For about a century now, scientists have theorized that the metals in our Universe are the result of stellar nucleosynthesis. This theory states that after the first stars formed, heat and pressure in their interiors led to the creation of heavier elements like silicon and iron. These elements not only enriched future generations of stars (“metallicity”), but also provided the material from which the planets formed.
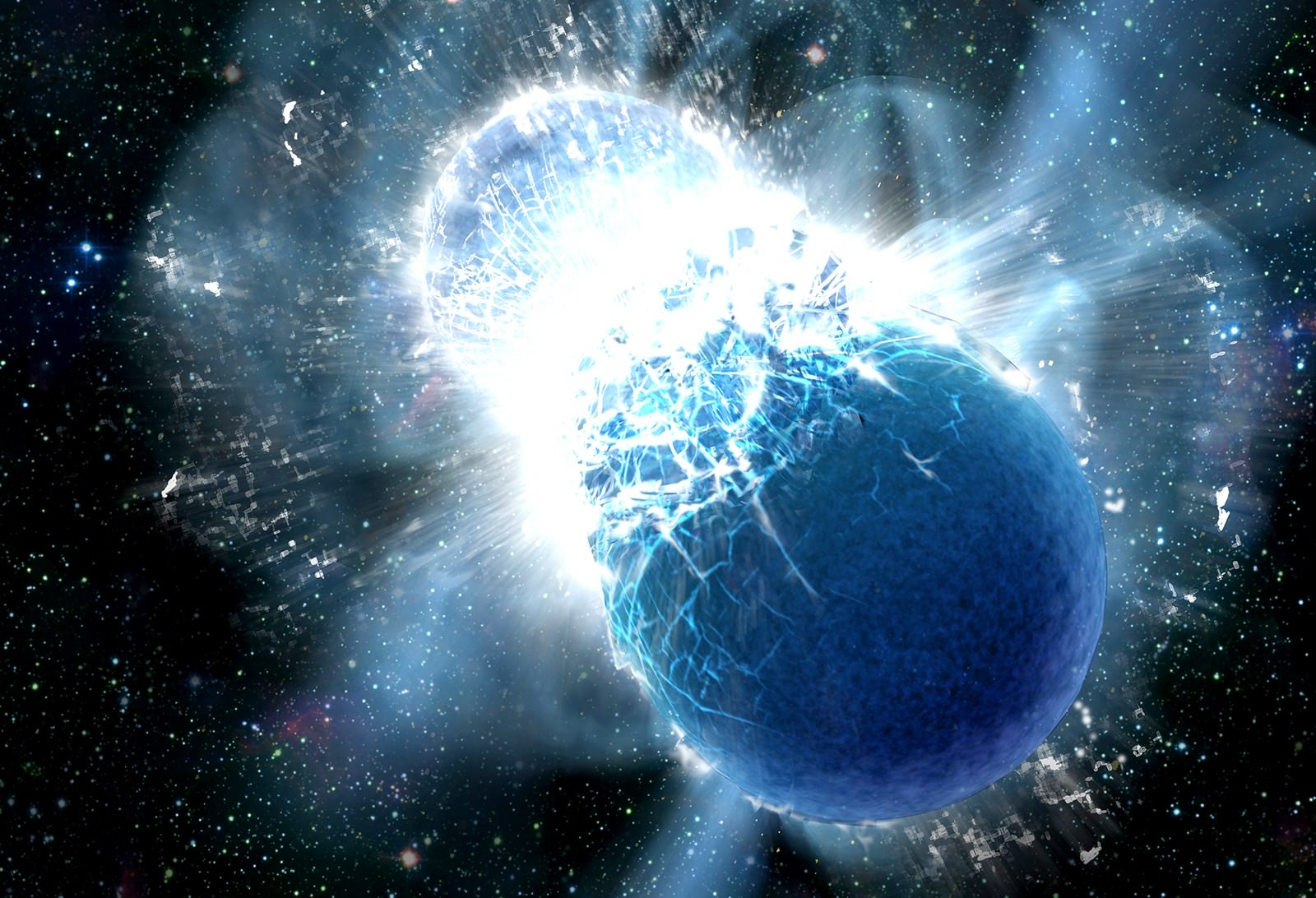
More recent work has suggested that some of the heaviest elements could actually be the result of binary stars merging. In fact, a recent study by two astrophysicists found that a collision which took place between two neutron stars billions of years ago produced a considerable amount of some of Earth’s heaviest elements. These include gold, platinum and uranium, which then became part of the material from which Earth formed.
Continue reading “Some of Earth’s Gold Came From Two Neutron Stars That Collided Billions of Years Ago”