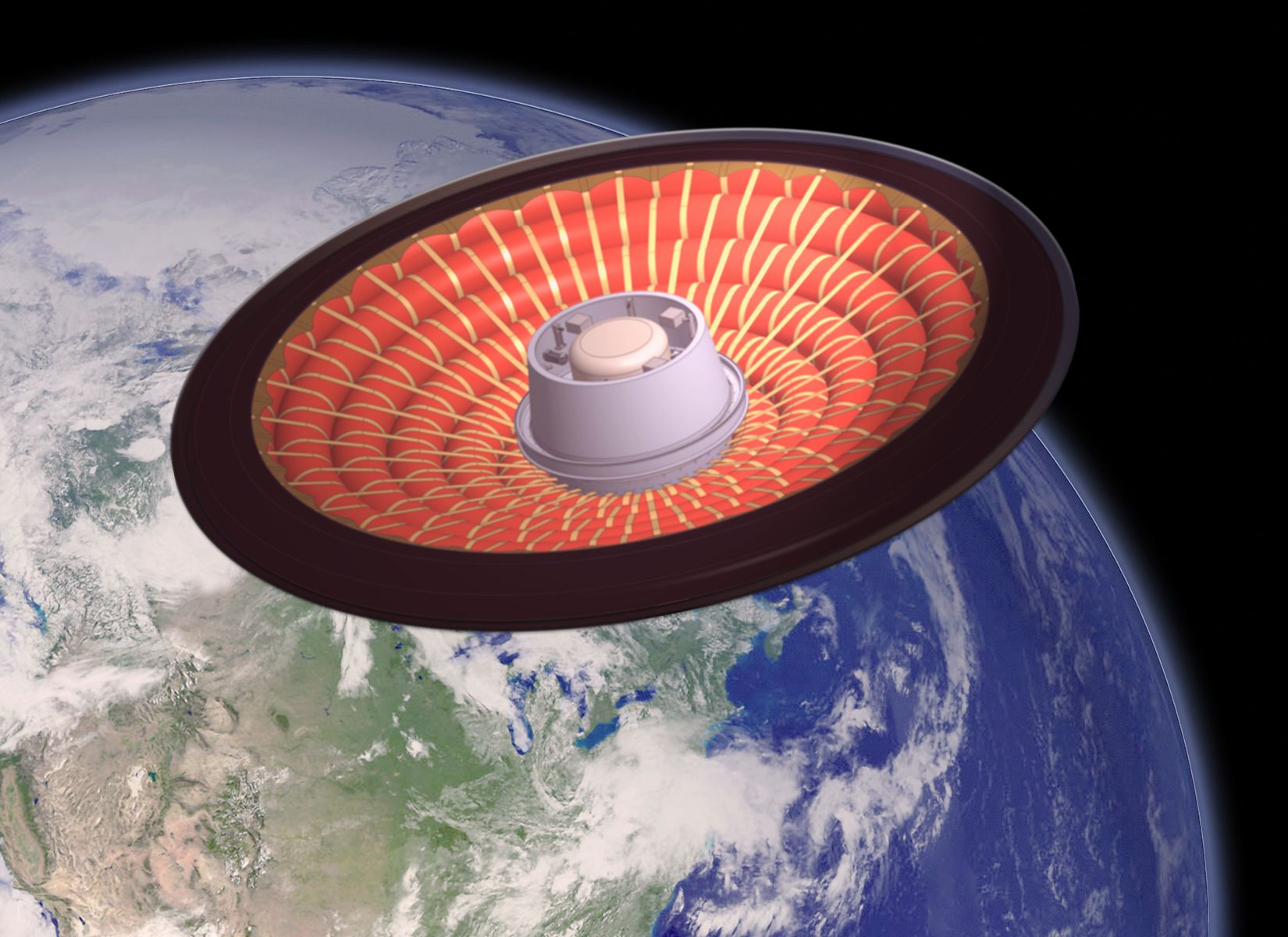
One of the greater challenges of sending payloads to Mars is having to contend with the planet’s atmosphere. While incredibly thin compared to Earth’s (with roughly half of 1% of Earth’s air pressure), the resulting air friction is still an issue for spacecraft looking to land there. And looking to the future, NASA hopes to be able to land heavier payloads on Mars as well as other planets – some of which may have atmospheres as dense as Earth.
A possible solution to this is the use of inflatable aeroshells (aka. heat shields), which offer numerous advantages over rigid ones. To develop this technology, NASA and United Launch Alliance (ULA) have partnered to develop an inflatable heat shield known as the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (