The history of the Moon is a tale told by geology, apparent in its rocks, craters, and other surface features. For centuries, astronomers have studied the Moon from afar and for the past few decades, it has been visited by countless robotic missions. Between 1969 and 1972, a total of twelve astronauts walked on its surface, conducted lunar science, and brought samples of lunar rock back to Earth for study.
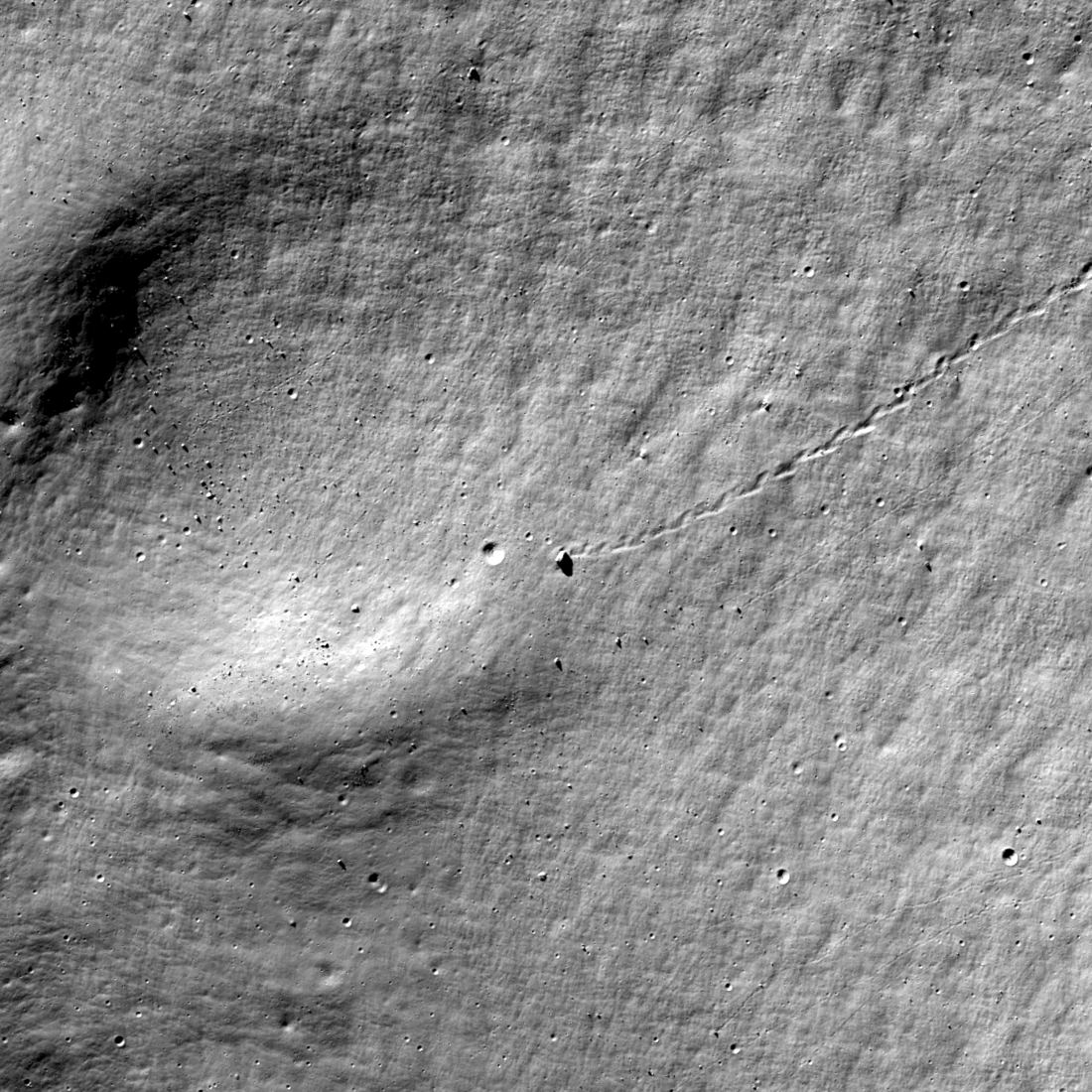
These efforts have taught us a lot about the things that have shaped the lunar surface, be they one-off events like the massive impact that formed the Shakleton crater to things that happened regularly throughout its 4.51 billion-year history. For instance, scientists recently discovered something unusual about the Antoniadi crater: a large boulder was perched on the rim of a smaller crater within after rolling about 1000 meters (1093 yards) downhill.
Continue reading “Rock Almost Rolled Into This Crater on the Moon… Almost”