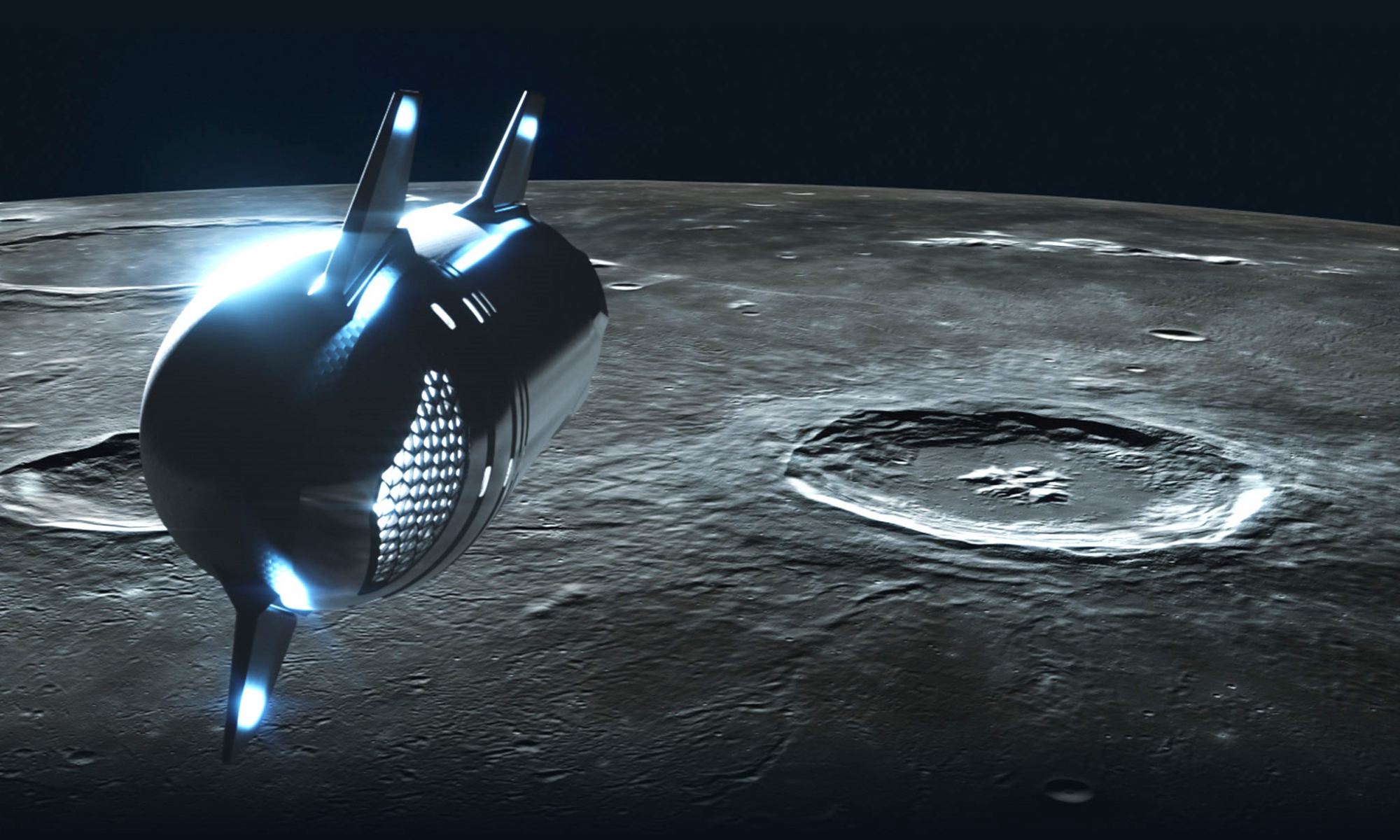
The Artemis Program represents NASA’s effort to return to the Moon. One of the goals of the project is to set up long-term exploration of the Earth’s only natural satellite. This will need much bulkier equipment than what the Apollo astronauts carried though, and this equipment needs to be transported to the Moon’s surface. Blue Origin and SpaceX, contracted by NASA to provide human landing systems, have begun developing vehicles that can safely deliver this equipment from space to the Moon’s surface.
Continue reading “NASA Wants Heavy Cargo Landers for the Moon”Suppressing Starlight: How to Find Other Earths
One underappreciated aspect of the current flood of exoplanet discoveries is the technical marvels that enable it. Scientists and engineers must capture and detect minute signals from stars and planets light years away. With the technologies of even a few decades ago, that would have been impossible – now it seems commonplace. However, there are still some technical hurdles to overcome before finding the “holy grail” of exoplanet hunting – an Earth analog. To help that discussion, a team of researchers led by Bertrand Mennesson at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory has released a paper detailing the current experimental and theoretical work around one of the most critical technical aspects of researching exoplanet atmospheres – starshades.
Continue reading “Suppressing Starlight: How to Find Other Earths”Highlights from the 10th Achieving Mars Workshop

Back in December, NASA officials, space industry experts, members of the academic community, and science communicators descended on Washington, D.C., for the Achieving Mars Workshop X (AM X). This workshop is hosted by Explore Mars Inc., a non-profit organization dedicated to bringing leading experts from disparate fields together to contribute to creating the first crewed missions to Mars. On May 17th, the results of this year’s workshop were summarized in a report titled “The Tenth Community Workshop for Achievability and Sustainability of Human Exploration of Mars.”
Continue reading “Highlights from the 10th Achieving Mars Workshop”Life Probably Played No Role in Mars’ Organic Matter
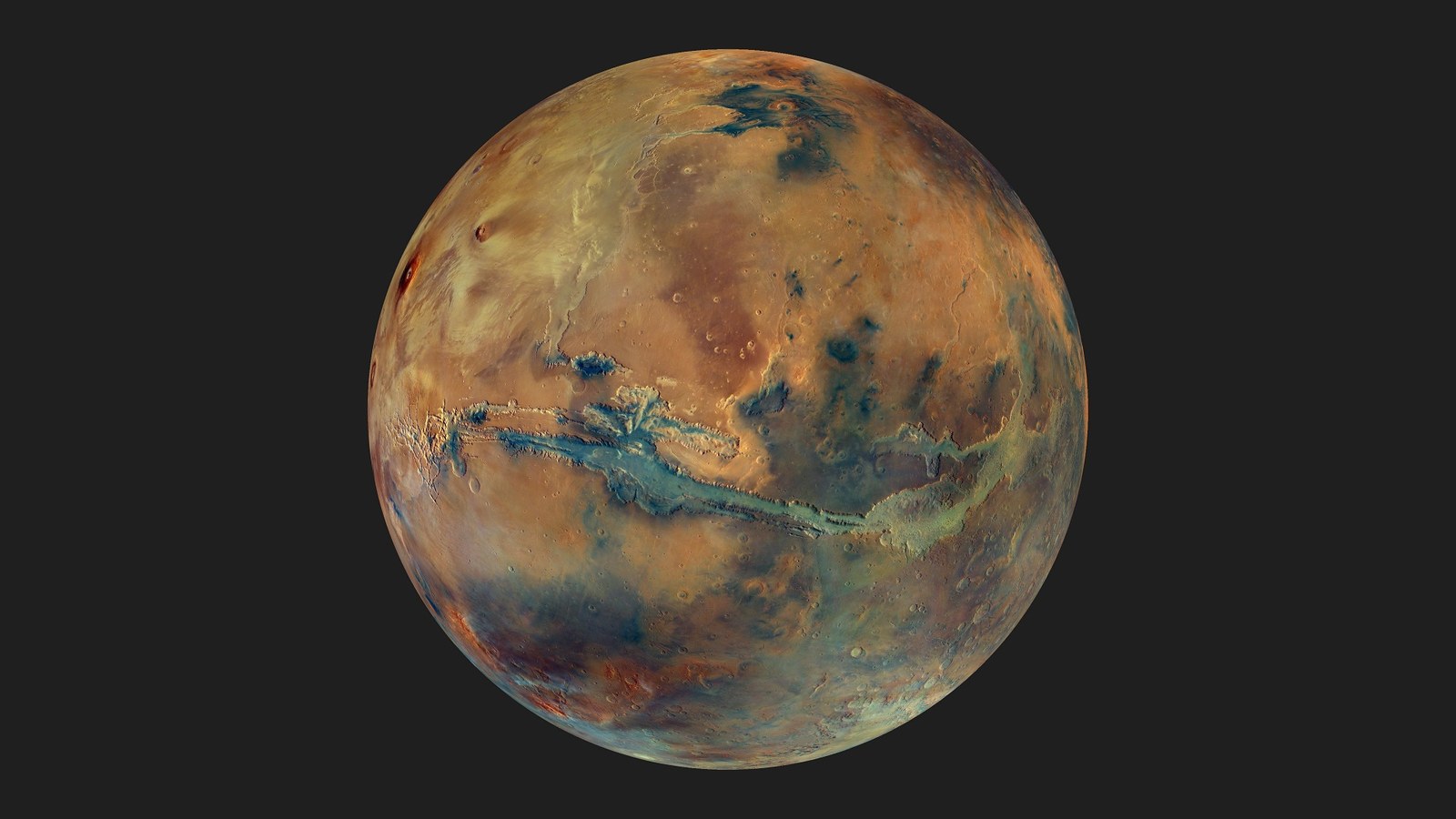

The Martian surface shows ample evidence of its warm, watery past. Deltas, ancient lakebeds, and dry river channels are plentiful. When the Curiosity rover found organic matter in ancient sediments in the Jezero Crater paleolake, it was tempting to conclude that life created the matter.
