Hosts:
Fraser Cain (universetoday.com / @fcain)
Dr. Kimberly Cartier (KimberlyCartier.org / @AstroKimCartier )
Dr. Morgan Rehnberg (MorganRehnberg.com / @MorganRehnberg & ChartYourWorld.org)
Dr. Brian Koberlein (briankoberlein.com / @BrianKoberlein)
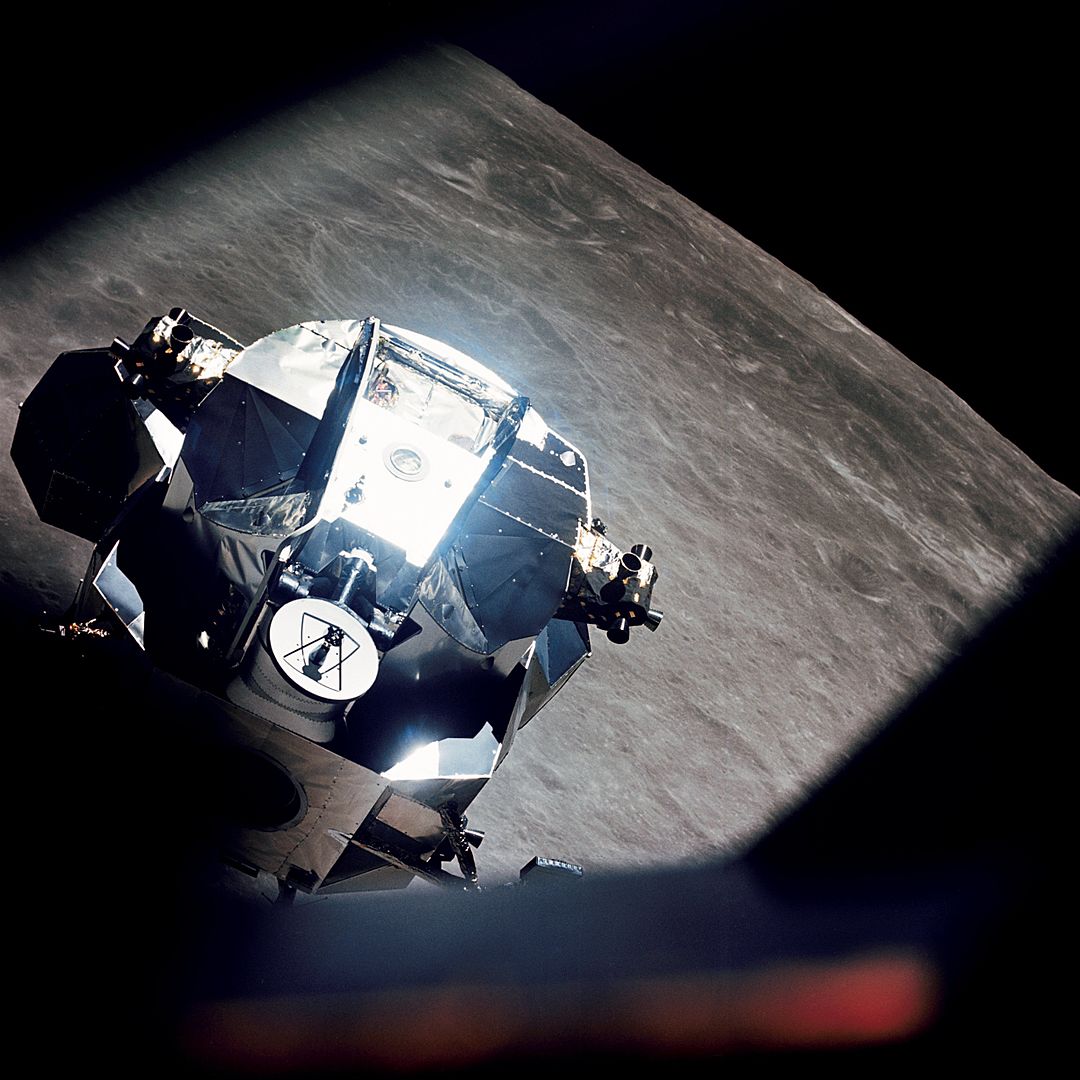
Apollo 10’s “Snoopy” Lunar Lander May Have Been Found in Space
Apollo 11 was the first mission to land people on the lunar surface. But Apollo relied on a lot of predecessor missions to lay the groundwork for the successful mission to the Moon. One of them was Apollo 10, the fourth crewed mission in the Apollo program.
