This week’s Carnival of Space is hosted by me at the CosmoQuest blog.
Click here to read Carnival of Space #633
Continue reading “Carnival of Space #633”

Space and astronomy news
This week’s Carnival of Space is hosted by me at the CosmoQuest blog.
Click here to read Carnival of Space #633
Continue reading “Carnival of Space #633”
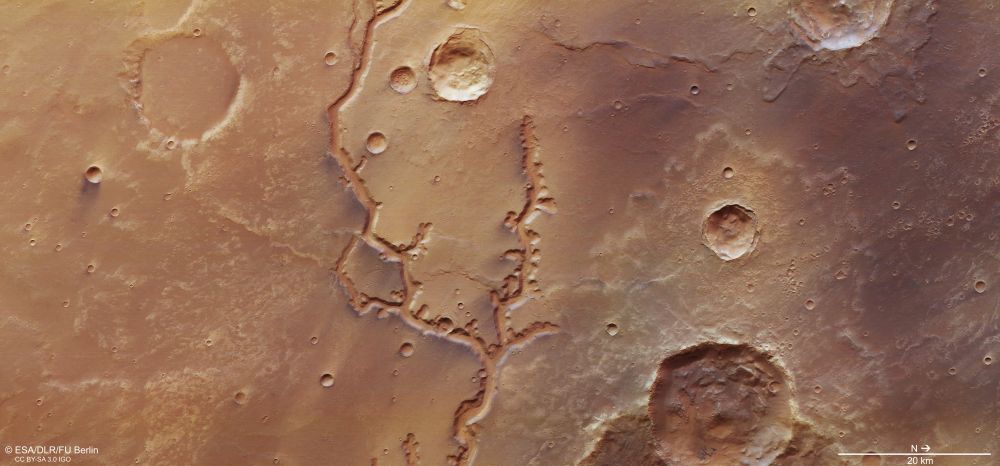

From some viewpoints, Mars is kind of like a skeleton of Earth. We can see that it had volcanoes, oceans, and rivers, but the volcanoes no longer fume and the water is all gone. A new image from the ESA’s Mars Express drives the point home.
Continue reading “This Dried Up Riverbed Shows that Water Once Flowed on the Surface of Mars”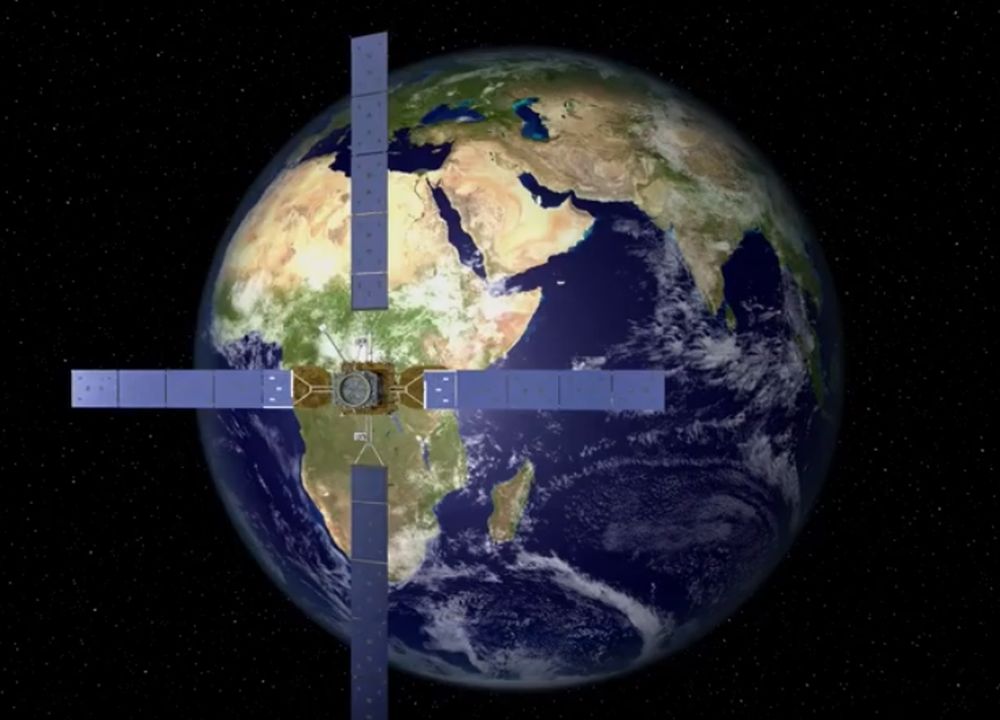
Space Logistics LLC, a subsidiary of Northrop Grumman, has launched a satellite that can extend the life of other satellites. The satellite is called MEV-1, or Mission Extension Vehicle-1. MEV-1 is the first of its kind.
