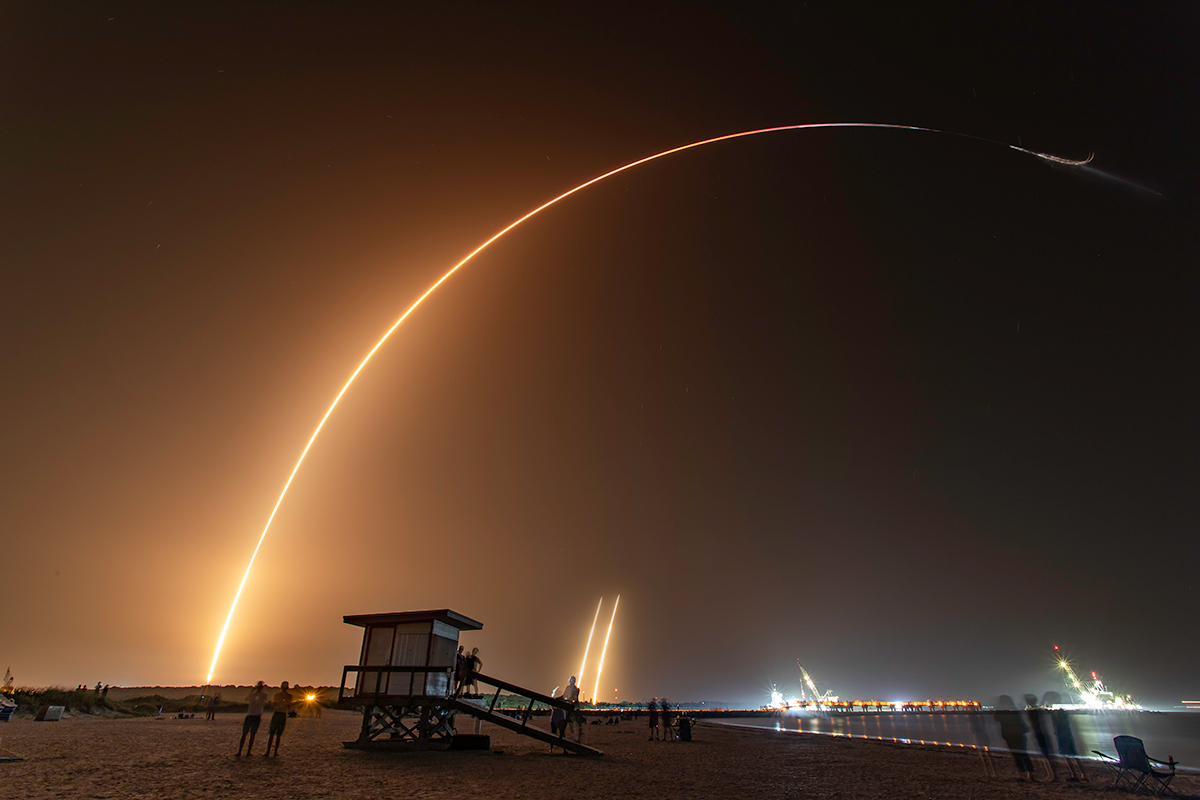
In what Elon Musk is calling their “most difficult” mission so far, SpaceX launched the Falcon Heavy rocket for the third time. The launch took place at 2:30 am ET Tuesday from a launch pad at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mission was called STP-2, and Universe Today sent a photographer to capture all the action.
Continue reading “Third Falcon Heavy Launch Blasts 24 Payloads Into Orbit Including a Solar Sail. Doesn’t Quite Stick the Landing”Third Falcon Heavy Launch Blasts 24 Payloads Into Orbit Including a Solar Sail. Doesn’t Quite Stick the Landing