Apollo 10 was an almost complete mission that including everything that Apollo 11 had, except for an actual landing on the Moon. It was a dress rehearsal, and was the second Apollo mission to orbit the Moon. It even had an Apollo Lunar Module that was flown to within 15 km of the lunar surface. But that module never landed, and eventually, after it rendezvoused with the command module and the crew disembarked, it was sent into orbit around the Sun.
And up until now, nobody knew where it was.
Continue reading “Apollo 10’s “Snoopy” Lunar Lander May Have Been Found in Space”1.2 billion years ago, a 1-km asteroid smashed into Scotland
In 2008, scientists from Oxford and Aberdeen University made a startling discovery in the northwest of Scotland. Near the village of Ullapool, which sits on the coast opposite the Outer Hebrides, they found a debris deposit created by an ancient meteor impact dated to 1.2 billion years ago. The thickness and extent of the debris suggested that the meteor measured 1 km (0.62 mi) in diameter and took place near to the coas
Until recently, the precise location of the impact remained a mystery to scientists. But in a paper that recently appeared in the Journal of the Geological
It’s Been Exactly One Year Since Opportunity Sent This Final Message Home – on its 5,111th Martian Day
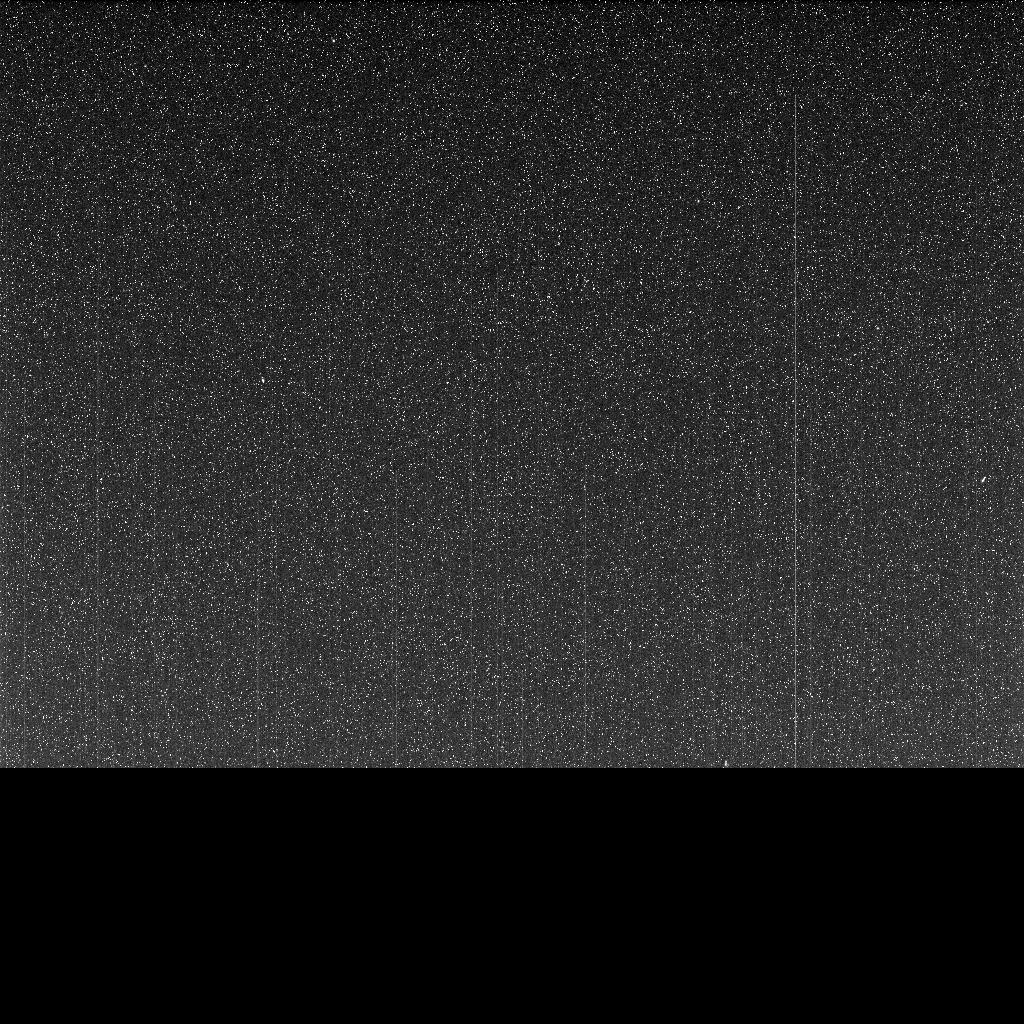

Opportunity’s final message home is not much to look at on its own. If you’re old enough to remember film cameras, it looks like the final exposure on a roll of film, developed but partly missing. It’s a suitable epitaph for Opportunity’s mission.
