The photograph is so detailed because the nebula is close (650 light-years) and visually the same size as our Moon in the night sky.
In one of the largest and most detailed celestial images ever made, the coil-shaped Helix Nebula is being unveiled tomorrow in celebration of Astronomy Day (Saturday, May 10).
The composite picture is a seamless blend of ultra-sharp NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) images combined with the wide view of the Mosaic Camera on the National Science Foundation’s 0.9-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory, part of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory, near Tucson, Ariz. Astronomers at the Space Telescope Science Institute assembled these images into a mosaic. The mosaic was then blended with a wider photograph taken by the Mosaic Camera. The image shows a fine web of filamentary “bicycle-spoke” features embedded in the colorful red and blue gas ring, which is one of the nearest planetary nebulae to Earth.
Because the nebula is nearby, it appears as nearly one-half the diameter of the full Moon. This required HST astronomers to take several exposures with the Advanced Camera for Surveys to capture most of the Helix. HST views were then blended with a wider photo taken by the Mosaic Camera. The portrait offers a dizzying look down what is actually a trillion-mile-long tunnel of glowing gases. The fluorescing tube is pointed nearly directly at Earth, so it looks more like a bubble than a cylinder. A forest of thousands of comet-like filaments, embedded along the inner rim of the nebula, points back toward the central star, which is a small, super-hot white dwarf.
The tentacles formed when a hot “stellar wind” of gas plowed into colder shells of dust and gas ejected previously by the doomed star. Ground-based telescopes have seen these comet-like filaments for decades, but never before in such detail. The filaments may actually lie in a disk encircling the hot star, like a collar. The radiant tie-die colors correspond to glowing oxygen (blue) and hydrogen and nitrogen (red).
Valuable Hubble observing time became available during the November 2002 Leonid meteor storm. To protect the spacecraft, including HST’s precise mirror, controllers turned the aft end into the direction of the meteor stream for about half a day. Fortunately, the Helix Nebula was almost exactly in the opposite direction of the meteor stream, so Hubble used nine orbits to photograph the nebula while it waited out the storm. To capture the sprawling nebula, Hubble had to take nine separate snapshots.
Planetary nebulae like the Helix are sculpted late in a Sun-like star’s life by a torrential gush of gases escaping from the dying star. They have nothing to do with planet formation, but got their name because they look like planetary disks when viewed through a small telescope. With higher magnification, the classic “donut-hole” in the middle of a planetary nebula can be resolved. Based on the nebula’s distance of 650 light-years, its angular size corresponds to a huge ring with a diameter of nearly 3 light-years. That’s approximately three-quarters of the distance between our Sun and the nearest star.
The Helix Nebula is a popular target of amateur astronomers and can be seen with binoculars as a ghostly, greenish cloud in the constellation Aquarius. Larger amateur telescopes can resolve the ring-shaped nebula, but only the largest ground-based telescopes can resolve the radial streaks. After careful analysis, astronomers concluded the nebula really isn’t a bubble, but is a cylinder that happens to be pointed toward Earth.
Original Source: Hubble News Release