However, new research suggests that non-living processes are responsible.
Continue reading “Life Probably Played No Role in Mars’ Organic Matter”What Impact Does Ozone Have on an Exoplanet?
As we discover more and more exoplanets – and the current total is in excess of 5,200 – we continue to try to learn more about them. Astrobiologists busy themselves analysing their atmospheres searching for anything that provides a sign of life. It is quite conceivable of course that the Universe is teeming with life based on very different chemistry to ours but we often look to life on Earth to know what to look for. On Earth for example, ozone forms through photolysis of molecular oxygen and is an indicator of life. Using the James Webb Space Telescope astronomers are searching stars in the habitable zone of their star for the presence of ozone and how it impacts their climate.
Continue reading “What Impact Does Ozone Have on an Exoplanet?”Part 2: The History and Future of Planetary Radar
To reach the U.S. National Science Foundation’s Green Bank Observatory, you take the road less traveled, winding through scenic and remote regions of the Allegheny Mountains and the Monongahela National Forest of West Virginia. About an hour away, you’ll start to lose cell phone service. The Green Bank Observatory – a collection of radio telescopes that search the heavens for faint radio signals from black holes, pulsars, neutron stars or gravitational waves — sits near the heart of the United States National Radio Quiet Zone, a unique area the encompasses an area of approximately 13,000 square miles, spanning the border between Virginia and West Virginia.
Here in the NRQZ, human-generated radio transmissions are limited to shield the radio telescopes from Earth-based radio signals called RFI (Radio Frequency Interference), which are high-frequency electromagnetic waves that emanate from electronic devices such as computers, cell phones, microwave ovens, and even digital cameras. Even the weakest RFI signals can drown out the faint radio waves coming from the cosmos.
Continue reading “Part 2: The History and Future of Planetary Radar”Chinese Probe Lands on Moon’s Far Side to Collect Samples for Return
After touching down on the moon’s far side, China’s Chang’e-6 lander is collecting samples to bring back to Earth — and sending back imagery documenting its mission.
Chang’e-6, which was launched May 3, went through weeks’ worth of in-space maneuvers that climaxed with its weekend landing in the moon’s South Pole-Aitken Basin region. The mission plan calls for the probe to collect samples of lunar soil and rock over the course of about two days, and then pack them up for the return trip.
If the operation is successful, Chang’e-6 would bring back the first fresh lunar samples ever collected on the moon’s far side — following up on the Chang’e-5 mission in 2020, which returned samples from the moon’s Earth-facing side.
Continue reading “Chinese Probe Lands on Moon’s Far Side to Collect Samples for Return”A New Way to Make Precise Maps of the Lunar Surface
There was a time when maps of the Moon were created from telescopic observations and drawings. Indeed Sir Patrick Moore created maps of the Moon that were used during the historic Apollo landings. Now researchers have enhanced a technique to create accurate maps from existing satellite images. Their approach uses a technique called ‘shape-from-shading’ and involves analyzing shadows to estimate the features and shape of the terrain. Future lunar missions will be able to use the maps to identify hazards on the surface making them far safer.
Continue reading “A New Way to Make Precise Maps of the Lunar Surface”Japanese Billionaire Calls Off His Starship Trip Around the Moon
Six years after he announced a grand plan to fly around the moon with a crew of artists in SpaceX’s Starship rocket, Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa said he was canceling the project due to delays in Starship’s development.
In a series of postings to the X social-media platform, Maezawa said he signed his contract with SpaceX “based on the assumption that dearMoon would launch by the end of 2023.”
“It’s a developmental project, so it is what it is, but it is still uncertain as to when Starship can launch,” he wrote. “I can’t plan my future in this situation, and I feel terrible making the crew members wait longer, hence the difficult decision to cancel at this point in time. I apologize to those who were excited for this project to happen.”
Continue reading “Japanese Billionaire Calls Off His Starship Trip Around the Moon”Planetary Protection: Why study it? What can it teach us about finding life beyond Earth?
Universe Today has recently investigated a plethora of scientific disciplines, including impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, solar physics, comets, planetary atmospheres, planetary geophysics, cosmochemistry, meteorites, radio astronomy, extremophiles, organic chemistry, black holes, and cryovolcanism, while conveying their importance of how each of them continues to teach researchers and the public about our place in the vast universe.
Continue reading “Planetary Protection: Why study it? What can it teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”