Continue reading “It’s Been Exactly One Year Since Opportunity Sent This Final Message Home – on its 5,111th Martian Day”New Instrument is Searching for Planets Around Alpha Centauri
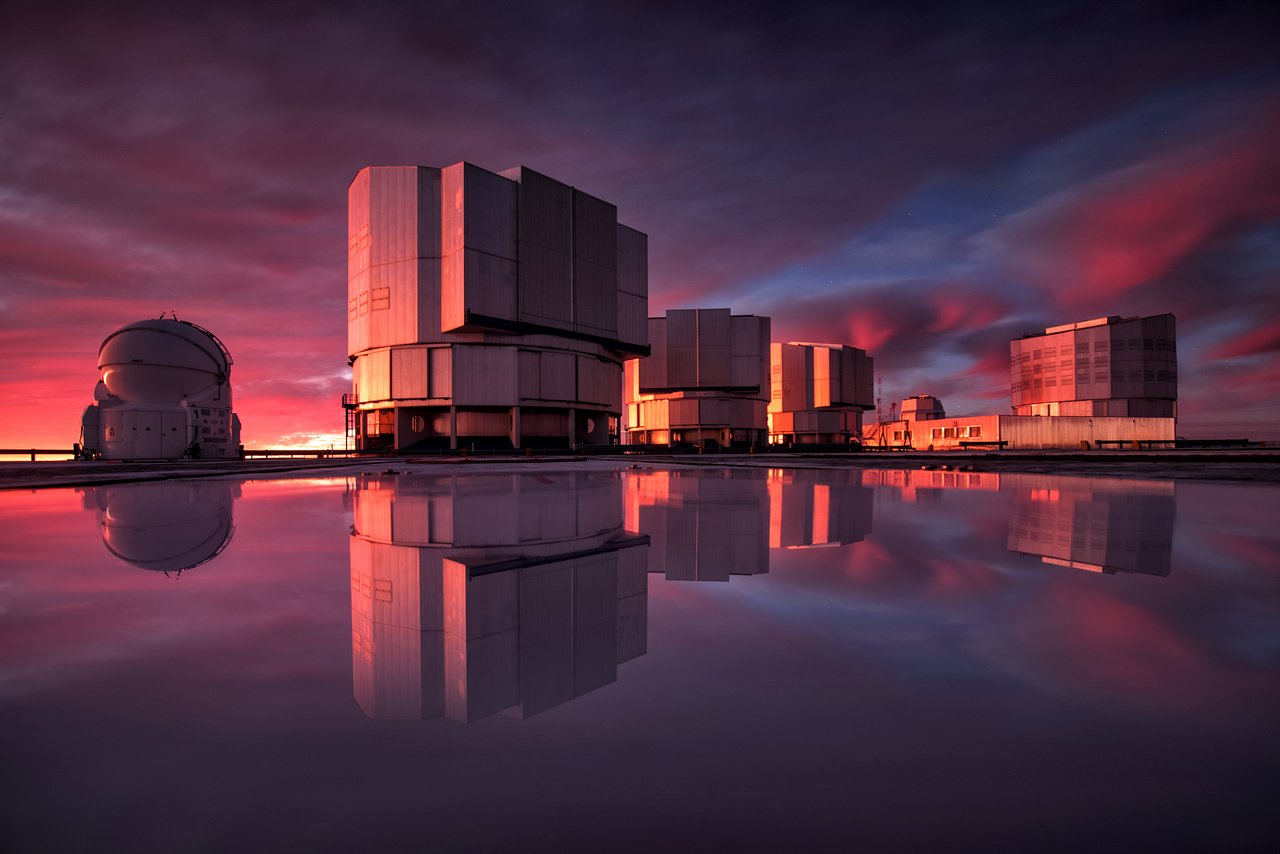

Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to us, at 4.37 light-years (about 25 trillion miles) away. In 2016, astronomers discovered an exoplanet orbiting one of the three stars in the Alpha Centauri system. Spurred on by that discovery, the European Southern Observatory (ESO) has developed a new instrument to find any other planets that might be in the Alpha Centauri system, and it’s busy looking right now.
