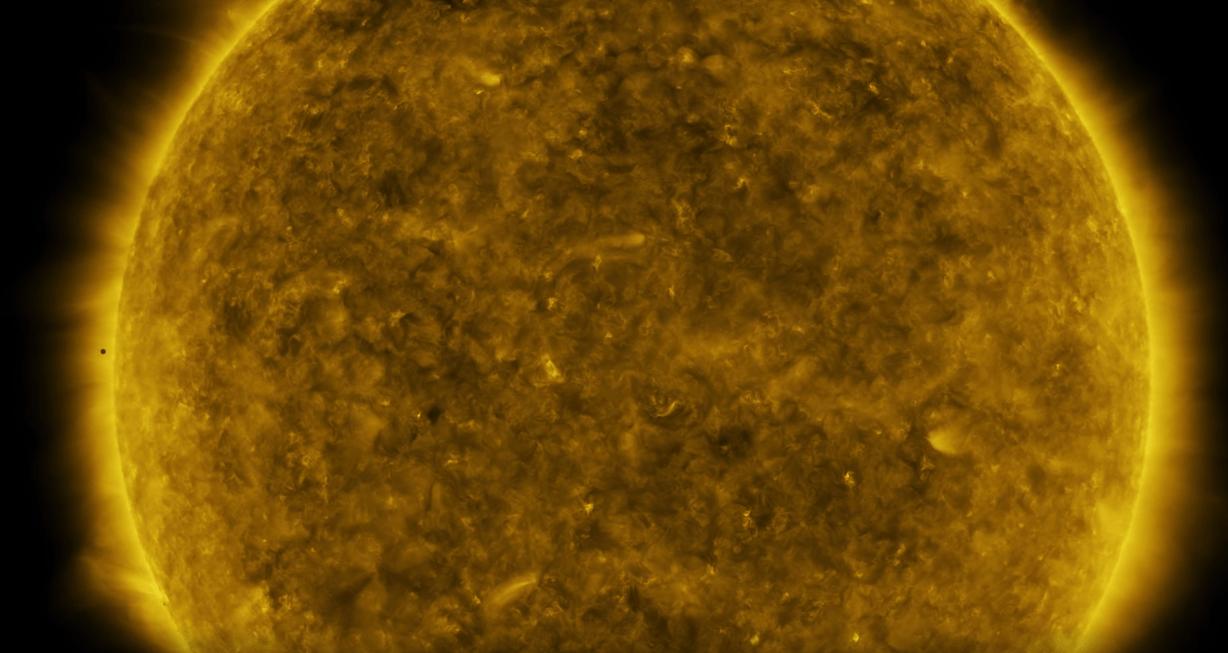
Do you wonder how astronomers find all those exoplanets orbiting stars in distant solar systems?
Mostly they use the transit method. When a planet travels in between its star and an observer, the light from the star dims. That’s called a transit. If astronomers watch a planet transit its star a few times, they can confirm its orbital period. They can also start to understand other things about the planet, like its mass and density.
The planet Mercury just transited the Sun, giving us all an up close look at transits.
Continue reading “Satellites Watched Mercury’s Transit From Space, Confirming That Yes, the Sun Has At Least One Planet”