Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the globular cluster known as Messier 92!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
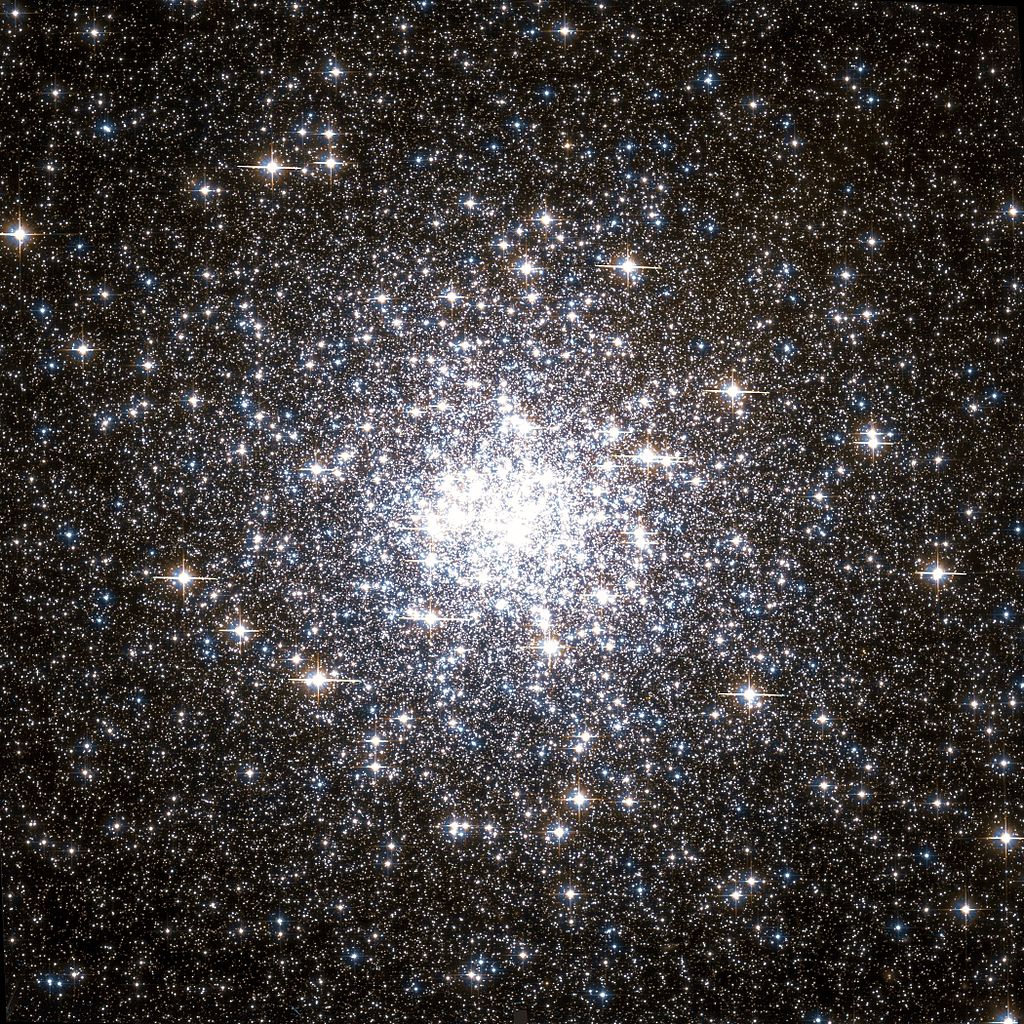
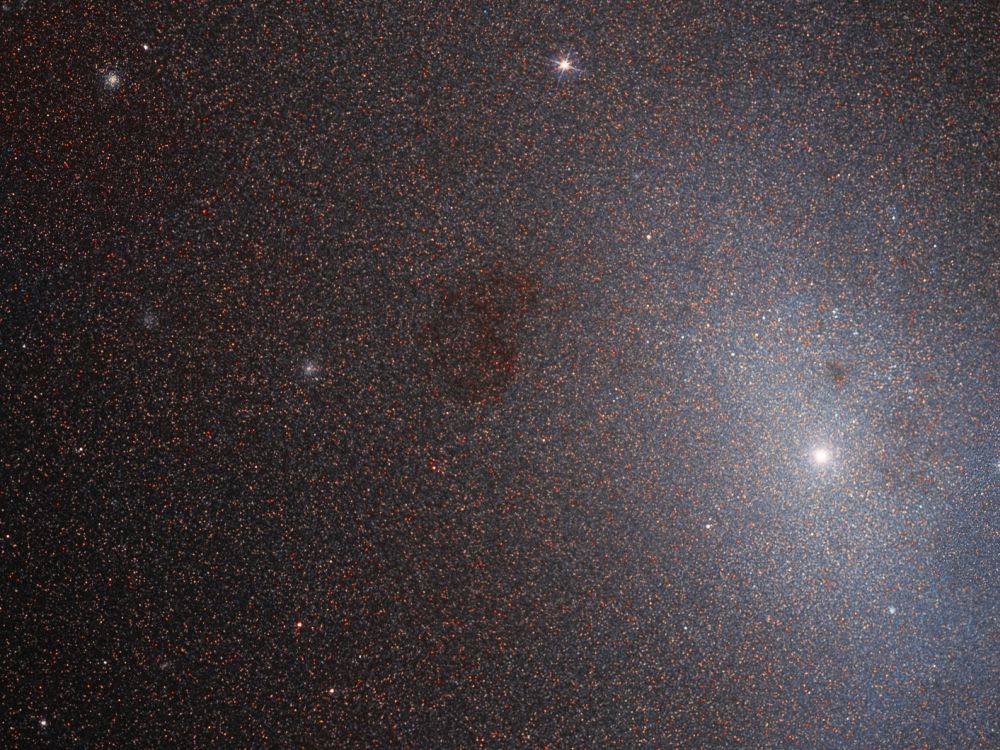
One of these objects is Messier 92, a globular cluster located in the northern constellation of Hercules. This cluster lies at a distance of 26,700 light-years from Earth and is also approaching our galaxy at a speed of about 112 km/s (403,200 km/h; 250,500 mph) – which means it will eventually merge with our own. With an average estimated age of 14.2 billion years (± 1.2 billion years), it is almost as old as the Universe itself!
Continue reading “Messier 92 – the NGC 6341 Globular Cluster”