Continue reading “A Satellite Just Launched Whose Job is to Extend the Life of Geosynchronous Satellites”
Venus is often referred to as “Earth’s sister planet“, owing to the number of similarities between them. Like Earth, Venus is a terrestrial (aka. rocky) planet and it resides with our Sun’s Circumstellar Habitable Zone (CHZ). And for some time, scientists have theorized that billions of years ago, Venus had oceans on its surface and was habitable – aka. not the hot and hellish place it is today.
However, after examining radar data on the Ovda Fluctus lava flow, a team scientists at the Lunar and Planetary Institute concluded that the highlands on Venus are likely to be composed of basaltic lava rock instead of granite. This effectively punches a hole in the main argument for Venus having oceans in the past, which is that the Ovda Regio highlands plateau formed in the presence of water.
Continue reading “Lava Flows on Venus Suggest That the Planet Was Never Warm and Wet”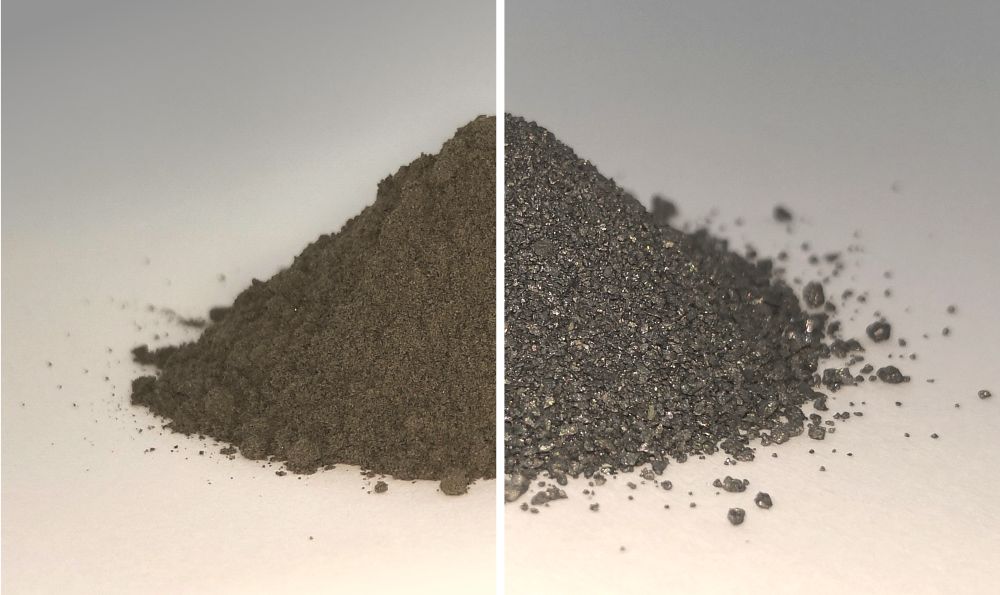
The Moon has abundant oxygen and minerals, things that are indispensable to any space-faring civilization. The problem is they’re locked up together in the regolith. Separating the two will provide a wealth of critical resources, but separating them is a knotty problem.
