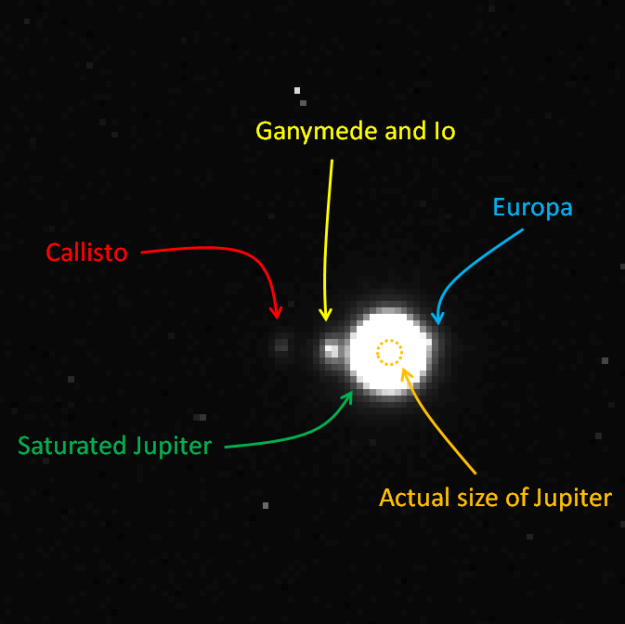
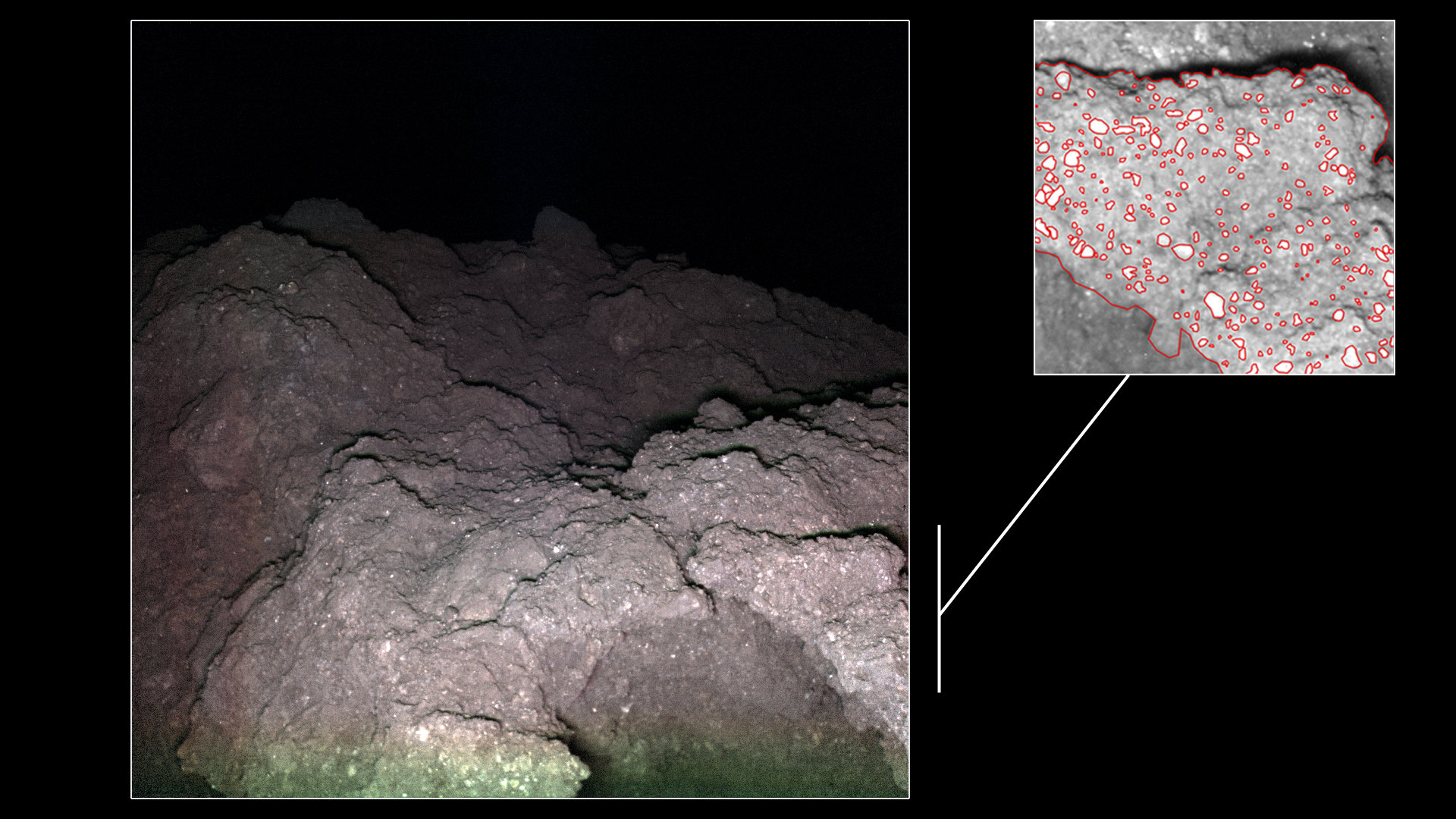
This week’s Carnival of Space is hosted by Brian Wang at his Next Big Future blog.
Click here to read Carnival of Space #626
And if you’re interested in looking back, here’s an archive to all the past Carnivals of Space. If you’ve got a space-related blog, you should really join the carnival. Just email an entry to [email protected], and the next host will link to it. It will help get awareness out there about your writing, help you meet others in the space community – and community is what blogging is all about. And if you really want to help out, sign up to be a host. Send an email to the above address.