Continue reading “New Instrument is Searching for Planets Around Alpha Centauri”That Explains a Lot. The Moon’s Largest Crater has a Chunk of Metal Embedded in it That’s 5 Times Bigger than the Big Island of Hawaii
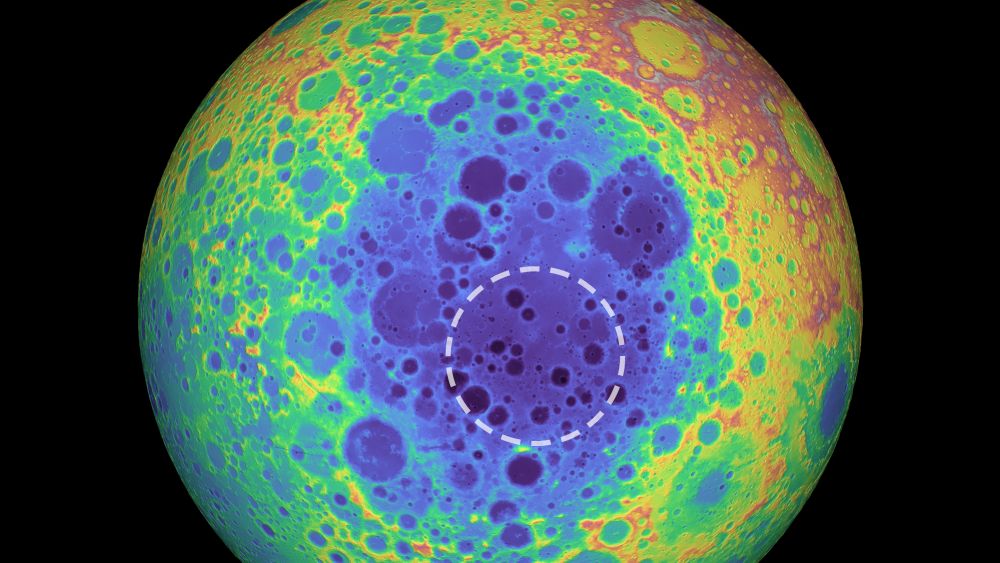
One of the largest craters in the Solar System is on our Moon. It’s called the South Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin and it’s 2,500 km (1,600 mi) in diameter and 13 km (8.1 mi) deep. A new study says that the basin may contain an enormous chunk of metal that’s larger than Hawaii’s Big Island.
Continue reading “That Explains a Lot. The Moon’s Largest Crater has a Chunk of Metal Embedded in it That’s 5 Times Bigger than the Big Island of Hawaii”Ep. 533: Indigenous South African Astronomy
Let’s move to another continent this week, and look at the astronomy that was going on in southern Africa in ancient times.
Continue reading “Ep. 533: Indigenous South African Astronomy”
Perfect Example of a Barred Spiral Galaxy, Seen Face On. This is What Our Milky Way Might Look Like

The Hubble Space Telescope has given us a beautiful image of the barred spiral galaxy NGC 7773. This is a classic galaxy of this type, and highlights the bright bar of concentrated stars that anchors the galaxy’s stately spiral arms. It was captured with the Hubble’s workhorse Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3.)
