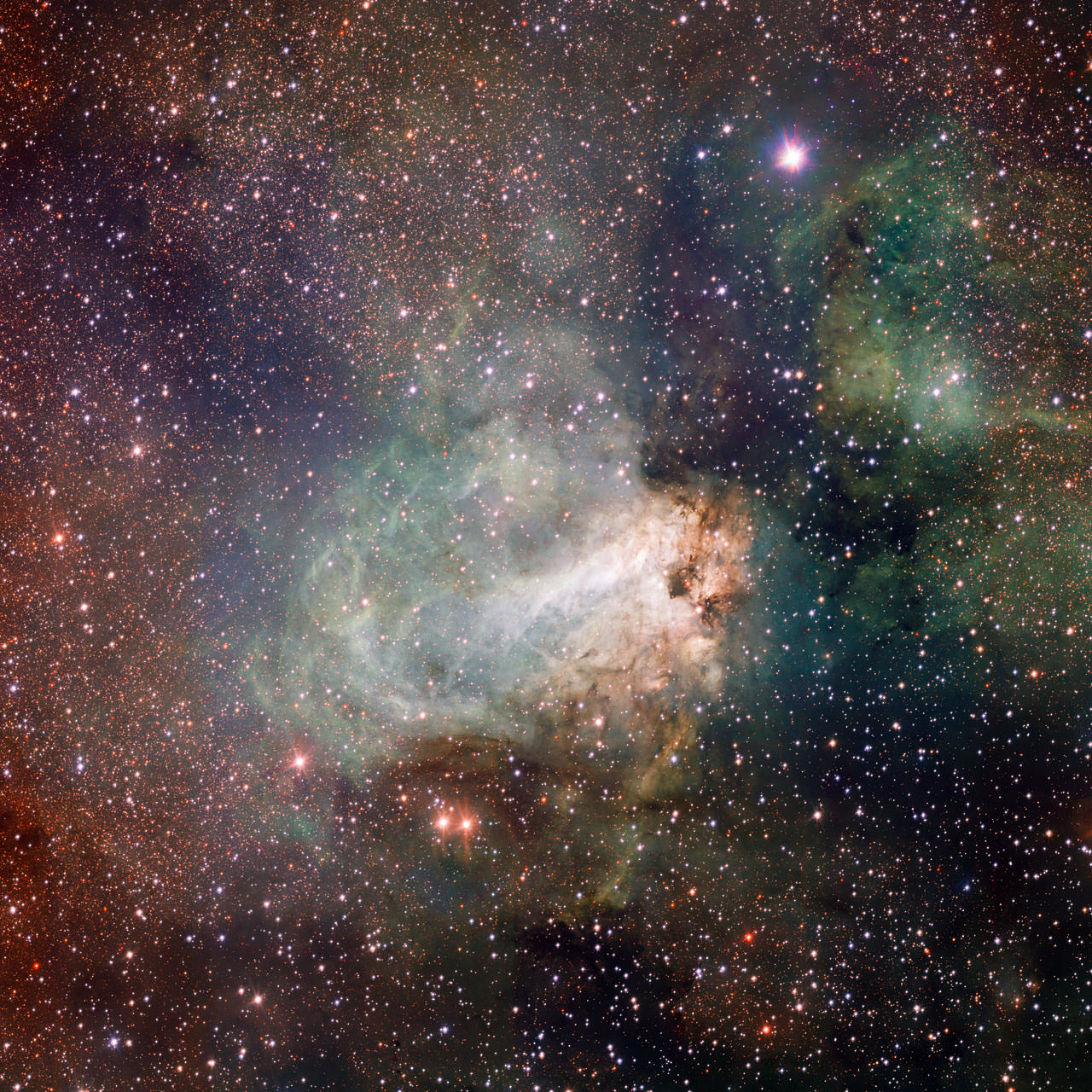
The Omega Nebula (Messier 17), also known as the Swan Nebula because of its distinct appearance, is one of the most well-known nebulas in our galaxy. Located about 5,500 light-years from Earth in the constellation Sagittarius, this nebula is also one of the brightest and most massive star-forming regions in the Milky Way. Unfortunately, nebulas are very difficult to study because of the way their clouds of dust and gas obscure their interiors.
For this reason, astronomers are forced to examine nebulas in the non-visible wavelength to get a better idea of their makeup. Using the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), a team of NASA scientists recently observed the Swan Nebula in the infrared wavelength. What they found has revealed a great deal about how this nebula and stellar nursery evolved over time.
Continue reading “New View of the Swan Nebula From NASA’s Airborne SOFIA Telescope”