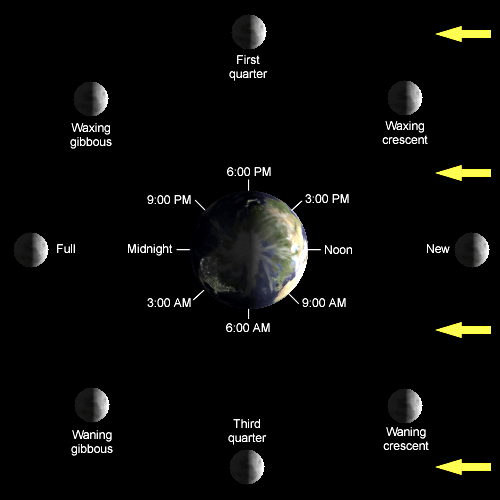
What is a Waning Moon?

Between a Full Moon and a New Moon, Earth's only satellite experiences a period of "waning", where the amount that is visible slowly decreases.
Continue reading
 Universe Today
Universe Today