Continue reading “Perfect Example of a Barred Spiral Galaxy, Seen Face On. This is What Our Milky Way Might Look Like”Messier 87 – the Virgo A Supergiant Galaxy
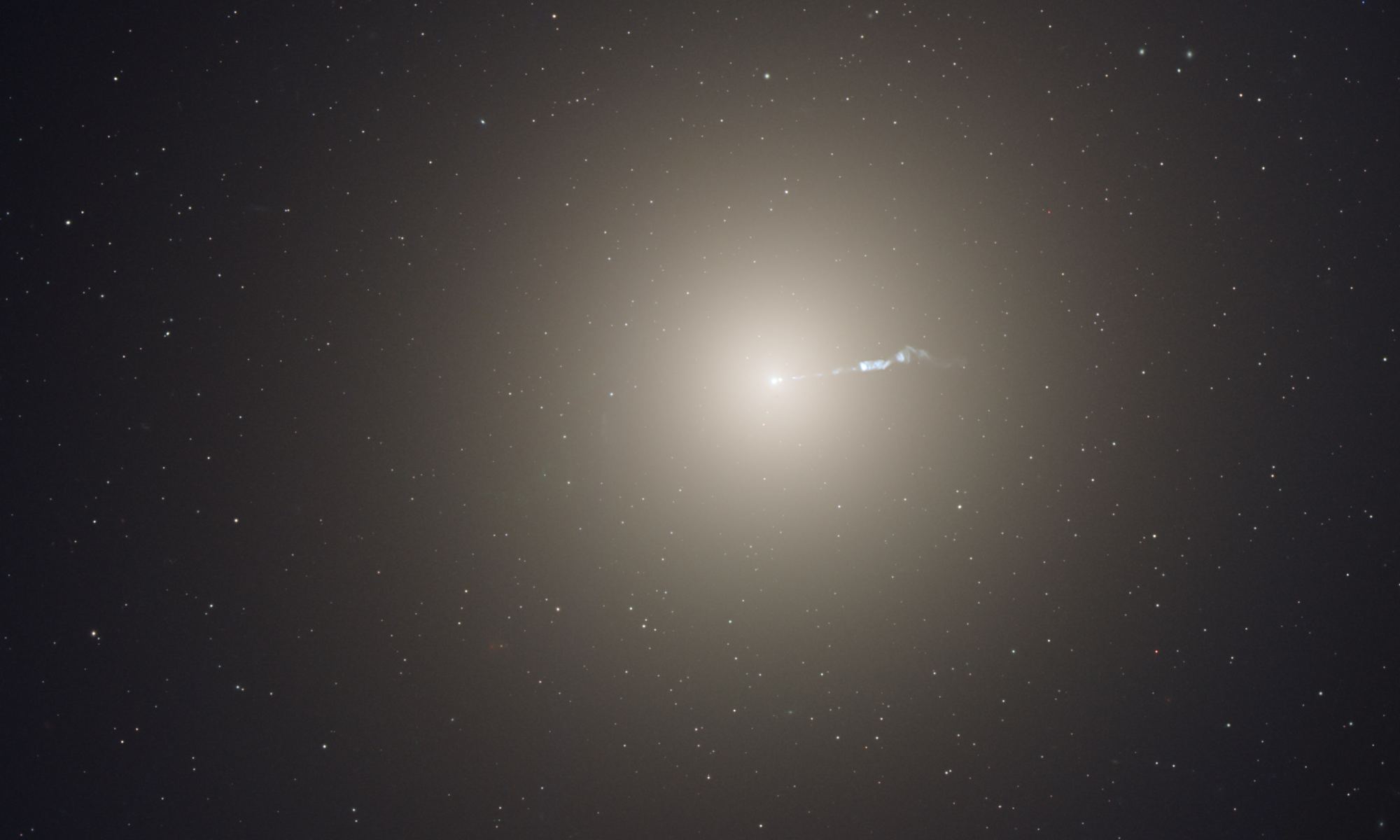

Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the supergiant elliptical galaxy known as Messier 87 (aka. Virgo A)!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
One of these objects is the supergiant galaxy Messier 87, also known as the Virgo A (or the Smoking Gun) galaxies. Located at a distance of about 53.5 million light years from Earth, this galaxy is home to several trillion stars, 15,000 globular clusters, and a supermassive black hole. It is one of the brightest galaxies in the northern part of the Virgo Cluster, second only to Messier 49, and the dominant member of that group.
Continue reading “Messier 87 – the Virgo A Supergiant Galaxy”
New observations from the Planck mission don’t resolve anomalies like the CMB “cold spot”

Back in 2013, the European Space Agency released its first analysis of the data gathered by the Planck observatory. Between 2009 and 2013, this spacecraft observed the remnants of the radiation that filled the Universe immediately after the Big Bang – the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) – with the highest sensitivity of any mission to date and in multiple wavelengths.
In addition to largely confirming current theories on how the Universe evolved, Planck’s first map also revealed a number of temperature anomalies – like the CMB “Cold Spot” – that are difficult to explain. Unfortunately, with the latest analysis of the mission data, the Planck Collaboration team has found no new evidence for these anomalies, which means that astrophysicists are still short of an explanation.
Continue reading “New observations from the Planck mission don’t resolve anomalies like the CMB “cold spot””