Continue reading “This is What Moondust Looks Like When You Remove All the Oxygen. A Pile of Metal”Hosts:
Fraser Cain (universetoday.com / @fcain)
Sondy Springmann (@sondy)
Beth Johnson (@planetarypan)
Michael Rodruck (@michaelrodruck)
This week we welcome Dr. Marina Kounkel, a postdoctoral scholar in the Physics and Astronomy Department at the Western Washington University. Her research focuses on observing the dynamics of young stars.
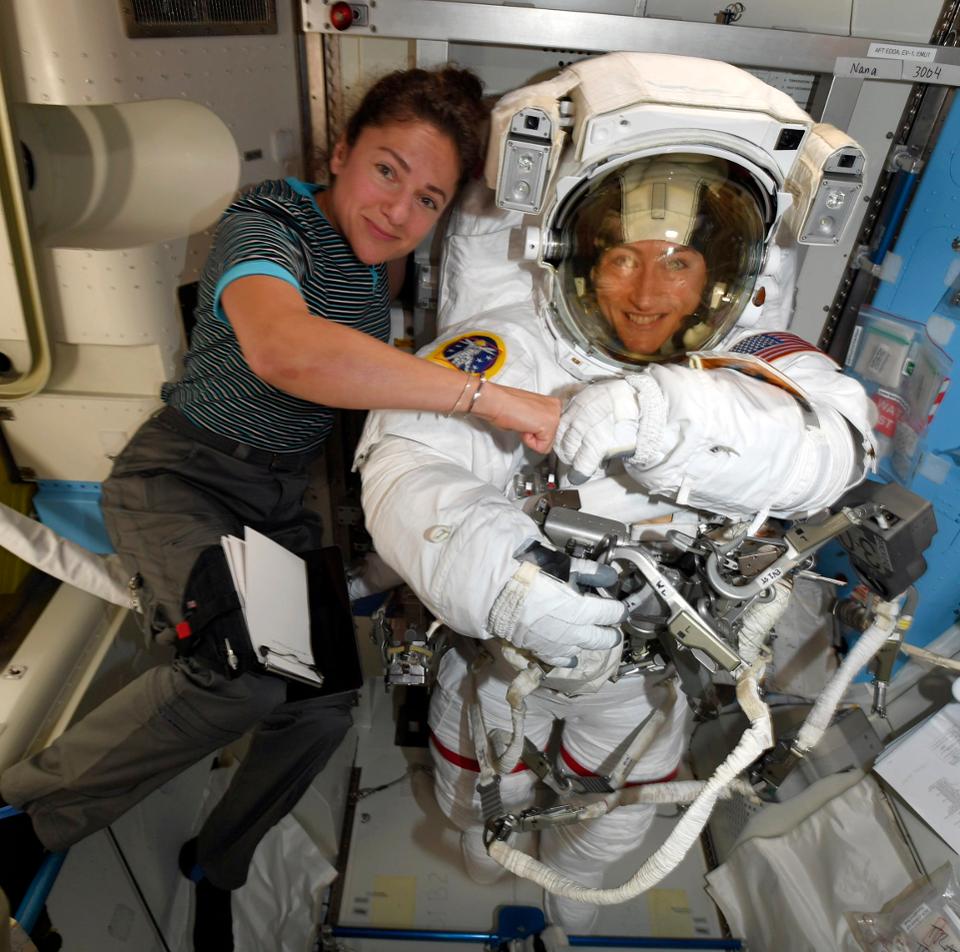

The all-female astronaut walk is back on.
Back on March 26th, 2019, NASA was forced to cancel the first all-female spacewalk because they didn’t have the right spacesuits available on the ISS. There was a short-lived social media storm over that development, as some claimed it was evidence of sexism on the part of NASA. But that small storm didn’t have legs and it died out, because no serious-minded observer thinks that NASA is actually sexist.
Now, the problem has been worked out, and the spacewalk will happen on October 21st, when astronauts Christina Koch and Jessica Meir will walk outside the ISS and install new lithium-ion batteries. Theirs is the first of five walks needed to complete the installation.
Continue reading “They’ve Got Spacesuits that Fit Now. Christina Koch and Jessica Meir Will Spacewalk on October 21st”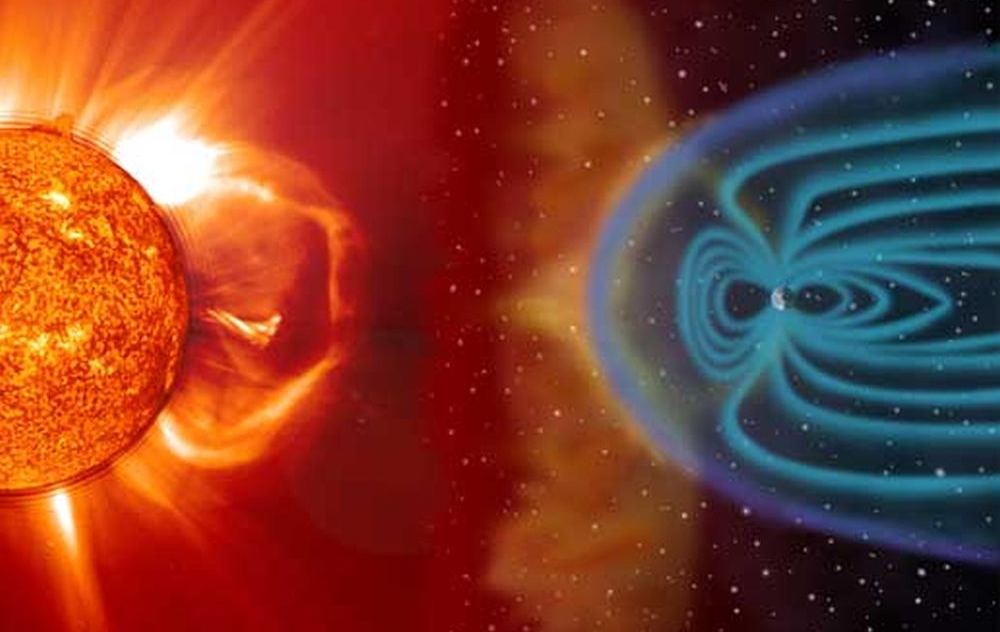
Exactly how dangerous are solar storms? Scientists think the Carrington Event was one of the most powerful ones to ever hit Earth. They also think that storms that powerful only happen every couple centuries or so. But a new study says we can expect more storms equally as strong, and more often.
Continue reading “Power Grids and Satellites Are More at Risk from Extreme Solar Storms Than We Thought”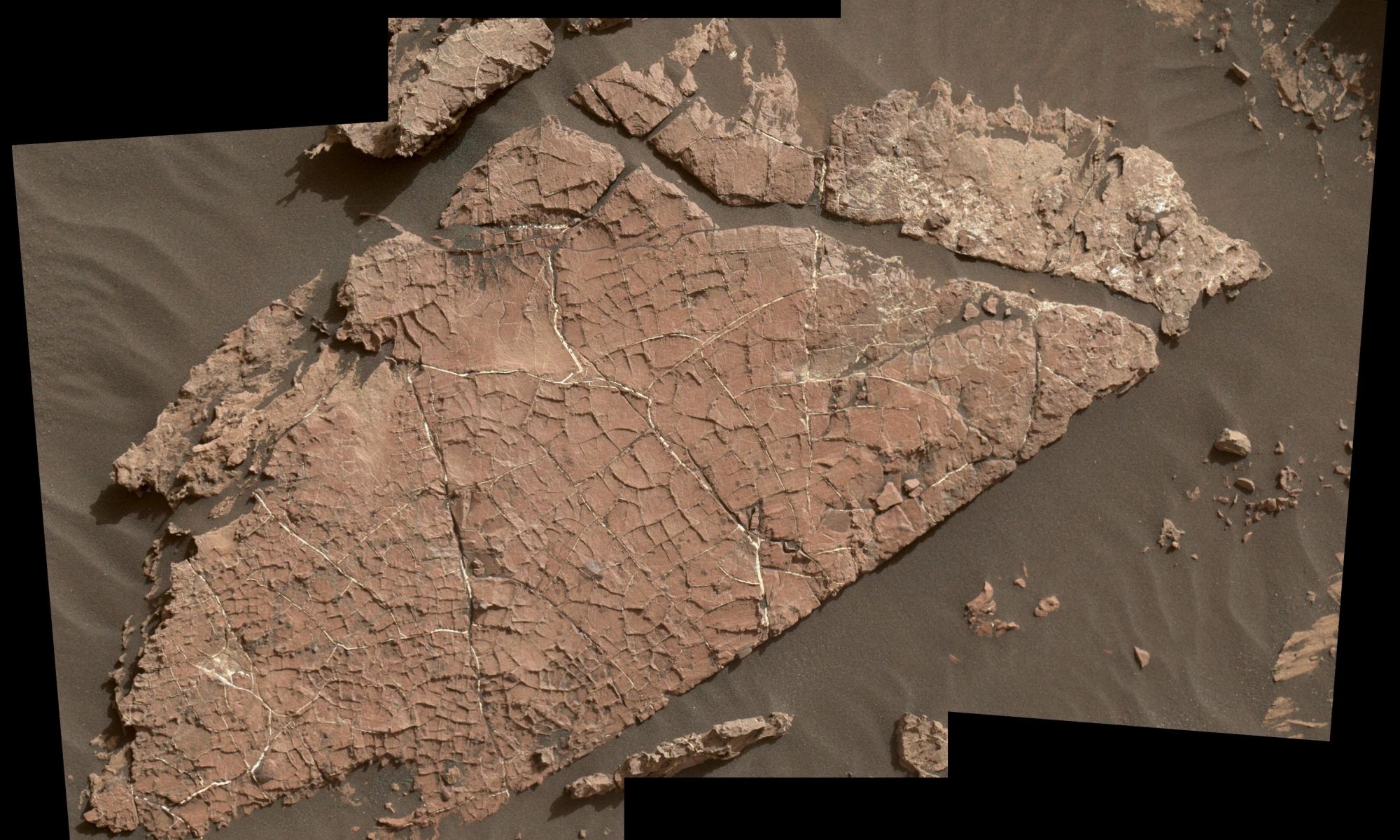
What happened to Mars? If Mars and Earth were once similar, as scientists think, what happened to all the water? Did there used to be enough to support life?
Thanks to the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Curiosity, we’re getting a better picture of ancient Mars and what it went through billions of years ago. A new study published in Nature Geoscience says that Mars likely underwent alternating periods of wet and dry, before becoming the frigid, dry desert it is now. Or at least, Gale Crater did.
Continue reading “Curiosity Finds A Region of Ancient Dried Mud. It Could Have Been an Oasis Billions of Year Ago”
The reign of Jupiter, named after the father of the Olympian gods, has been long and sweet. Aside from being the largest planet in the Solar System, it was this gas giant that demonstrated in the 17th century that planets other than Earth can support a system of moons. Between its size, powerful magnetic field, and system of 79 moons, Jupiter looked set to remain the king of the planets
But it looks like Saturn, named after the father of Jupiter in Greco-Roman mythology, might have just knocked Jupiter off that pedestal. Thanks to a team led by famed astronomer Scott S. Sheppard 20 new moons have been discovered orbiting Saturn. That brings the total number of Saturnian (or Cronian) satellites to 82, putting it ahead of Jupiter’s 79. And the best part? You can help name them!
Continue reading “Astronomers Find 20 – Yes 20 – New Moons for Saturn”